What does WHMIS stand for?
Workplace Hazardous Material Information System
Give three examples of fluids
Any liquid or gas or substance that flows.
What are the two types of pure substances?
There is a solution of coffee. Identify the solute and solvent.
Coffee is the solute and the solvent is the water.
Draw the particles in all three states of matter.
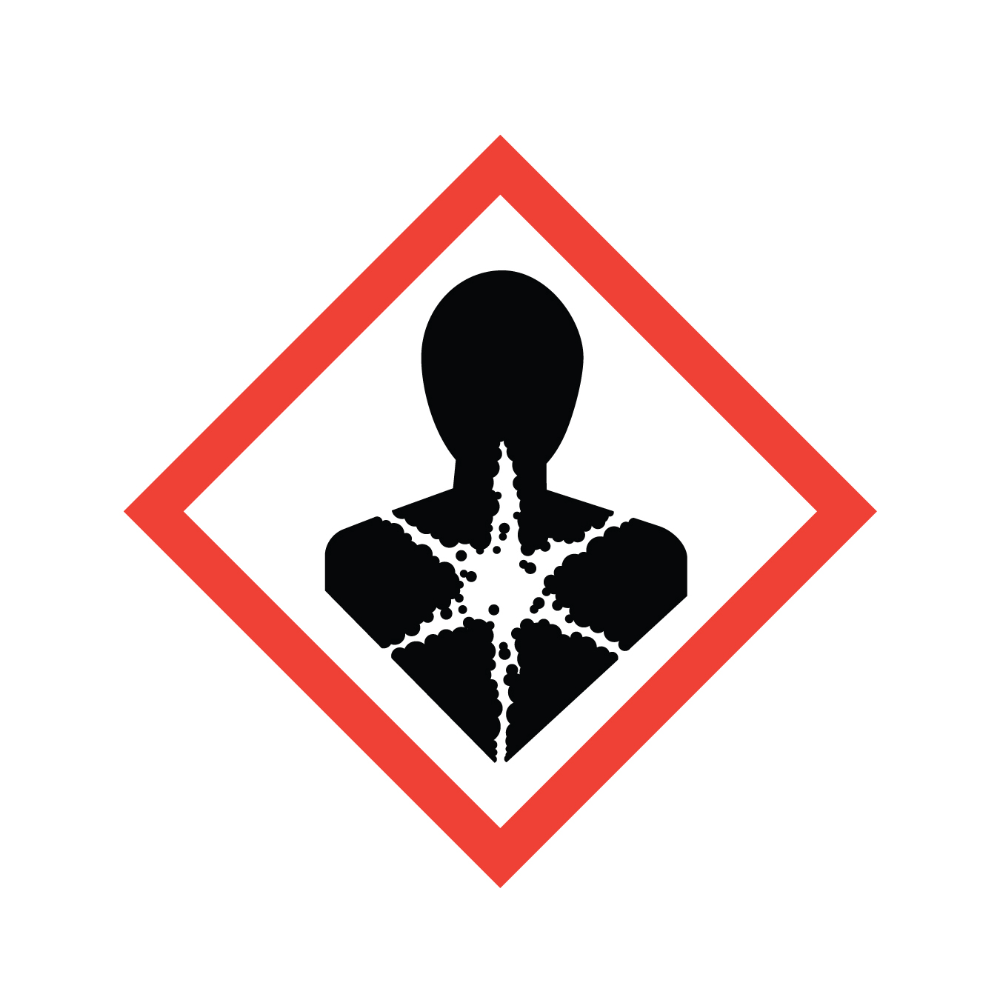 What is this symbol?
What is this symbol?
Health Hazard
What is a fluid?
Anything that has no fixed shape and can flow.
What are homogeneous and heterogenous mixtures? Give examples
Homogeneous: Can’t see the different substances that make them up. Solution
Heterogeneous: Can see the different parts. Colloid, mechanical mixture, suspensions
What is concentration?
The amount of solute (g or kg) dissolved in a specific amount of solvent (mL or L) in a solution; written as g/L or kg/L. Means amount of solute/amount of solvent.
If the 2 substances with different size particles are mixed together explain what is happening.
The smaller particles will fill spaces between the larger particles.
