lim_{x to 4} f(x)
Check left and right on the function to see if they match.
Find the derivative.
f(x) = 3 ln(x) +4/(sqrt(x^3)) -e^4 + arcsec(x)
Basic and power rules
Given f(x) = x^2 +5x-1 , find the equation of the tangent line at x=3 and find the linear approximation of f(3.1) .
Take the derivative. Plug in 3 to get slope at x=3. Plug 3 into function to get y-value. Plug both into point-slope form to find equation of the tangent line at x =3.
Plug 3.1 into equation of line found in first part to get linear approximation.
int ( 3/sqrtx + 5/x - 4e^x + 2 cos x - pi) dx
Basic and power rules. Don't forget +c!
Find the derivative of
f(x) = int_-3^tanx u/(u^3 -5) du
FTC Part 1! Take off the integral, plug in the tanx, then multiply and take the derivative of tanx.
lim_{x to -3} (t^2 -9)/(2t^2+7t+3)
Plug in, 0/0, algebra and cancel.
Find the derivative.
f(x) = (x sinx)/(1+x)
Find the absolute extrema of f(x) = x^3-3x^2+1 on the interval [-1/2, 4] .
Plug critical points and end points into function to see which has the greatest and least y-value.
Given int_-1^6 f(x) = 7 , int_-1^3 f(x) = 2 , and int_3^6 g(x) dx = -3 , find
int_3^6 (5f(x) -g(x) +4 )dx
Use additivity to find int_3^6 f(x) dx , then break up the addition/subtraction and constant multiplier, and use
int_a^b c dx = c(b-a)
Use the limit definition of derivative to find the derivative of
f(x) = x^2+2x-1 .
lim_{h to 0} (f(x+h) - f(x))/h
lim_{x to 0} (x-5)/(x^4)
Plug in, number over 0, vertical asymptote -> check both sides!
Find the derivative.
f(x) = sqrt( (cotx - lnx)/(x^2+3x)
Chain Rule!
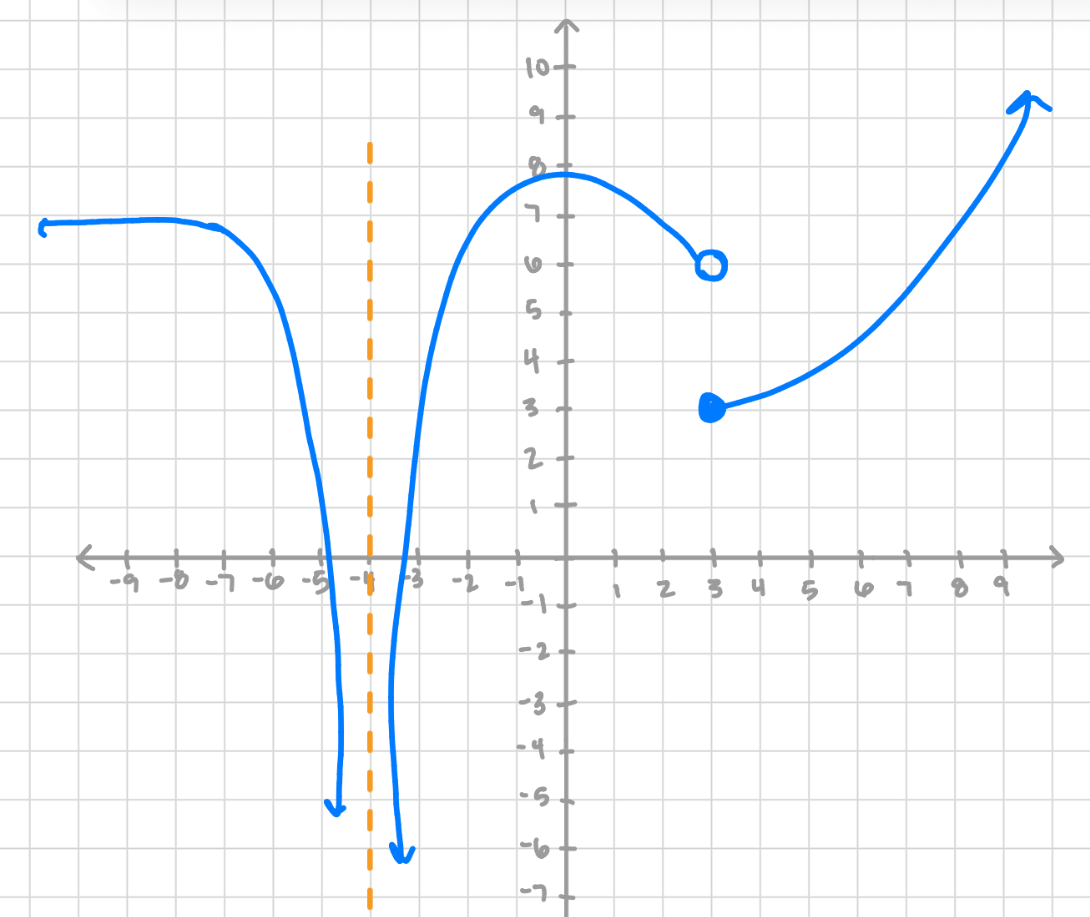
Sketch the curve given the info:
Domain:
(4, 10) \cup (10, oo)
lim_{x to oo} f(x) =1 , lim_{x to 10^+} f(x) = -oo , lim_{x to 10^-} f(x) = oo
f(5) = 0, f(11) =0, f'(12) = 0, f''(15) = 0
f'(x) > 0 when x is in
(4, 10) \cup (10, 12)
f'(x) < 0 when x is in
(12, oo)
f''(x) > 0 when x is in
(4, 10) \cup (15, oo)
f''(x) < 0 when x is in
(10, 15)
Domain gives overall check.
