Increasing temperature, smaller molecule size, steeper concentration gradient, and more channel proteins are ways to increase OR decrease the rate of diffusion across a membrane?
Increase
A solution with more H+ than OH- is classified as:
Acidic or low pH
Which of the 4 major/general tissue types contains mostly nonliving matrix, specialized cells (e.g., fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells), and is never exposed to the outside environment?
Connective tissue
What is the name of the process in which RNA polymerase synthesizes a copy of a gene in the DNA.
Transcription
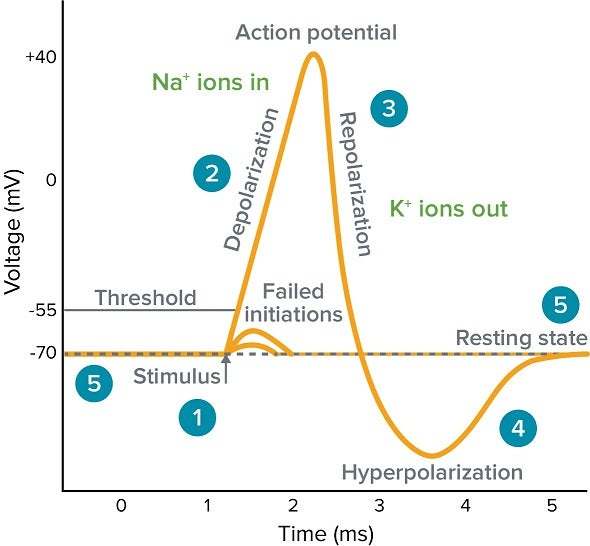
This changes the charge in the local area of the cell based on the strength of the stimulus.
Graded Potential
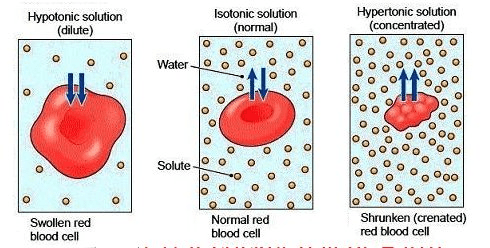
Water exits the cell via osmosis when the cell is in this type of solution.
Hypertonic
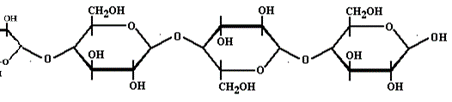
In what biomolecule class is this?
Carbohydrate
Which major/general tissue type is avascular (no blood vessels)?
Epithelial tissue
What is the first CODON translated from this gene (DNA)?
T T A C C G T A C T G C A T G G C A T
AUG...it's always AUG
The Na+/K+ Pumps (active transport) and Leak Channels (facilitated diffusion) together work to generate this in a neuron.
Resting Membrane Potential (-70mV)
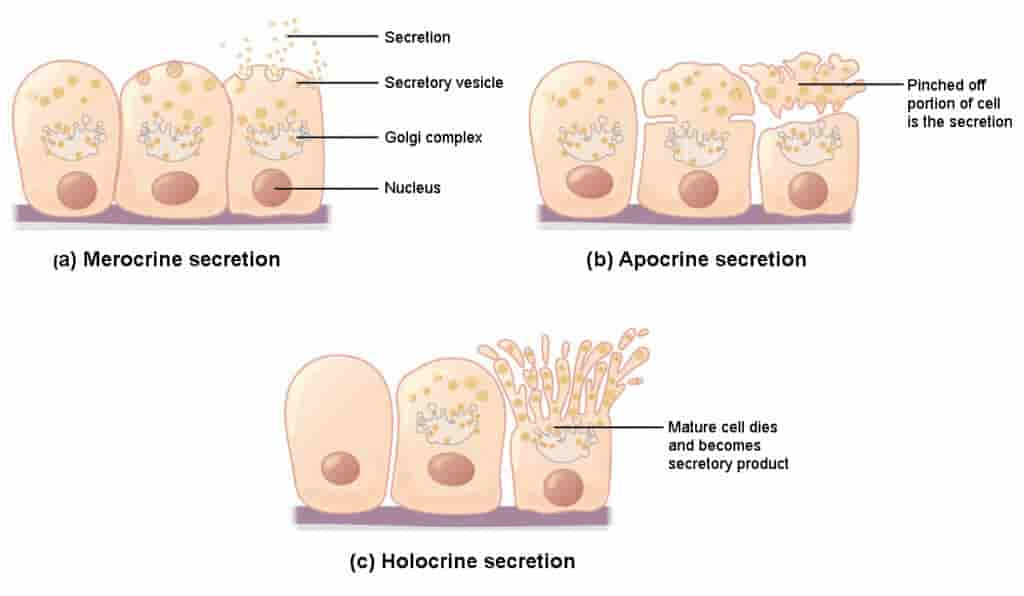
In this type of gland, the whole cell disintegrates to release its contents.
