What are the most common organisms associated with right- vs left- sided endocarditis?
Right = S. aureus (think indwelling line or IVDA)
Left = Strep viridans

List some characteristics of complex febrile seizures.

Painless rectal bleeding < 5 yo?
Meckel's diverticulum
Ectopic gastric mucosa is the most common form of ectopic tissue found within Meckel’s diverticulum and frequently ulcerates causing patients to present with painless rectal bleeding.
List the criteria for diagnosis of massive hemoptysis.
> 50 mL once; > 500 mL in 24 hours
Most common cause and treatment of epididymitis <35 yo? >35 yo?
< 35 yo = STI = IM Rocephin + Rx for doxy
> 35 yo = E. Coli = FQ

List all 4 indications for thrombolytics in acute stroke.
> 18 yo
<4.5 hours from sx onset
No head bleed
No other reversible cause (like hypoglycemia)
First-time/SE disadvantaged parents p/w seizing infant. Most likely diagnosis? Treatment?
Hyponatremia 2/2 formula dilution. 3% HS (4-6 mL/kg over 20 min)
What vent settings would be appropriate for an ARDS patient?
High PEEP (5-20)
Low Tidal Volume (4-6cc/kg)
Inspiratory Pressure < 30
Supp O2 for Sats in Low 90s

List the organism associated with these buzz phrases for pneumonia:
Alcoholic with currant jelly sputum
Cystic fibrosis with green sputum
Bullous myringitis
Alcoholic with currant jelly sputum = Klebsiella
Cystic fibrosis with green sputum = Pseudomonas
Bullous myringitis = mycoplasma
How do you treat seizures secondary to:
Eclampsia?
Isoniazid overdose?
Hyponatremia?
Mag
B6
Hypertonic saline
Pt presents with fever, stridor, and barky cough, but they are toxic-appearing. Most likely diagnosis? Treatment?
Bacterial tracheiitis. IV abx, airway in OR.

