This type of lipoprotein is the primary contributor to atheroma formation.
LDL cholesterol
This type of arrhythmia is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death post-MI.
ventricular fibrillation
Between 1–3 days post-MI, the myocardium is predominantly infiltrated by these cells.
Neutrophils
This common side effect of beta-blockers.
bradycardia
Ischemic preconditioning refers to brief episodes of ischemia that protect the heart from this.
subsequent prolonged ischemic injury
These cells are formed when macrophages engulf oxidized LDL
Foam Cells
Rupture of the papillary muscle following MI can lead to this valvular condition
acute mitral regurgitation
By day 3–14, granulation tissue appears with infiltration by these cells.
macrophages
ACE inhibitors used post-MI may lead to this electrolyte abnormality. (can you tell me why)
hyperkalemia (indirectly through inhibition of Aldosterone)
Ischemic preconditioning reduces damage by limiting this process associated with reperfusion.
free radical–induced injury
This is the first step in atherogenesis, triggered by factors like hypertension or hyperlipidemia.
endothelial dysfunction
This late autoimmune complication of MI involves pericarditis and fever
Dressler Syndrome
The earliest histologic change within 4 hours of MI is described as this.
Wavy Fiber
(non-contractile muscle fibers being pulled by adjacent contractile fibers) 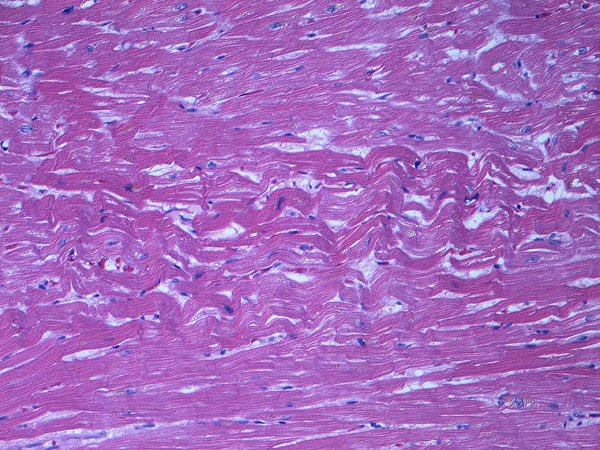
Thrombolytic therapy increases the risk of this life-threatening cerebral event.
intracranial hemorrhage
Opening of these mitochondrial channels during preconditioning reduces calcium overload.
ATP-sensitive potassium channels
This process, driven by smooth muscle cells, involves the deposition of collagen and proteoglycans.
extracellular matrix formation or fibrous cap formation
This mechanical complication causes a new holosystolic murmur and acute right heart failure.
ventricular septal rupture (acute VSD)
This microscopic feature in reperfused myocardial tissue is caused by calcium influx.
contraction bands
(associated with reprofusion)
![]()
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) may lead to this paradoxical tissue injury.
reperfusion injury
This enzyme pathway, activated by preconditioning, inhibits apoptosis and enhances survival signaling.
PI3K-Akt pathway
Arteriosclerosis is a multifactorial inflammatory disease of the intima, manifesting at points of __________________.
hemodynamic shear stress
This structural complication presents as a persistent ST elevation weeks after MI and risk of mural thrombus.
Left Ventricular aneurysm
After 2 weeks, healing involves dense deposition of this substance, leading to scar formation.
collagen
Dual antiplatelet therapy post-PCI most commonly leads to this adverse effect.
gastrointestinal bleeding
Preconditioning triggers involve the release of these autacoids that bind G-protein coupled receptors.
adenosine, bradykinin, and opioids