Holocrine
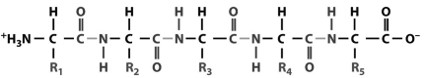
The biomolecule class of this molecule is:
Protein
(polymer: polypeptide)
The skin in the plantar and palmar regions differs from other skin in 3 ways. What is ONE of these differences?
1. Has a Stratum Lucidum
2. Lacks hair
3. Very thick epidermis
In the Golgi Apparatus, the proteins are not only sorted and their carbohydrates trimmed, but they obtain their ____________ structure.
Quaternary
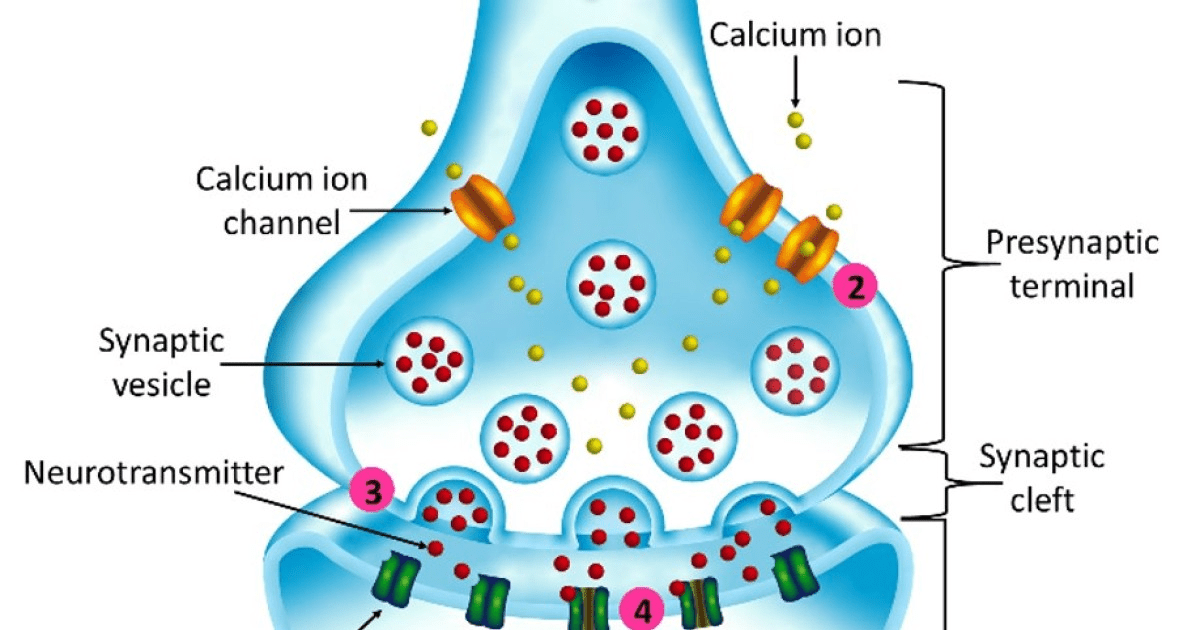
When the Action Potential's depolarization opens the Voltage-gated Calcium Channels in the Axon Terminal, the influx of calcium triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse via this type of membrane transport.
Exocytosis
The antecubital region is _______ to the Olecranal region.
Ventral or Anterior
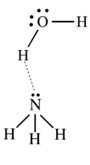
The two molecules are held together by a(n):
Hydrogen (H+) bond
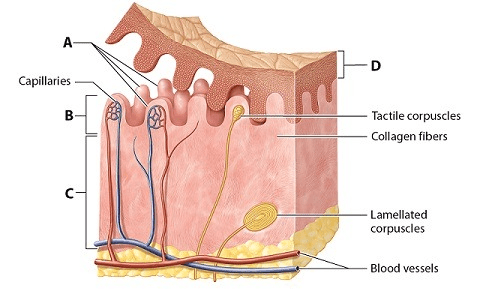
These structures provide space for capillaries and nervous system structures to encounter the epidermis, and create friction ridges in the thick skin.
