What is one key factor that helps you narrow down your differential diagnosis list after taking a history?
Onset and duration of symptoms, risk factors, associated symptoms, pattern recognition, red flags
pulmonary artery
What is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart?
How can wall thickness help differentiate between a vein and an artery?
Thicker walls are for arteries due to elastic fibres to help maintain pressure. Thinner walls for veins
What are the three types of nerves?
motor nerves, sensory nerves and mixed nerves
What is a neural plexus?
Network of intersecting spinal nerves that that redistribute spinal nerves into different peripheral nerves
What does differential diagnosis mean?
the process of differentiating between two or more conditions which share similar signs or symptoms
What is the layer in the middle of a blood vessel?
Tunica media
When looking at a cross section of either vessel, what can help differentiate between a vein and an artery?
Veins have a disfigured lumen and can contain valves if they are in the limbs to prevent backflow of blood. Arteries are more circular and have a thicker wall and maintain that shape with no valves.
What are sensory nerves?
Afferent nerves that carry information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system
What is the organisational structure of a neural plexus
Roots, trunks, divisions, cords, branches
What does the term “working diagnosis” mean in the context of differential diagnosis?
It is the most likely diagnosis based on current information, used to guide initial investigations and management
Muscular, Capillaries, Arterioles, Metarterioles, Elastic artery
elastic artery --> muscular --> arterioles --> metarterioles --> capillaries
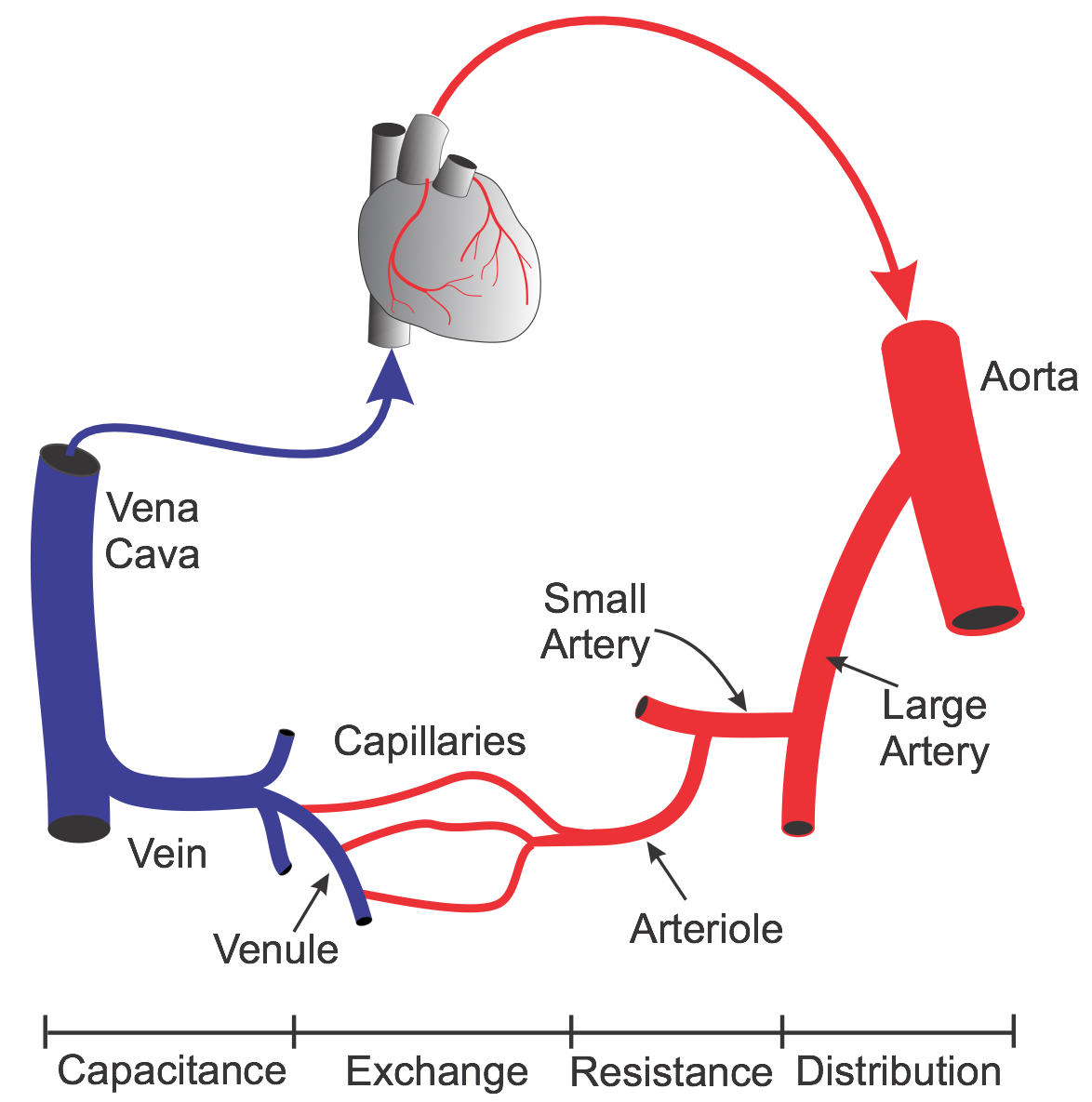
During dissection, how can colour help differentiate between an artery and a vein?
artery has more elastic tissue which will make it appear paler than a vein. veins can sometimes be slightly coloured with a hint of blue/purple.
What are motor nerves?
Efferent nerves that carry signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands
What type of spinal nerves contribute to a nerve plexus
The anterior rami contribute to nerve plexus formation, posterior rami contribute to the muscles and skin of the back
What are some errors that could arise if not considering a differential diagnosis? *Monday workshop helps!
Premature closure: Arriving at a conclusion based on the available evidence (which may be insufficient or incomplete) and not considering additional or alternative diagnoses.
What other role does blood vessels have other than oxygen transporation?
Transport of immune cells to set off the infection, Hemostasis, Transport of waste, Gas exchange, fluid regulation (water, electrolytes)
how can the placement of the vessel help differentiate between an artery and a vein?
Veins tend to be more superficial but can sometimes run along arteries deep. arteries are in deeper to protect from injuries.
What are mixed nerves, and which nerves are mixed?
Nerves that have both sensory and motor nerve fibres. The 31 spinal nerve pairs and four cranial nerves (eg. vagus nerve) are mixed nerves
What spinal nerves are involved in the brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is formed from C5–T1 spinal nerves and is responsible for the sensory and motor innervation of the entire upper limb
Describe the steps you would take to develop a differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with an undifferentiated symptom like fatigue or chest pain.
HOPC, systems review, physical examination, prioritise differentials based on urgency and likelihood, order appropriate tests etc
name 5 arteries that use pulsatile flow?
aorta, carotid arteries, subclavian and brachial artery, femoral artery, radial artery
Aorta – Strongest pulsations due to direct output from the left ventricle.
Carotid arteries – Easily palpable; strong pulse due to proximity to the heart.
Subclavian and brachial arteries – Prominent pulsation, especially during blood pressure measurement.
Femoral artery – Large and superficial; used for pulse checks in emergency medicine.
Radial artery – Commonly used for pulse taking due to strong and consistent pulsation.
Since veins dont have a thick elastic wall, what can help them push blood along towards the heart?
Skeletal muscles help by contracting around veins to help push blood.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Division of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal functions, divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.

Why do peripheral nerves differ in distribution from dermatome maps
Because nerve plexuses mix fibers from different spinal nerves, the areas served by peripheral nerves don’t match the neat, segmental pattern of dermatomes.