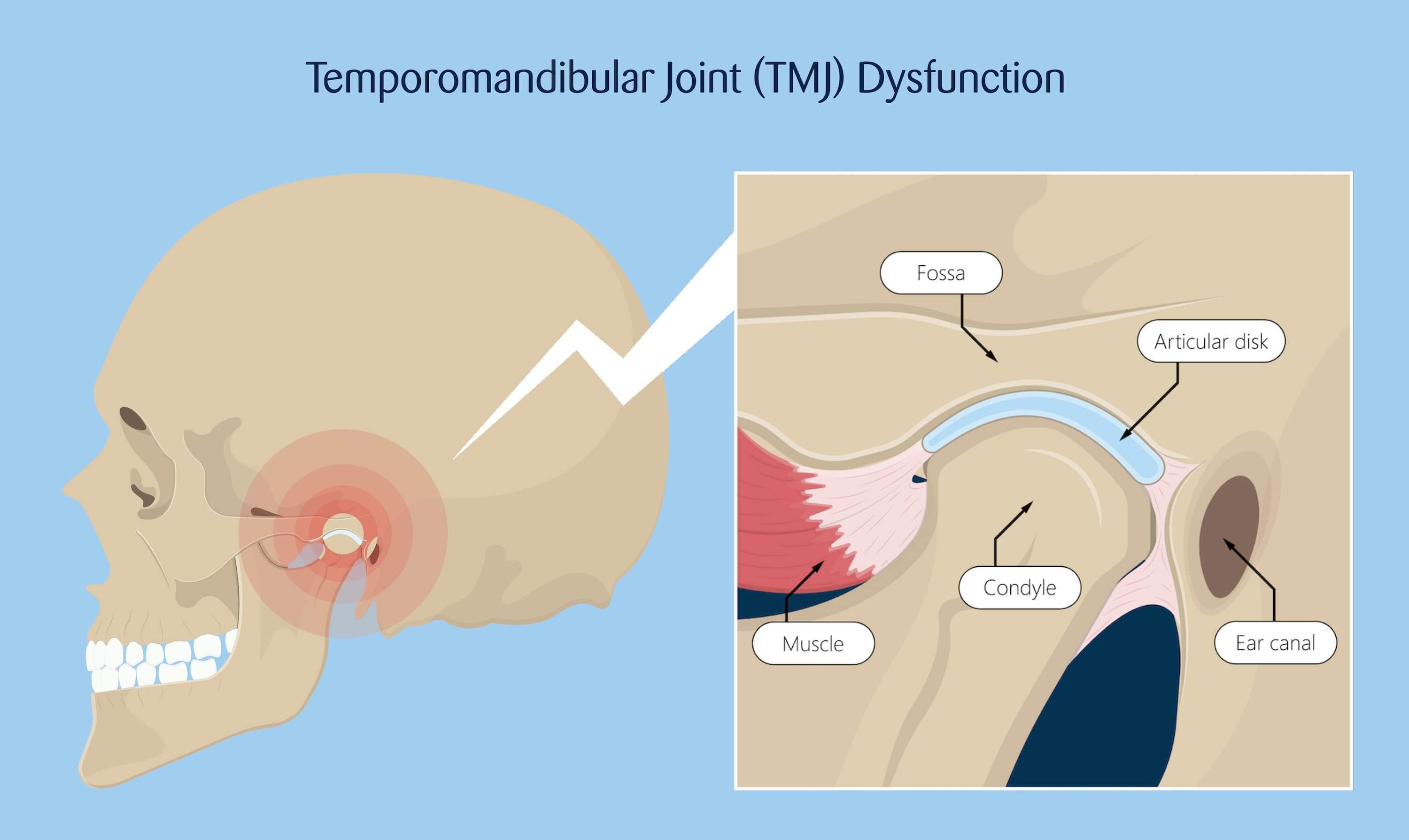
The mandibular condyle articulates with the temporal bone at this structure.
Mandibular fossa
The extrinsic eye muscles insert on this LAYER of the eye.
Fibrous Tunic

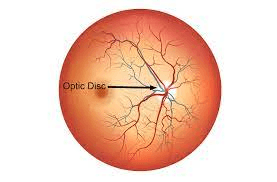
In this structure of the eye, there are no photoreceptors because the optic nerve must exit the eye.
Optic Disc or Blind Spot
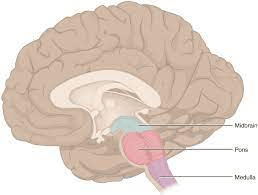
Autonomic centers that control blood pressure and heart rate are in this major brain region.
Medulla oblongata
Within the skin, these detect very fine touch with fine spatial resolution.