Dermal papillae
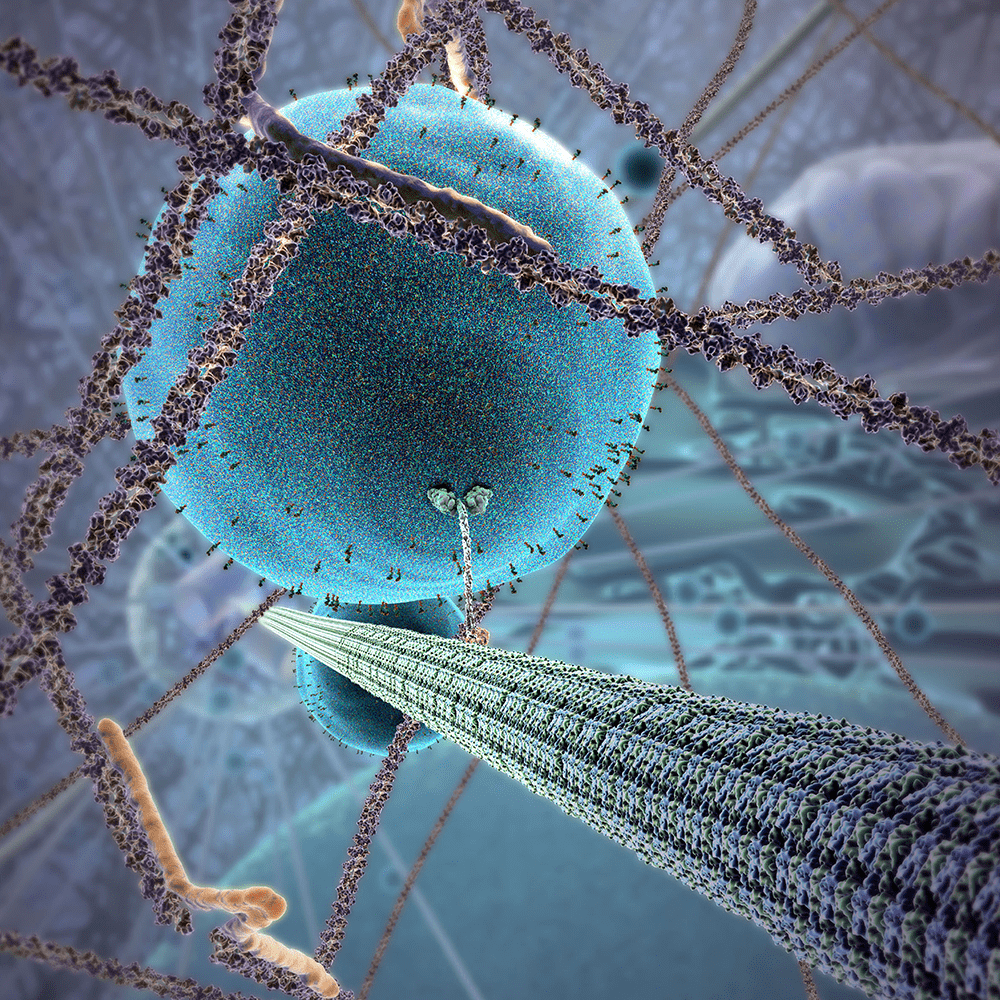
Molecular motors carry transport vesicles down "train tracks" made of this type of cytoskeleton fiber.
Microtubule
When a stimulus is strong enough to depolarize the local area of the cell to the threshold voltage of -55mV, these channels open, triggering an Action Potential.
Voltage-Gated Na+ Channels
What type of reaction is this?
