Which roots supply the musculocutaneous nerve?
C5–C7
What muscle does the musculocutaneous nerve pierce?
Coracobrachialis muscle
What are the 3 defining structures at the apex of the axilla and their significance?
1st rib, Clavicle, Superior edge of scapula - the space where compression can occur in thoracic outlet syndrome
What nerve innervates this muscle? :watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/extensor-carpi-radialis-longus-muscle/rXSbhSX8hjUGzEnnmYkvEg_7YnjyJFPzq_Musculus_extensor_carpi_radialis_longus_2.png)
Radial nerve
What are the borders of the cubital fossa?
- Medial: Pronator teres
- Lateral: Brachioradialis
- Superior: Line between epicondyles
What passes through the quadrangular space?
Axillary nerve & posterior circumflex humeral artery
A pin shows a structure attaching to the olecranon and the posterior surface of the ulna. What muscle inserts here?
Triceps brachii
Label all parts of the humerus

What muscles are innervated by the median nerve in the hand?
LOAF
Lumbricals 1 & 2
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
What structures pass through the triangular interval?
Radial nerve and the profunda brachii artery
What is the acronym for the 5 branches from the medial cord of the brachial plexus?
UMMMM (Ulnar, Median, Medial antebrachial cutaneous, Medial pectoral, Medial brachial cutaneous)
Which muscles attach to the coracoid process of the scapula?
Pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis, short head of biceps brachii
Label all parts of the scapula
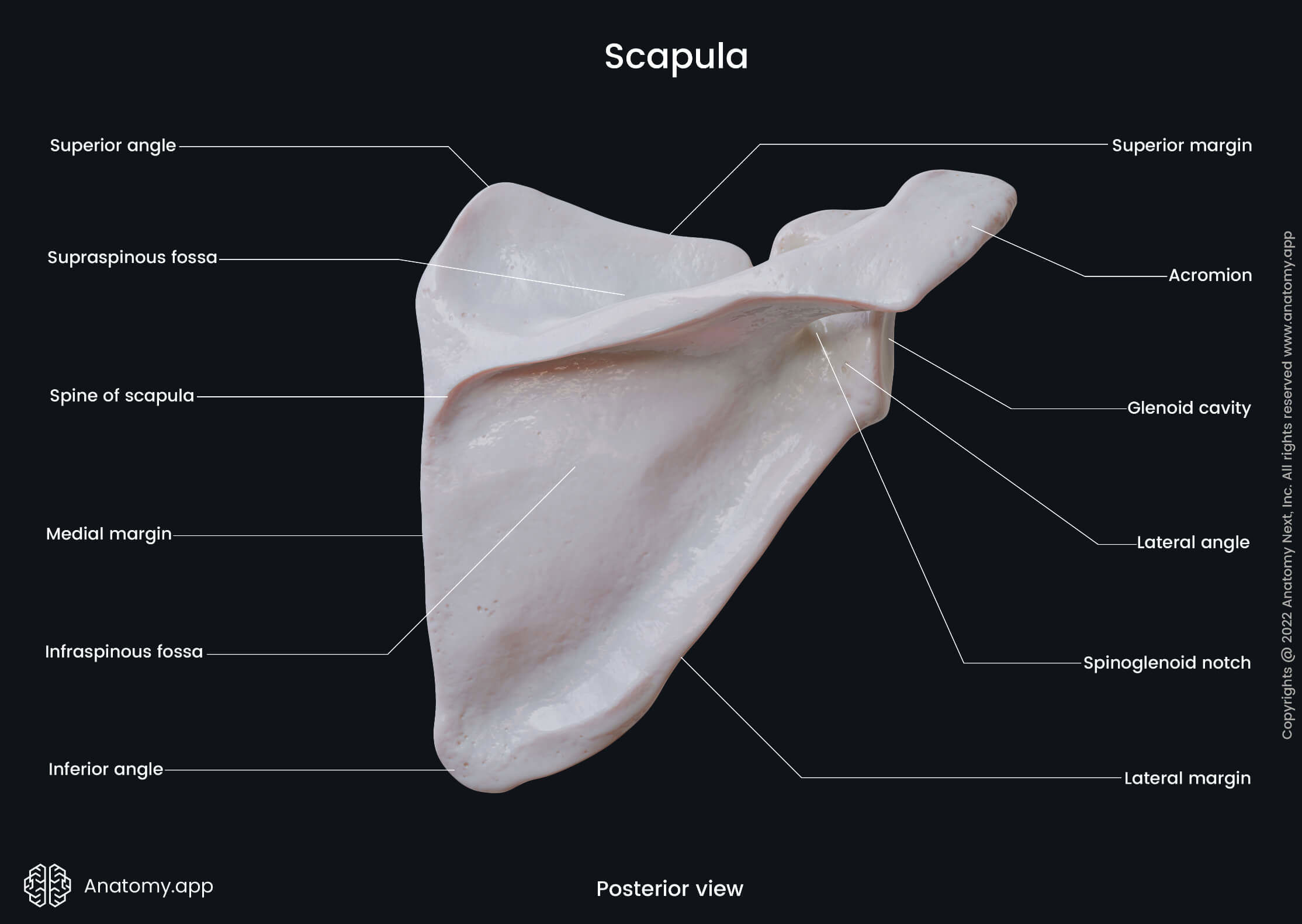
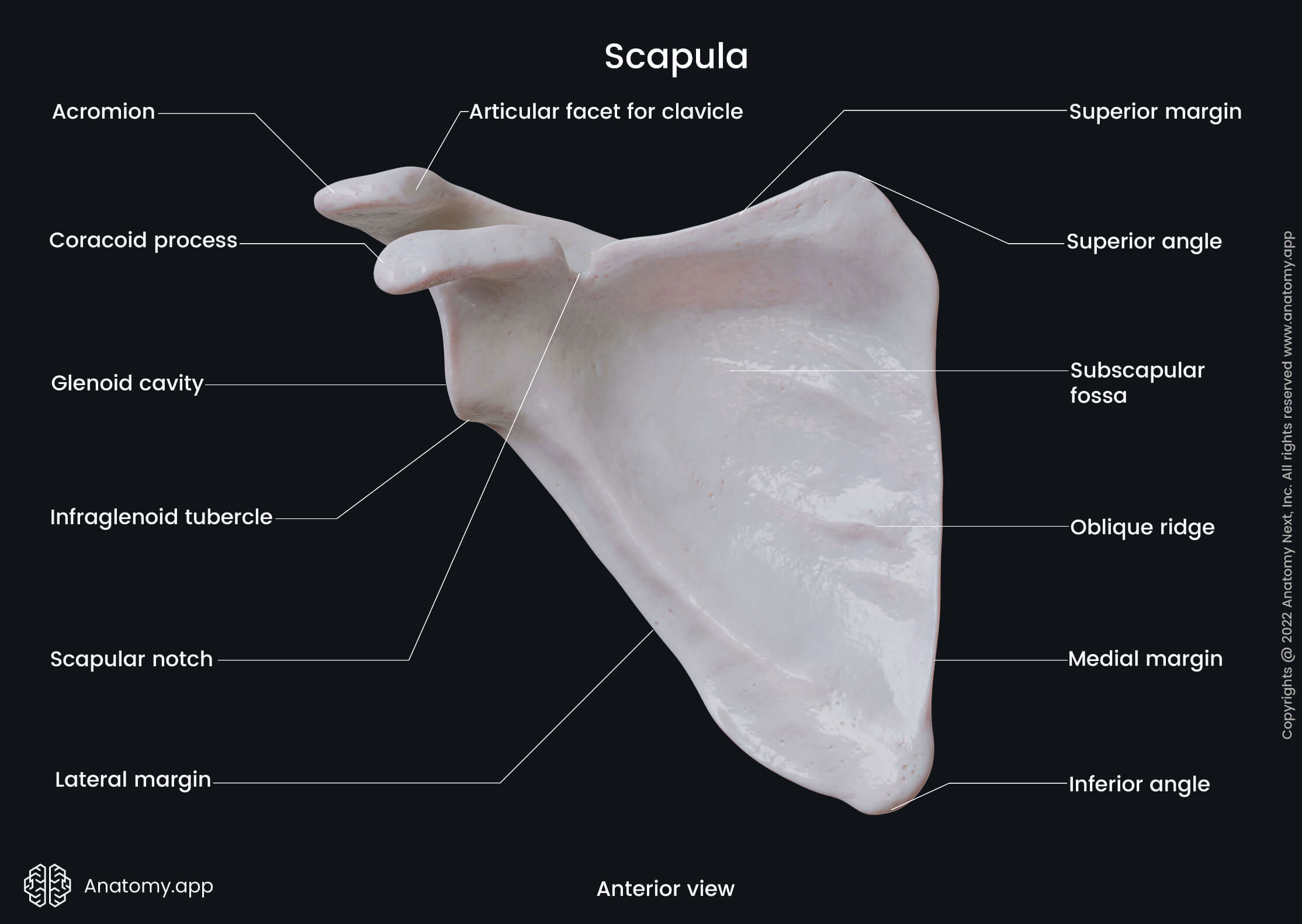
A cadaver dissection shows a muscle originating from the supraglenoid tubercle and inserting on the radial tuberosity. Which muscle is described, and which nerve innervates this muscle?
