How many bones are in the human body?
206
What kind of cell can an osteoblast turn into?
Osteocyte
How are bones created?
Through Ossification
What osteo cell is responsible for bone deposition?
Osteoblasts
What causes bone fractures when you are young?
Trauma
What does the word "osteo" mean?
Bone
What kind of cell do Osteoprogenitor cells most often times turn into?
Osteoblast
Why do bones thicken (get wider)?
In response to increased mechanical stress or weight gain.
What osteo cell is responsible for bone resorption?
Ostoeclasts
What causes bone fractures when you are older ~<45?
Weakness of bone due to thinning
What does the human skeleton start off as initially?
Cartilage
What kind of Osteo Cell can an Osteoprogenitor cell turn into?
Any other osteo cell.
How do bones grow in width?
Through appositional growth
What are the two parts to Bone Remodeling?
Bone Deposition and Bone Resorption
What is unique about the skull?
Only area where all bones are fused together.
What are the four general types of bone shapes?
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular
800 point question:
What are the organic and inorganic parts of the bones?
Organic: Osteo cells
Inorganic: Mineral salts ~ hydroxyapatites.
How do bones grow in Length?
Through interstitial growth
What is Wolf's Law?
Bones grow or remodel in response to demands placed on them.
Where does bone lengthening occur on the bone?
On the epiphyseal line/plate
What is the difference in Red and Yellow Bone Marrow?
Red bone marrow is found in spongy bone and produces blood cells.
Yellow bone marrow is found in the medullary cavity and is responsible for fat storage.
Have a member of your team come up to the board and draw any long bone and label the diaphysis, both epiphyses, the epiphyseal line, medullary cavity, spongy bone, and compact bone.

Put the five steps to ossification in order from one to five:
_____ Periosteal bud invades cavities, leading to formation of spongy bone
_____ Epiphyses ossify
_____ Bone collar forms around diaphysis (shaft) of cartilage model
_____ Diaphysis elongates, and medullary cavity forms
_____ Central cartilage in diaphysis calcifies, then develops cavities
1. Bone collar forms around diaphysis (shaft) of cartilage model
2. Central cartilage in diaphysis calcifies, then develops cavities
3. Periosteal bud invades cavities, leading to formation of spongy bone
4. Diaphysis elongates, and medullary cavity forms
5. Epiphyses ossify
What are two things that can be explained by Wolf's Law?
Handedness (right- or left-handed) results in thicker and stronger bone of the corresponding upper limb
Curved bones are thickest where most likely to buckle
Trabeculae form trusses along lines of stress
Large, bony projections occur where heavy, active muscles attach
Bones of fetus and bedridden people are featureless because of lack of stress on bones
What zone does the majority of bone lengthening occur at?
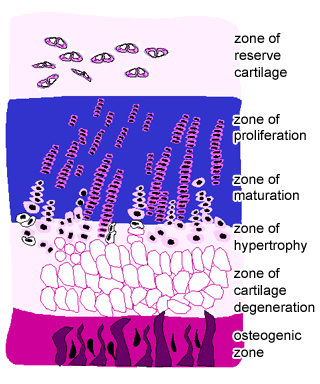
Proliferation zone.