Spinothalamic Pathway
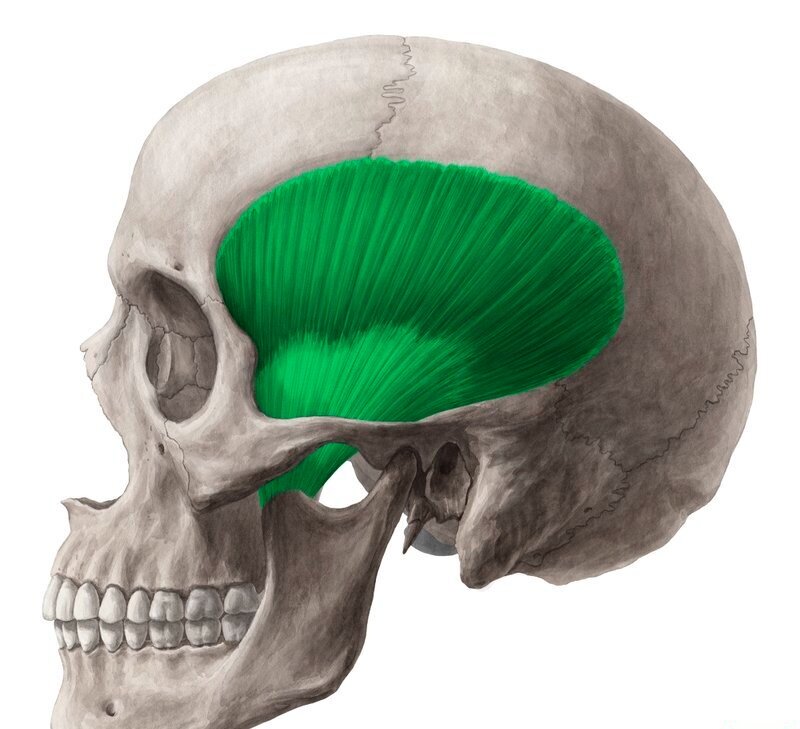
The temporalis muscle passes deep to this structure (made up of 2 bones).
Zygomatic arch
What raises her eyebrows?

Occipitofrontalis
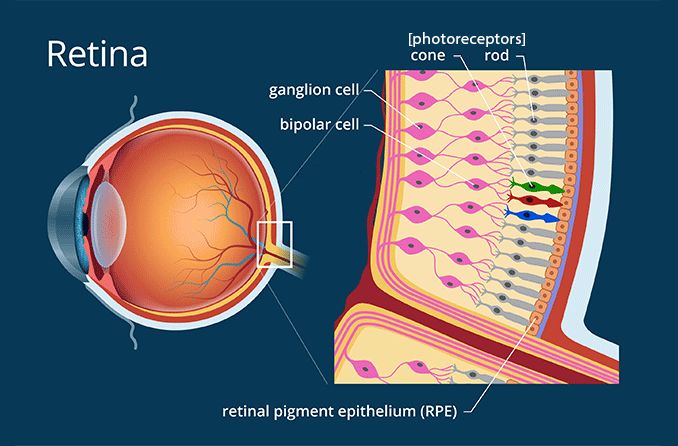
These photoreceptors require abundant light to be stimulated, which allows them to be used only in light environments (daytime).
Cones
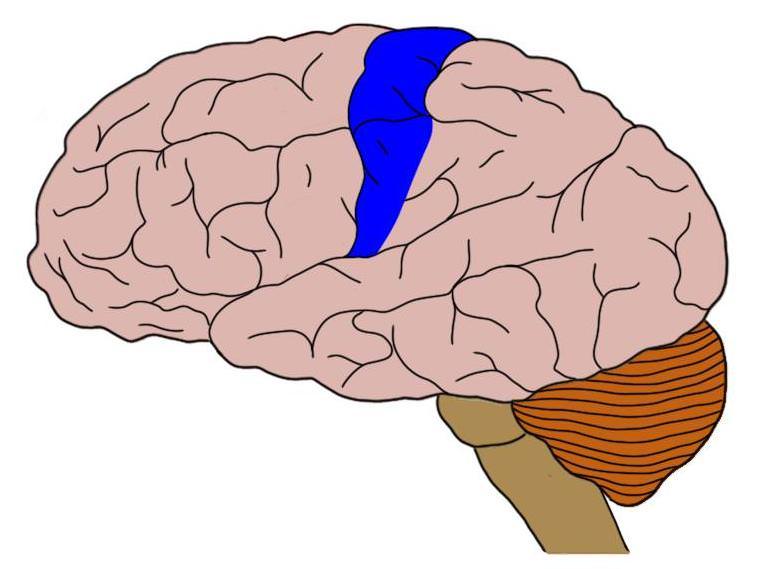
All sensory information from the body is routed to the Somatosensory Cortex, which is located on this.