When would you start steroids for a patient with PCP/PJP pneumonia?
PaO2 < p70, A-a gradient > 35
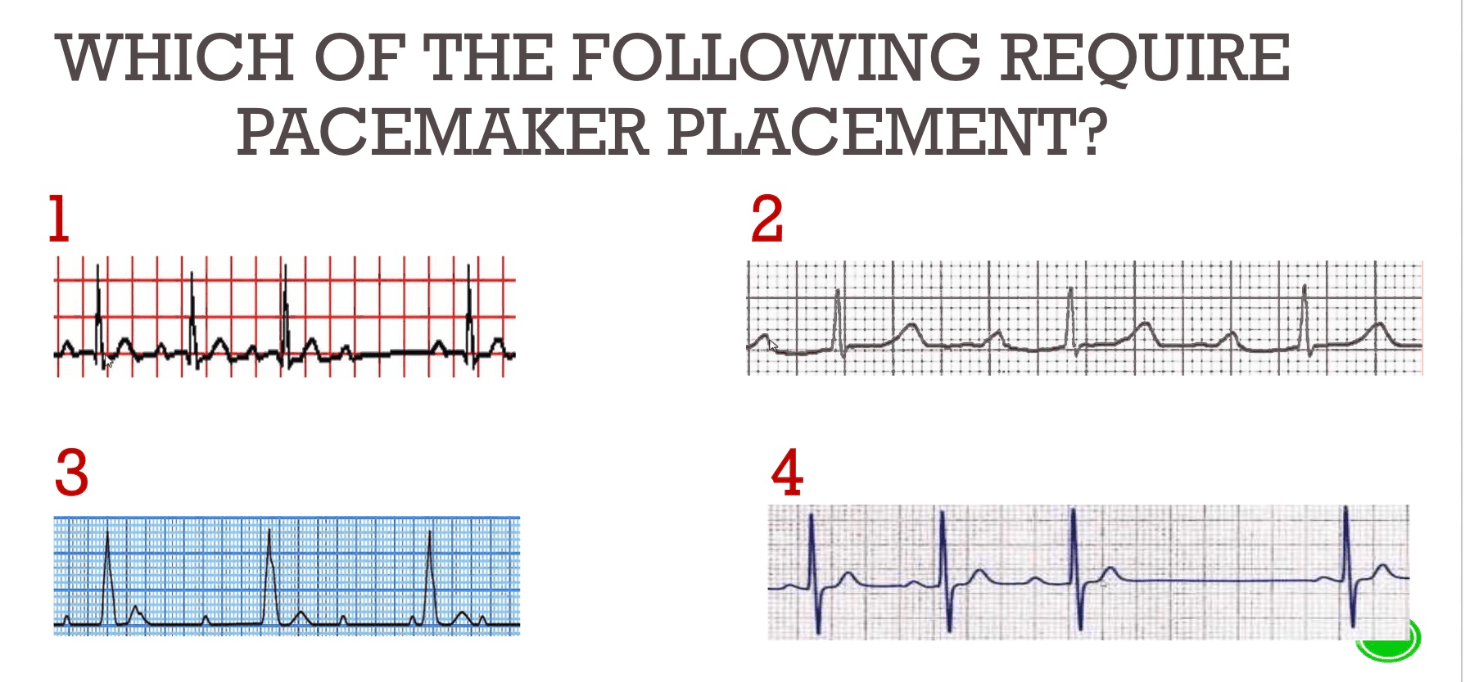
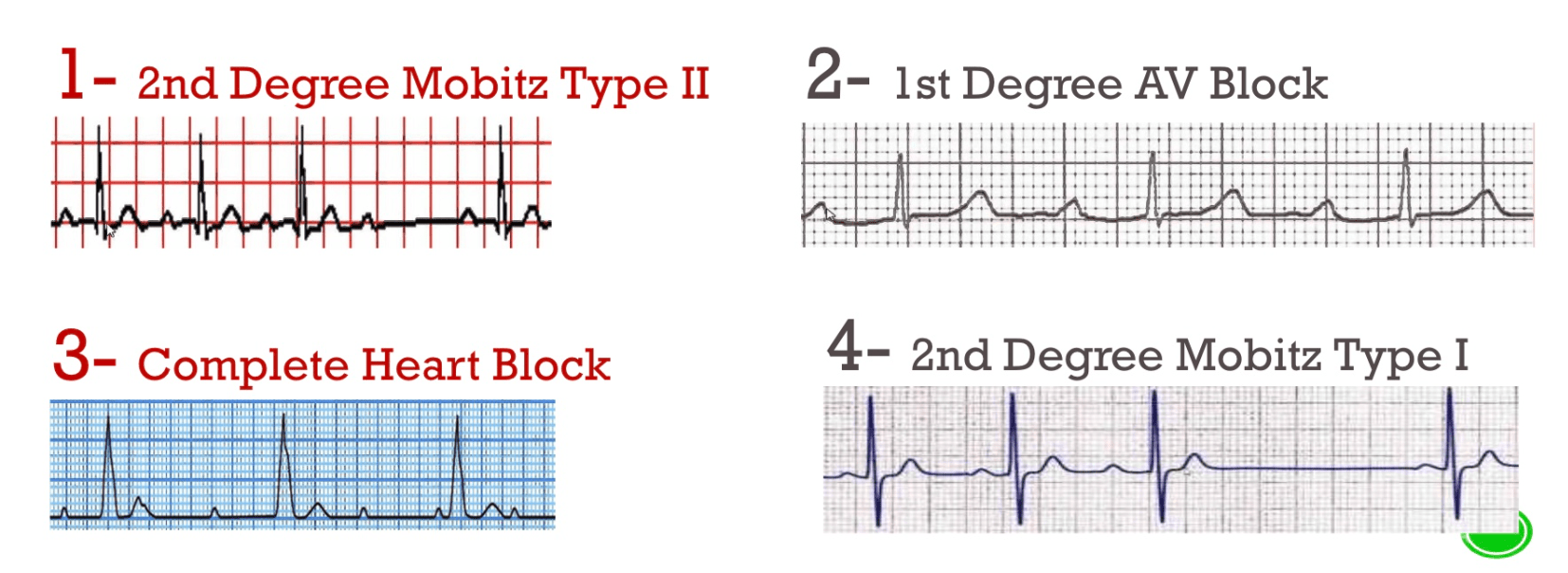
1st Degree AV Block
PR >200, QRS after every P wave
GOOD: Nothing to Do
2nd Degree (Mobitz I)
PR interval increases, then dropped beat (Wenckebach)
GOOD: Nothing to Do
2nd Degree (Mobitz II)
Stable PR interval, dropped beat
BAD: Needs Pacemaker
3rd Degree AV Block
P waves and QRS disconnected
BAD: Needs Pacemaker
How many major and/or minor Duke criteria are required for a diagnosis of IE? Name the two major and at least two minor criteria.
2 major, 1 major + 3 minor, 5 minor
Where is the lesion (vascular)? 83 yo p/w two hours of …
RLE weakness/numbness
Aphasia + R facial and RUE weakness/numbness
Binocular vision changes
1. RLE weakness/numbness: ACA
2. Aphasia + R facial and RUE weakness/numbness: MCA
3. Binocular vision changes: PCA
Infant p/w inconsolable crying. Was being watched by nonparent. Suspect dx? Name at least three findings that would support your suspicion.
NAT: corner (bucket handle) fx, fx in different stages of healing, bruising on non-bony prominences, retinal hemorrhages, history not consistent with developmental age, patterned bruising/burns, skull fx, delayed presentation, extremely fearful/withdrawn child
Describe pacemaker: oversensing, undersensing, failure to capture
Undersensing = fails to sense native cardiac activity
Oversensing = electrical signal are inappropriately recognised as native cardiac activity and pacing is inhibited
Failure to capture = paced stimulus does not result in myocardial depolarisation
List the organism associated with these buzz phrases for pneumonia:
Bird owner with high fever and relative bradycardia
Young pt with rat exposure and ARDS
CD4 < 200, high LDH
Bird owner with high fever and relative bradycardia: psitticosis
Young pt with rat exposure and ARDS: Hanta virus
CD4 < 200, high LDH: PCP PNA

A sickle cell patient p/w right-sided weakness for one hour. CTH is negative. Treatment?
Exchange transfusion