Biceps brachii, Musculocutaneous nerve
What is the significant relationship between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus?
FDS splits to allow FDP tendons to pass to distal phalanges
A stab wound to the upper arm completely severs the musculocutaneous nerve. Which actions will be completely lost and are weakened? Explain why actions will be lost or weakened.
Completely lost: none
Weakened:
Elbow flexion: brachialis and biceps brachii lost but brachioradialis (radial nerve) still flexes elbow
Forearm supination: biceps brachii lost but supinator (radial nerve) still supinates forearm
Shoulder flexion: coracobrachialis lost but deltoid and pectoralis major still flex shoulder
Name the muscles responsible for arm abduction at 0–15°, 15–90°, and >90°?
0–15°: Supraspinatus
15–90°: Deltoid
>90°: Trapezius + Serratus anterior
A muscle attached to the spine of the scapula and acromion is tagged. What is this muscle, and what is its primary action on the scapula?
Superior fibers of trapezius, Elevation of scapula
Thoracodorsal nerve contains which roots?
C6–C8
Name the superficial layer posterior forearm muscles from lateral → medial
Brachioradialis → ECRL → ECRB → ED → EDM → ECU (+ Anconeus)
Draw out the brachial plexus and label all parts
Draws: Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Terminal Branches
C5 root, C6 root, C7 root, C8 root, T1 root, dorsal scapular nerve, long thoracic nerve, upper (superior) trunk, middle trunk, lower (inferior) trunk, suprascapular nerve, nerve to subclavius, anterior division, posterior division, lateral cord, posterior cord, medial cord, lateral pectoral nerve, medial pectoral nerve, medial brachial cutaneous nerve, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve, upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal (middle subscapular) nerve, lower subscapular nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, lateral root of median nerve, medial root of median nerve, median nerve, ulnar nerve, axillary nerve, radial nerve,
A patient fractures the humerus and injures the radial nerve proximal to the forearm. Which wrist or finger actions are completely lost and which are weakened? Explain why actions will be lost or weakened.
Completely lost:
MCP extension of digits: all long extensors (extensor digitorum, extensor indices, extensor digiti minimi) are innervated by the radial nerve.
Weakened:
Wrist extension: ECRL may be partially spared depending on lesion level, finger extensors provide some passive force
Grip strength: paradoxically weaker because flexors work poorly when wrist flexes
Thumb abduction: APL mostly radial nerve bu APB (median) weakly assists
A child refuses to leave the park, and the parent yanks on the child’s arm to pull them towards the car. What structures are at risk? (bones, ligaments)
Radial bone and annular ligament
A volleyball player tears suprascapular nerve at suprascapular notch. Which shoulder actions are lost and which are weakened?
Completely lost: none
Weakened:
Shoulder abduction: supraspinatus initiates, but deltoid can still abduct
Shoulder external rotation: infraspinatus is gone but teres minor helps
Stabilization of humeral head: weakened but not absent because teres minor and deltoid compress head
Shoulder flexion: minimally weakened (supraspinatus contributes) but anterior deltoid and pectoralis major intact
What structures are found in the cubital fossa?
Median nerve, brachial artery, biceps tendon, radial nerve, median cubital vein, bicipital aponeurosis.