(Structure AND Lobe)
Postcentral Gyrus of Parietal Lobe
The term for a neuron crossing the midline of the body (as it would have to do in order to inform the contralateral cerebral hemisphere of sensory stimuli).
Decussation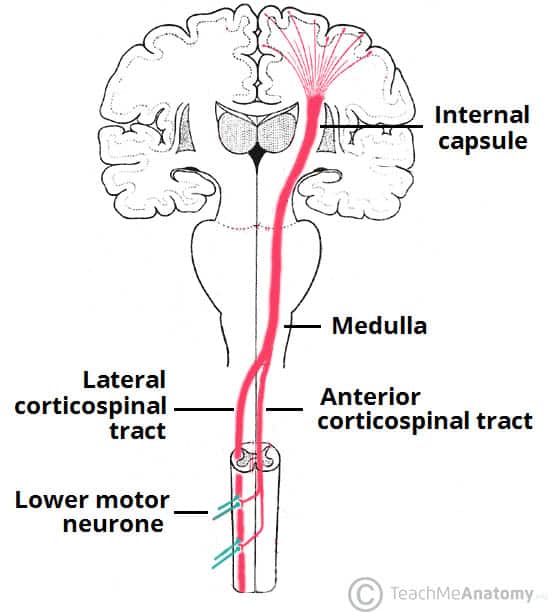
The hard palate (roof of the mouth) is formed by these boneS.
Palatine and Maxilla bones

Name an extrinsic eye muscle used to look at the bridge of the nose.
Medial Rectus
(Inferior Rectus looks at the tip of the nose)
When sound waves bend these, the hair cells depolarize, release a neurotransmitter, and trigger an action potential.
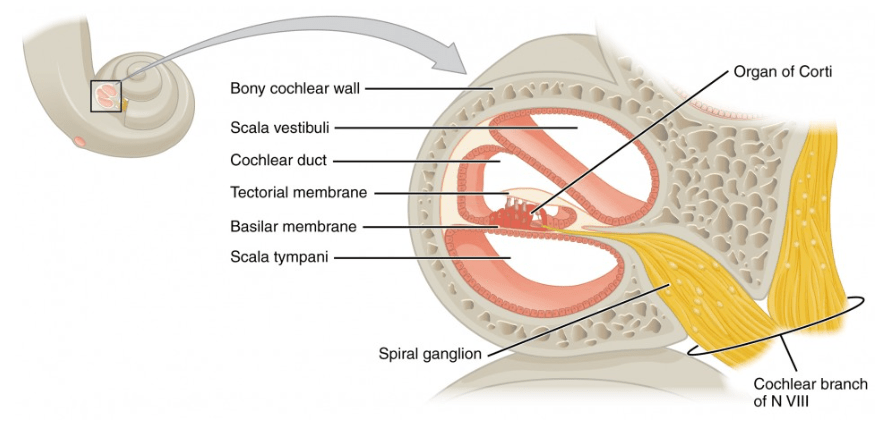 Stereocilia
Stereocilia
Within each brain ventricle, this filters the blood to generate new Cerebrospinal Fluid.
Choroid Plexus
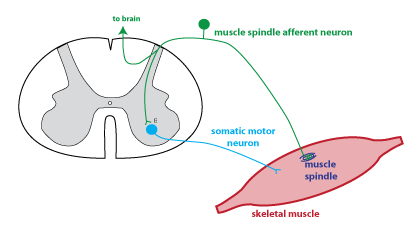
Receptors that monitor the position of joints are collectively called this.
Proprioceptors
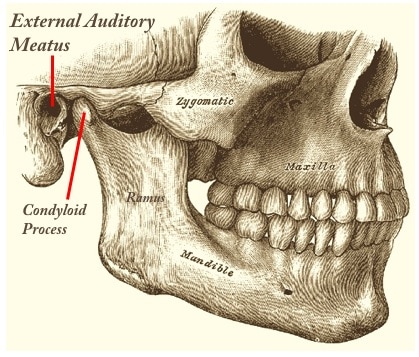
The ear canal passes through this structure.
External Acoustic (Auditory) Meatus
These muscles originate on the sphenoid bone and can move the mandible left and right.
Pterygoids
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13165/RMAIUJzxCtk7Wlt1fZbQ_Lateral_pterygoid_muscle.png)
When this muscle contracts, it makes the lens thicker, which refracts/bends the light from a nearby object more.
Ciliary muscle/body
This primary brain vesicle is retained in the adult brain, and contains the thalamus.
Diencephalon
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/interbrain/3pCnJ3C0QrGDikwTwhiww_Diencephalon.png)
Within the skin, these detect very fine touch with fine spatial resolution.
Merkel Cell Fibers