HA on right at 1.
VA at 10, going up on left and down on right.
x-intercepts at 5 and 11.
Increasing from 4 to 10 and 10 to 12. Decreasing greater than 12. Local max at 12.
Concave up 4 to 10 and greater than 15. Concave down between 10 and 15. Inflection point at 15.
Find the area bounded by y = f(x), x = -1, x = 1, and the x-axis, where
f(x) = 1/ \sqrt(1-x^2)
Set up integral and solve!
Determine if the function is continuous at x = 1.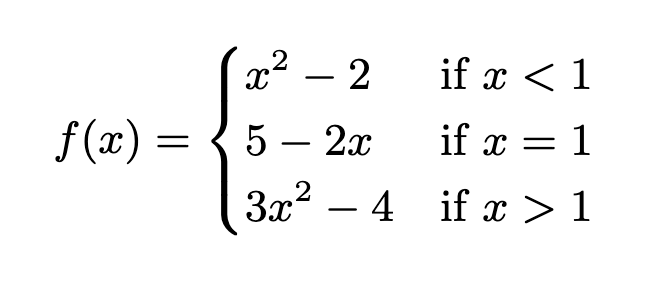
If it is continuous, verify all conditions of continuity. If it is discontinuous explain why.
Need to check
1. Limit exists (left = right)
2. Function value exists
3. Limit and function value are equal
lim_{x to - oo} (e^(3x) - e^(-3x))/(e^(3x) + e^(-3x))
Limit at infinity, will get (- oo)/(-oo), could try L'Hospital's (wouldn't work), need to use algebra and true facts.
Find the derivative.
f(x) = ((x+1)/(x-1))^cosx
Logarithmic Differentiation
If 1200 sq cm of material is available to make a weird cylinder package with a circular base and an open top, find the largest possible volume of the package.
Optimization. Set up two equations one of surface area (known-constraint equation) one of volume (unknown-optimization equation). Use constraint equation to get optimization equation in one variable. Take derivative of optimization equation, set it equal to zero, and solve.
The velocity of a sprinter is given by the table.
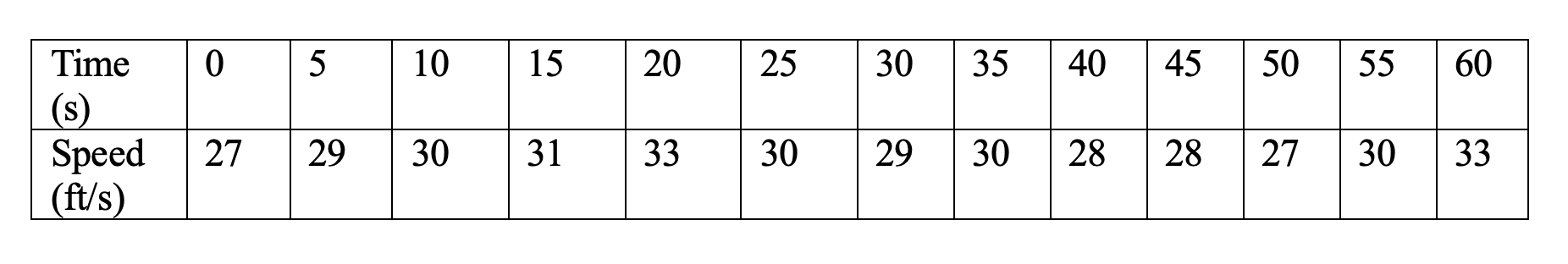
Use a Riemann Sum with 6 subintervals and midpoints to estimate the distance traveled by the sprinter.
6 intervals would give us a width of 10 seconds and midpoints would give the time values t = 5, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55.
So we'd sum the speed values for those times and multiply by 10.
Suppose that
4 \leq f'(x) \leq 8
for all x. What's the largest possible distance between f(2) and f(10)?
Mean Value Theorem!
lim_{x to 0} (cosx)^csc x
Find the derivative.
x^2y^5 + cos (2x+3y) = 11x^2 - e^y
Implicit differentiation.
A water tank has the shape of an inverted circular cone with base radius 2 m and height 4 m. If water is being pumped into the tank at a rate of 2 cubic meters per minute, find the rate at which the water level is rising when the water is 3 m deep.
The volume of a circular cone is
V = 1/3 pi r^2 h
Related Rates!
Draw a picture and label everything that you can.
Identify what is changing.
Take the derivative of the equation, making sure that anything changing is derivative implicitly with respect to time.
Plug things in and solve.
int_0^{pi/3} sinx \cdot e^cos x dx
Express the definite integral
int_1^4 (2x^2-5) dx
as a limit of a Reimann sum using right endponts.
Need to find \Delta x = (b-a)/n , x_i = a + i \cdot \Delta x , and f(x) .
Then plug into
lim_{n to oo} \sum_{i = 1}^n f(x_i) \Delta x