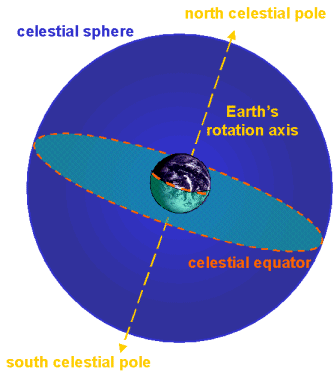
An imaginary sphere used to map the positions of stars and other objects in space.
What is the CELESTIAL SPHERE?
![]()
Earth's rotation on its axis results in this type of motion.
What is DIURNAL MOTION?
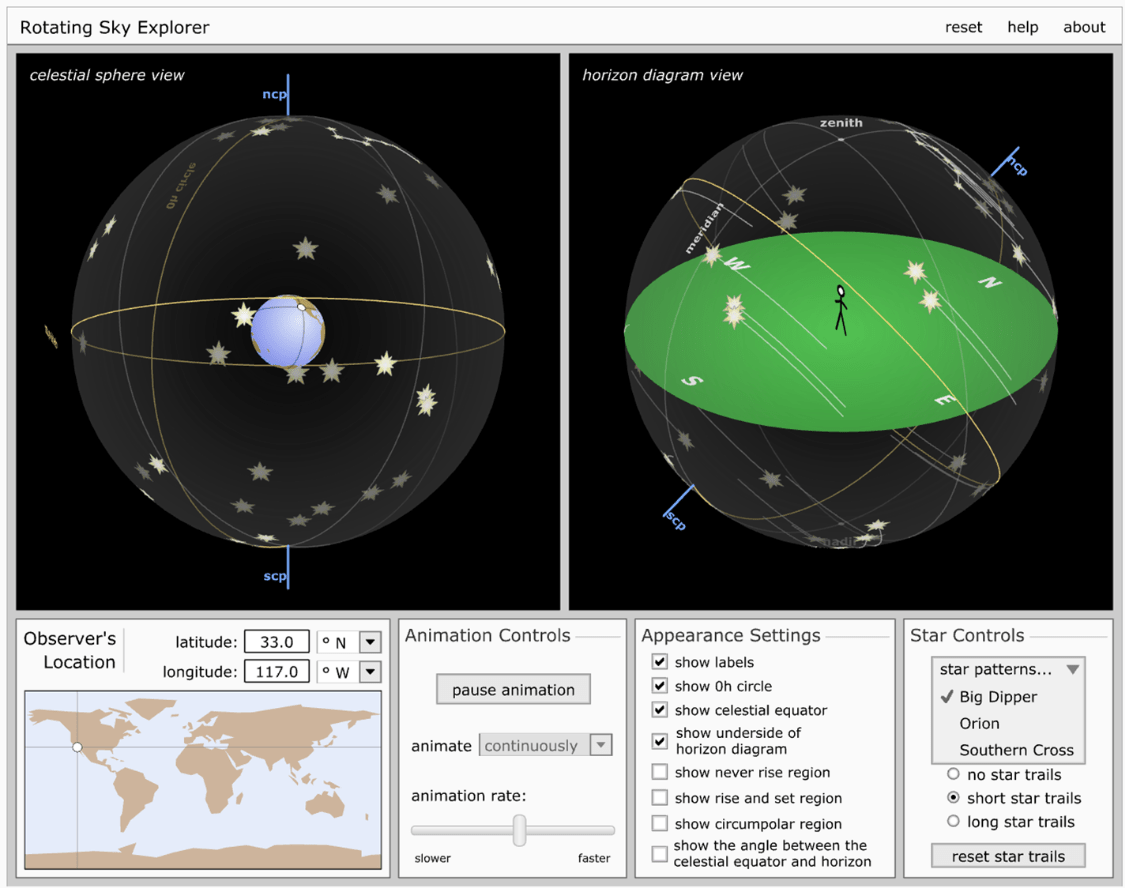
The ancient instrument used to measure the altitude of stars above the horizon that helped navigators calculate latitude and tell time based on celestial observations.
What is an ASTROLABE?
This constellation represents a hunter in Greek mythology.
What is ORION?

The point directly above an observer’s head on the celestial sphere.
What is the ZENITH?