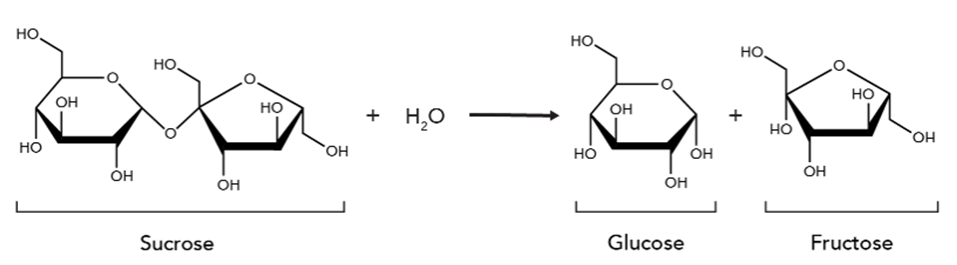
Hydrolysis
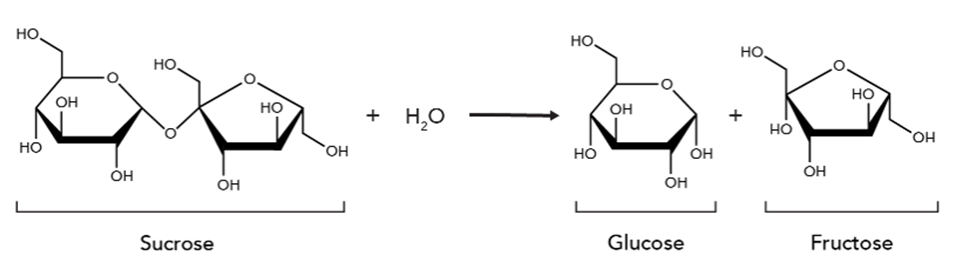
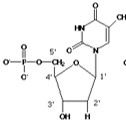
This specific molecule is called a(n):
RNA nucleotide
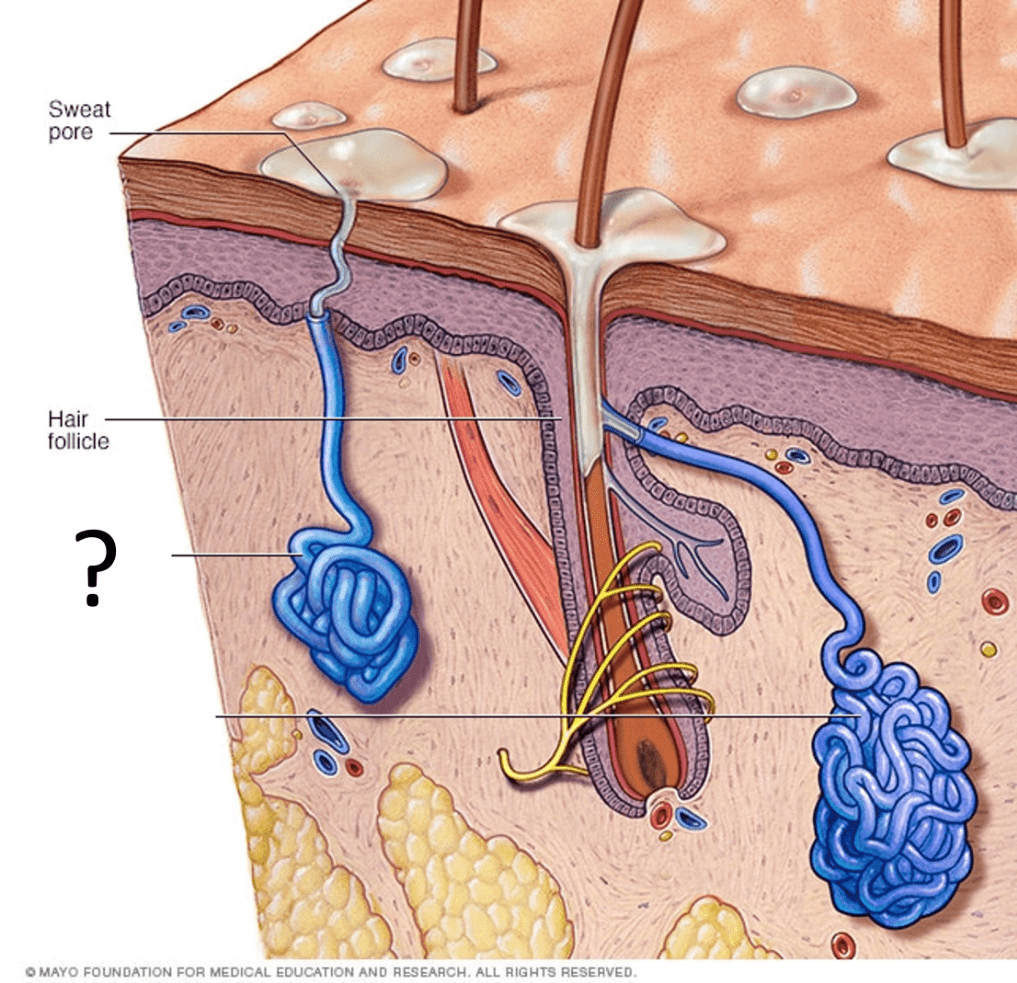
The specific structure?
