(but really, you should know these!)
This chronic respiratory condition involves reversible bronchoconstriction triggered by inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness.
What is asthma?
A patient is recovering from a mild case of pneumonia and needs low-flow supplemental oxygen to maintain SpO2 above 93%. The nurse chooses this device.
What is a nasal cannula?
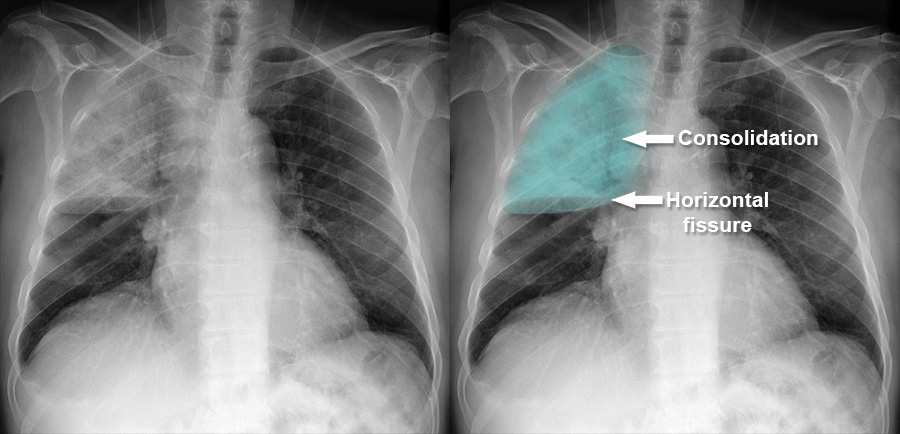
This condition shows lobar consolidation or patchy infiltrates on a chest x-ray.
What is pneumonia?
This condition is caused by bleeding into the pleural space following a trauma.
What is a hemothorax?
Identify the imbalance AND the degree of compensation.
pH 7.29
PaCO2 55
HCO3 24
What is uncompensated respiratory acidosis?
Rationale:
pH= acidic, PaCO2= acidic (matches pH), HCO3 still normal (hasn't started compensating yet)
This chronic, progressive disease leads to airflow obstruction, air trapping, and reduced elastic recoil.
What is COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)?
A patient with COPD has an SpO2 of 88%. The nurse knows this delivery device is ideal to deliver a precise, controlled FiO2 and avoid knocking out their hypoxic drive.
What is a venturi mask?

A ______ is caused when trapped air in the thoracic cavity pushes the heart, trachea, and mediastinum away from the affected side.
What is mediastinal shift?
This common chest injury causes point tenderness and ecchymosis and is usually treated conservatively with pain management and a chest binder for stabilization.
What is a rib fracture?
Identify the imbalance AND the degree of compensation.
pH: 7.32
PaCO2: 48
HCO3: 34
Partially compensated respiratory acidosis.
Rationale:
Ph= NORMAL (closer to acidic); PaCO2= acidic (started the problem); HCO3= alkaline (correcting the problem)
This disorder causes permanent dilation of the bronchi, leading to chronic cough, thick mucus production, and recurrent infections.
What is bronchiectasis?
A patient comes into the ED with severe dyspnea and an SpO2 of 80%. The nurse anticipates that the doctor will order this oxygen delivery device.
What is a non-rebreather mask?