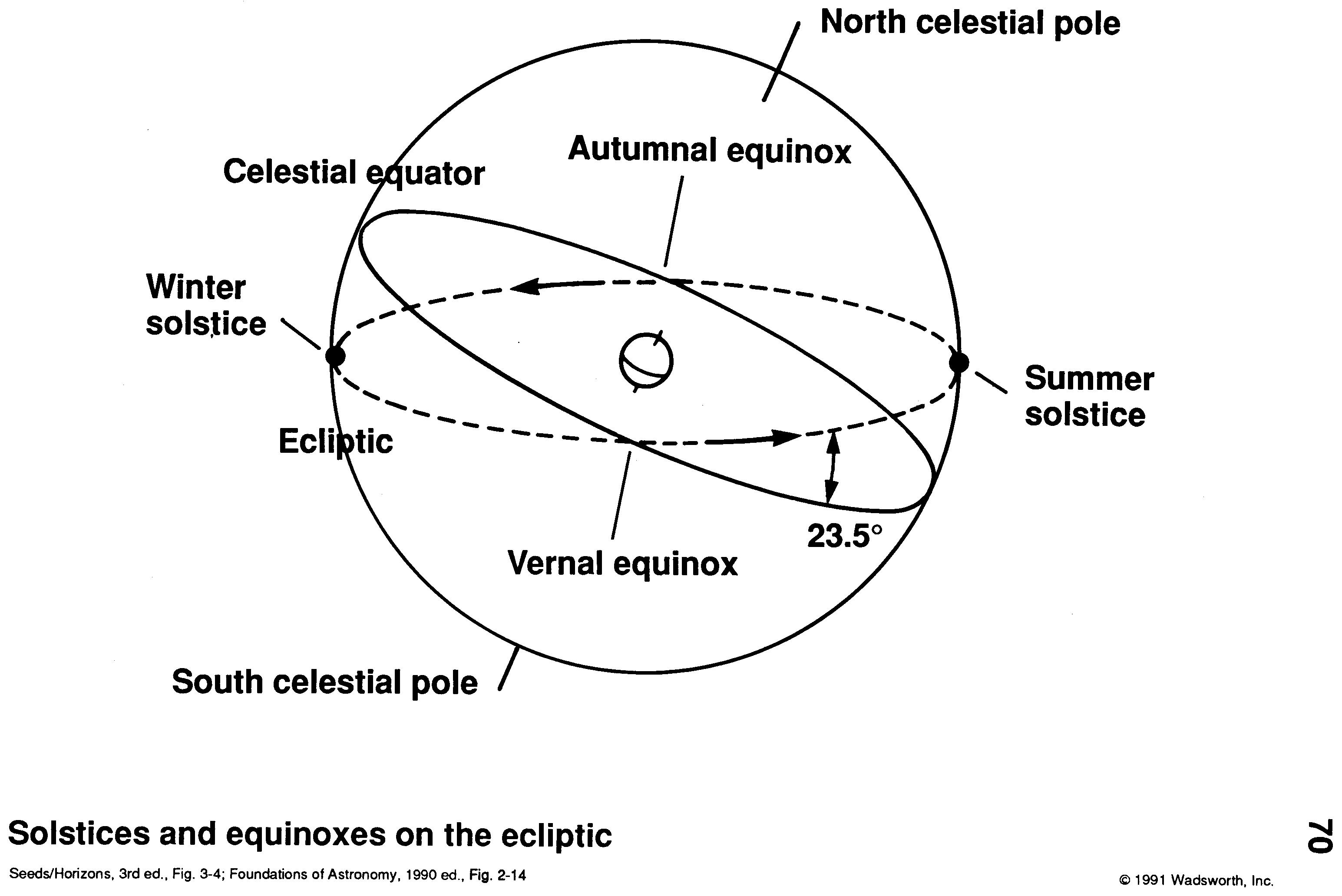
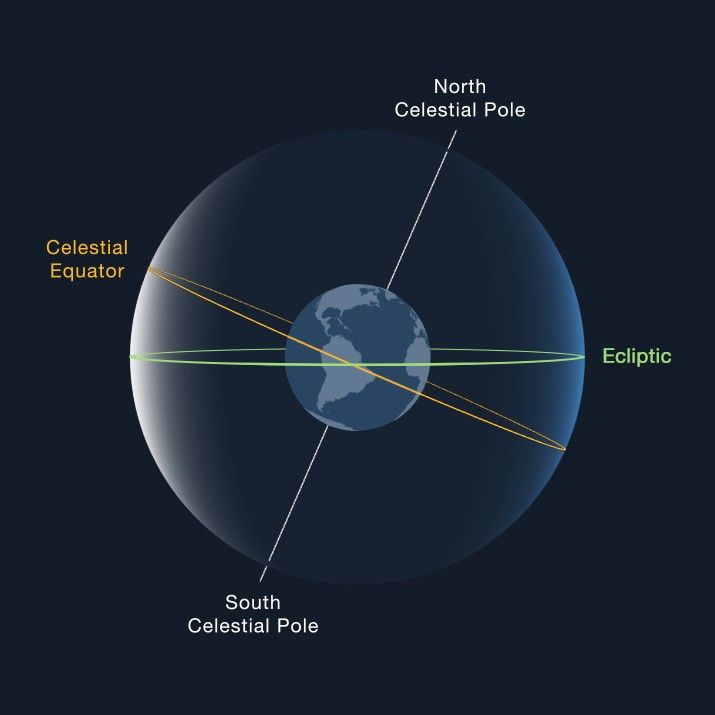
The apparent path the Sun takes across the celestial sphere is called this.
What is the ECLIPTIC?
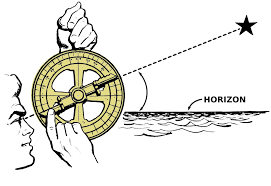
Instrument developed in the 18th century that measured the angle between a celestial object and the horizon. It was more precise and improved navigation accuracy on long voyages.
What is a SEXTANT?
This constellation is tied to the Greek myth of Callisto who was transformed into a bear by Zeus.
What is URSA MAJOR (the Big Bear)?