What symbol is this and what does it mean?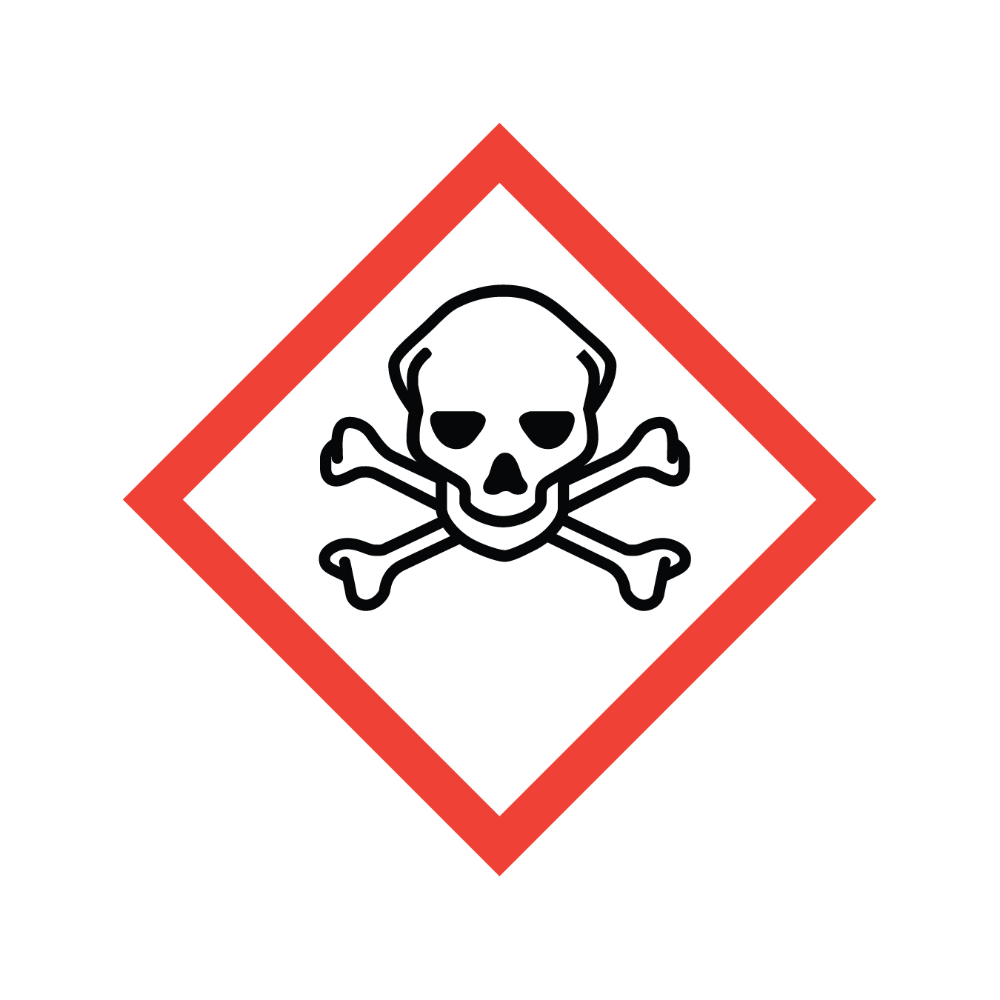 
Skull and cross bones. Can cause death or toxicity with short exposure and exposure to small amounts.
What is hydraulics?
A system that uses fluid under pressure to perform work or move loads.
What is a suspension? Give an example
Cloudy mixture in which droplets or tiny pieces of one substance are held within another substance. If you leave a suspension alone, it will separate into its parts.
Salad dressing.
Which of the following is the more concentrated solution A: 15g/25 ml or solution B: 25g/150 ml? Explain why.
Solution A because the concentration is higher.
List the 4 points of the particle model of matter
All matter is made up of tiny particles.
Particles are always moving and vibrating.
Particles are attracted to each other or bonded.
Particles have spaces between them.
Draw and label the appropriate symbols for warning, danger and caution.
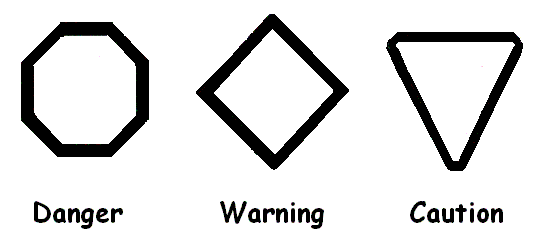
What is pneumatics?
A system that uses gas under pressure to perform work and move loads.
What is a mechanical mixture? Give an example
You can see the different substances. Example: Soil, chocolate chip cookie
What is the difference between a saturated , unsaturated and super saturated solutions?
Saturated solution: Once you reach maximum solubility.
Unsaturated solution: more solute can still be dissolved.
Supersaturated solution: a solution that contains more than the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved at a given temperature
What does it mean if a solution is insoluble?
The solute and solvent will not dissolve together.
There are many lab safety rules that MUST be followed. List three.
1. Read all written instructions before doing an activity.
2. Listen to all instructions and follow them carefully.
3. Wash your hands carefully after each activity and after
handling chemicals.
4. Wear safety goggles, gloves, or an apron as required.
5. Think before you touch. Equipment may be hot and
substances may be dangerous.
6. Smell a substance by fanning the smell toward you with
your hand. Do not put your nose close to the substance.
7. Do not taste anything in the lab.
8. Tie back loose hair and roll up loose sleeves.
9. Never pour liquids into containers held in your hand.
Place a test tube in a rack before pouring substances
in it.
10. Clean up any spilled substances immediately as instructed
by your teacher.
11. Never look into test tubes or containers from the top.
Always look through the sides.
12. Never use cracked or broken glassware. Make sure you
follow your teacher’s instructions when getting rid of any
broken glass.
13. Label any container you put chemicals in.
14. Report all accidents and spills immediately to your teacher.
Explain what a slurry and binder are and give an example of each.
Slurry: are a mixture of solids and water. Slurry technology is the transport of solids in water. Example: Dirty water.
Binder: Substances called binders; they keep the slurry together. Example: Molasses.
Black coffee is an example of a ______________ mixture. It can be classified as a _____________.
Homogeneous mixture
Solution
What is solubility and what are the three factors that affect solubility?
Solubility: Maximum amount of solute you can add to a fixed volume of solvent at a given temperature
Type of solute
Type of solvent
Temperature
What is thermal pollution and how does it have an effect on the environment?
Industrial plants use water as a coolant in their processes.
The water is returned to lakes and rivers as WARM water.