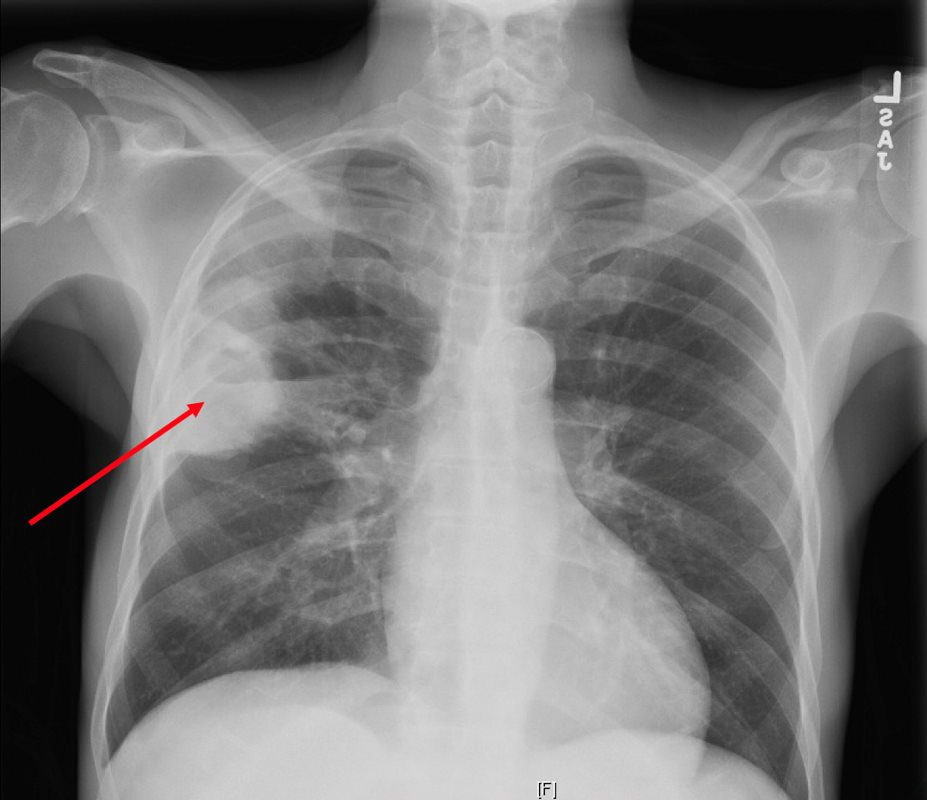
This slowly progressing respiratory disease may show upper-lobe cavitations or nodular infiltrates.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
This injury that occasionally requires chest wall stabilization (CWS) occurs when three or more consecutive ribs are fractured in two or more places.
What is flail chest?
Identify the imbalance AND the extent of compensation:
pH:7.45
PaCO2:48
HCO3:33
What is fully compensated metabolic alkalosis?
Rationale: pH=NORMAL (closer to alkaline)*, PaCO2=acidic (compensating), HCO3= alkaline (caused the problem)
This lung infection causes the alveoli to fill with fluid or pus, leading to fever, cough, and crackles on auscultation.
What is pneumonia?
A patient with sleep apnea is admitted after being found apneic at home. The nurse explains that this device delivers continuous pressure to keep their upper airway open.
What is a CPAP?
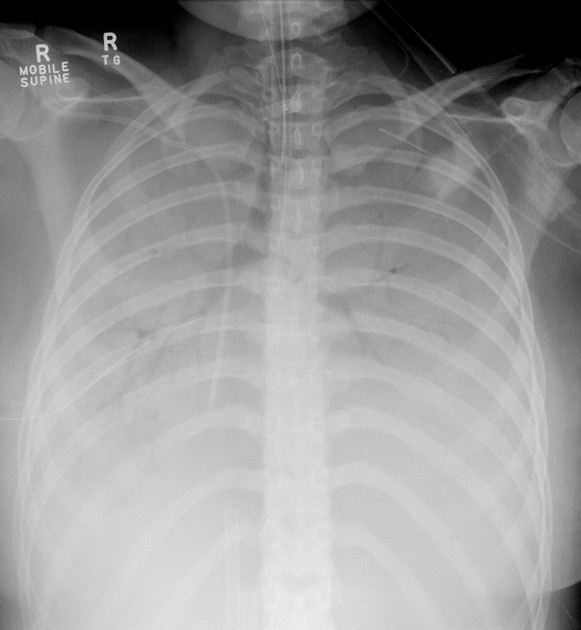
This condition presents with diffuse bilateral infiltrates often described as a "white-out" appearance on a chest X-ray.
What is acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
This traumatic emergency occurs when an open chest wound allows air to enter the pleural space, causing a "sucking" sound and respiratory distress.
What is an open pneumothorax
Identify the imbalance AND the extent of compensation:
pH: 7.50
PaCO2: 28
HCO3: 22
What is uncompensated respiratory alkalosis?
Rationale: pH= alkaline; PaCO2= alkaline (not enough acid); HCO3= normal (hasn't started to compensate yet)
This infectious disease is caused by Mycobacterium; presents with night sweats, weight loss, and a persistent cough; and requires airborne precautions.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
A patient in the ED ha worsening respiratory distress with increased work of breathing. The nurse explains that this device provides two levels of pressure (one for inhalation and one for exhalation) to improve ventilation and reduce CO2 retention.
What is a BiPAP?
This complication that often follows aspiration pneumonia appears on a chest x-ray as a thick-walled cavity containing both air and fluid/pus.
What is a pulmonary abscess?
This life-threatening condition occurs from penetrating trauma when the opening in the chest acts as a one-way valve, allowing air into the chest cavity but not back out.
What is a tension pneumothorax?
Daily Double!
This would be the appropriate intervention for a patient with a PaO2 of 85.
A) Nasal Cannula
B) Simple facemask
C) Non-rebreather mask
D) Continue to monitor