This imaginary line divides the celestial sphere into the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
What is the CELESTIAL EQUATOR?
Stars appear to rise in the east and set in the west due to this direction of Earth's rotation.
What is from WEST TO EAST?
Earth rotates counterclockwise (west to east) making the stars appear to rise in the east and set in the west from Earth's perspective.
Before accurate clocks, sailors struggled to measure longitude (east-west position). With the invention of this tool in the 18th century, navigators could keep accurate time on board, which, combined with observations of the Sun or stars, allowed them to determine longitude.
What is a CHRONOMETER?

This constellation is a dark shape formed by dust clouds in the Milky Way rather than by stars. It appears in the night sky and was used by Aboriginal Australians to tell when it was time to collect a certain type of egg.
What is the EMU IN THE SKY?

These are the points where Earth's rotational axis intersects the celestial sphere.
What are the CELESTIAL POLES?
This is the boundary between the visible and invisible parts of the celestial sphere.
What is the HORIZON?
The horizon is the boundary between the Earth and the sky.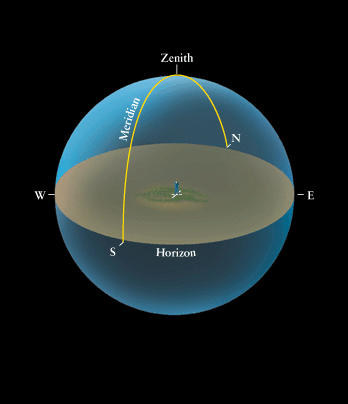
This way of keeping time corresponds to one cycle of the Moon’s phases, which lasts about 29.5 days.
What is the LUNAR CALENDAR?

The Inca in South America identified not only star constellations but these types of constellations in the Milky Way, such as the “Llama” and the “Fox,” formed by dark patches within the galaxy.
What are DARK CONSTELLATIONS?