Eccrine or Merocrine Sweat Gland
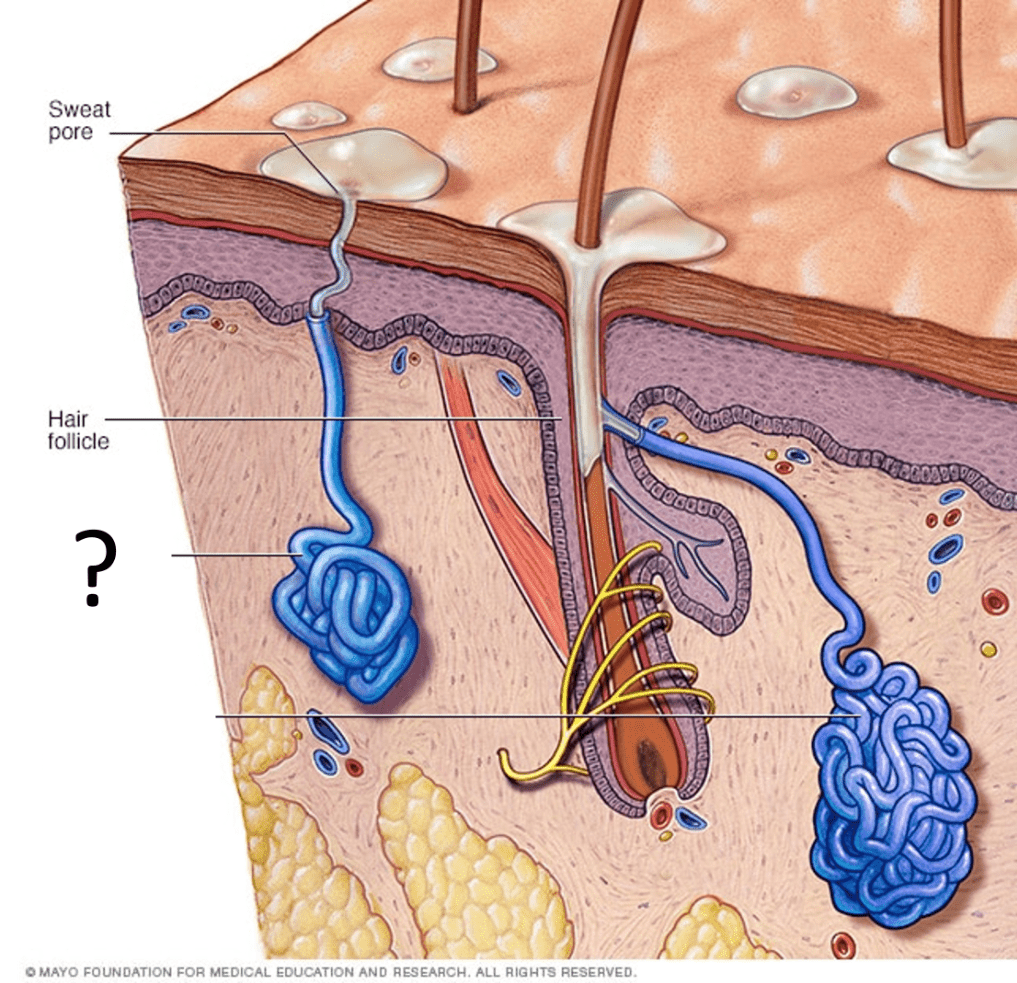
This organelle synthesizes lipids and glycogen, and breaks down toxins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The sluggish closing of the Voltage-gated K+ channels causes the cell to become ________________, making it relatively difficult for the cell to reach threshold for a brief time.
Hyperpolarized