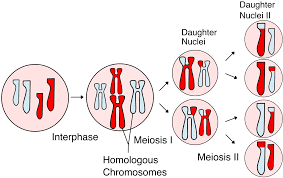
What process produces gametes (sperm and eggs) in sexually reproducing organisms?
Meiosis
What is the structure of an ionic substance?
A 3D lattice

What causes the apparent movement of the Sun across the sky each day?
Earth’s rotation on its axis.
What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
Kinetic = energy of motion; potential = stored energy due to height of an object.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype is the combination of alleles for a particular gene, phenotype is the physical trait or expression of those genes.
Why do metals conduct electricity but covalent molecular substances usually don’t?
Metals have delocalised electrons; covalent molecular substances have no free charges.
Why are tides higher during full and new moons?
Gravitational forces from the Sun and Moon align, producing spring tides.
A 10 kg object is lifted 2 m. Calculate its potential energy gain.
Ep = mgh = 10 x 10 x 2 = 200J
When is a mutation inheritable, when is it not?
Mutations that happen during meiosis in gametes (reproductive cells) can be passed on to offspring, mutations in body cells (somatic cells) cannot be passed on to offspring.
Why is an alloy stronger than a pure metal?
Because it has atoms of different sizes so they can't slide past each other like they can in a metal with all the same sized atoms.

Explain why the Moon appears to go through phases over a month.
As the Moon orbits Earth, we see different portions of its sunlit half.

Because, not all of the energy will turn into kinetic energy, some of it will be lost to heat and sound energy due to friction/air resistance.
How can gene tracking and DNA sequencing help breeding programmes aimed at conservation for a species?
- Identifying the most genetically different individuals to breed together
- Ensuring there is no inbreeding
Explain why some substances dissolve in water while others do not.
Water is a polar solvent, so it dissolves polar or ionic substances because the water molecules attract and separate the charged particles. Non-polar substances (like oils) don’t dissolve because there is no attraction between the molecules and water.
Describe what causes a King tide.
A king tide is the highest high tide of the year, occurring when the gravitational pulls of the sun and moon align during a new or full moon and the moon is at its closest point to Earth (perigee)
What are the three different types of heat transfer? Give a brief description of them each.
Radiation, Convection, Conduction

Discuss how genetic bottlenecks can reduce variation and affect a species’ long-term survival.
A population bottleneck reduces gene pool diversity, making it less able to adapt to future environmental changes or disease.
Describe how the properties of covalent network substances differ from those of metallic and molecular substances, and explain why.
Covalent network solids have very strong bonds throughout → high melting points and hardness, unlike metals (mobile electrons) or molecules (weak forces).
Why does Dunedin have more variation in daylight than Auckland over the course of the year?
Earth’s tilt means Dunedin’s angle to the Sun changes more through the year, giving bigger daylength variation than nearer the equator (Auckland).
A 60 W bulb runs for 5 minutes. Calculate the total energy used.
E = Pt = 60×300 = 18,000 J