These dark constellations were integrated into Incan mythology and had agricultural significance, signaling planting and harvest times.
The 2 celestial coordinates used to locate objects in the sky.
What are RIGHT ASCENCION AND DECLINATION?
Declination is like latitude but for the sky.
Right ascension is like longitude but for the sky.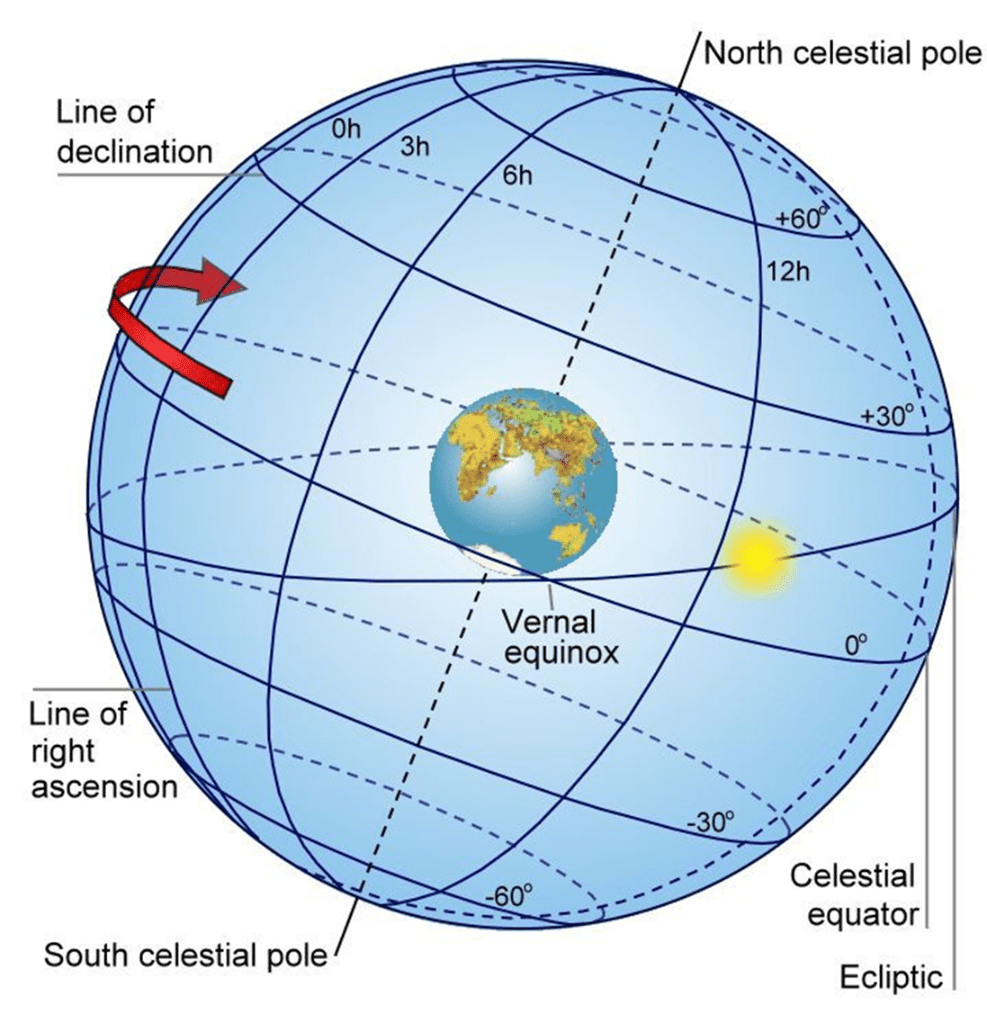
In some parts of the sky, these certain types of stars don’t set at all.
What are CIRCUMPOLAR STARS?
These stars move in circles around the celestial poles. Ex: Polaris (the North star)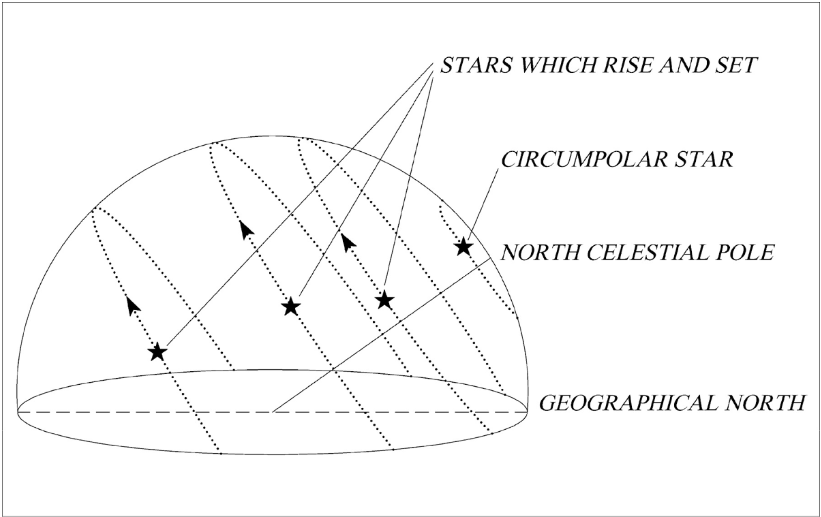
This way of keeping time is based on Earth’s orbit around the Sun and is 365.25 days, so we add an extra day every four years (leap year) to keep our calendar aligned with Earth’s position in its orbit.
What is the SOLAR CALENDAR?

This ancient structure in England is one of the best-known structures aligned with the Sun’s movements. At the summer solstice, the Sun rises directly above the “Heel Stone,” marking the longest day of the year. This alignment indicates that it likely served as a calendar or observatory, helping its builders track the seasons.
What is STONEHENGE?

