What is an environmental value system (EVS)?
A worldview that shapes how individuals or societies perceive and respond to environmental issues.
What perspective believes that humans should live in harmony with nature and minimize their impact?
Eco-centric
What are the two main types of systems in environmental studies?
Open and Closed systems.
What is equilibrium in a natural system?
Equilibrium refers to a state where the inputs and outputs of a system are balanced, resulting in a stable system over time.
What does resilience mean in the context of ecosystems?
The ability of an ecosystem to recover from disturbances and maintain its essential functions and structure.
Which perspective sees humans as the managers of sustainable development?
Anthropocentric
In which perspective is the belief that human ingenuity and technology can solve environmental problems?
Technocentric
What is an example of a closed system in nature?
The Earth ( In terms of matter, not energy.)
What is the difference between stable and steady-state equilibrium?
Stable equilibrium means the system remains unchanged over time, while steady-state equilibrium involves small, dynamic changes, but overall stability is maintained.
Which ecosystems are likely to be more resilient: those with high or low biodiversity?
Ecosystems with high biodiversity are more resilient because they have more species to fill roles and recover from disruptions.
What is the main focus of an ecocentric approach when making environmental decisions?
It emphasizes the inherent worth of nature and advocates for minimal human interference in natural processes.
Which worldview believes in equal consideration for both humans and nature?
Eco-centric
What is the difference between an open and a closed system?
An open system exchanges both energy and matter with its surroundings, while a closed system exchanges only energy, not matter.
In environmental systems, how does feedback affect equilibrium?
Feedback mechanisms, such as positive or negative feedback, can either push a system away from or help maintain equilibrium.
How does resilience relate to an ecosystem’s tipping point?
Resilience helps an ecosystem resist reaching a tipping point, where it might shift to a completely new state.
Which perspective is most likely to support technological solutions to environmental problems?
Technocentric perspective.
Which perspective holds that economic growth is key to solving environmental issues?
Technocentric
How does a model help in understanding systems?
Models simplify complex systems to help predict changes and understand interactions within the system.
What is a tipping point in relation to equilibrium in an ecosystem?
A tipping point occurs when a system experiences so much stress or disturbance that it shifts from one equilibrium state to another.
Can human activities increase the resilience of ecosystems?
Yes, through practices like conservation, restoration, and reducing stressors like pollution, resilience can be supported.
How does the deep ecologist view human development?
Deep ecologists believe human development should be minimal to preserve nature’s rights and intrinsic value.
Who believes that humans are the dominant species and can sustainably manage the Earth for future generations?
Anthropocentric
What type of system is this?
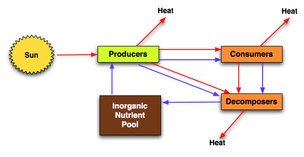
Closed system.
How can human activities disrupt the equilibrium of an ecosystem?
Human activities, such as pollution, deforestation, and climate change, can introduce disturbances that shift ecosystems away from their natural equilibrium.
What role does resilience play in the recovery of ecosystems after disturbances?
Resilience allows ecosystems to absorb shocks and recover from disturbances, maintaining their functions and structure, thereby ensuring the continued provision of ecosystem services.