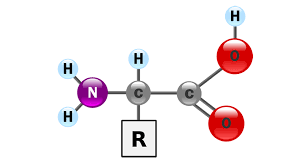
the monomer of a protein or polypeptide
What is an amino acid?
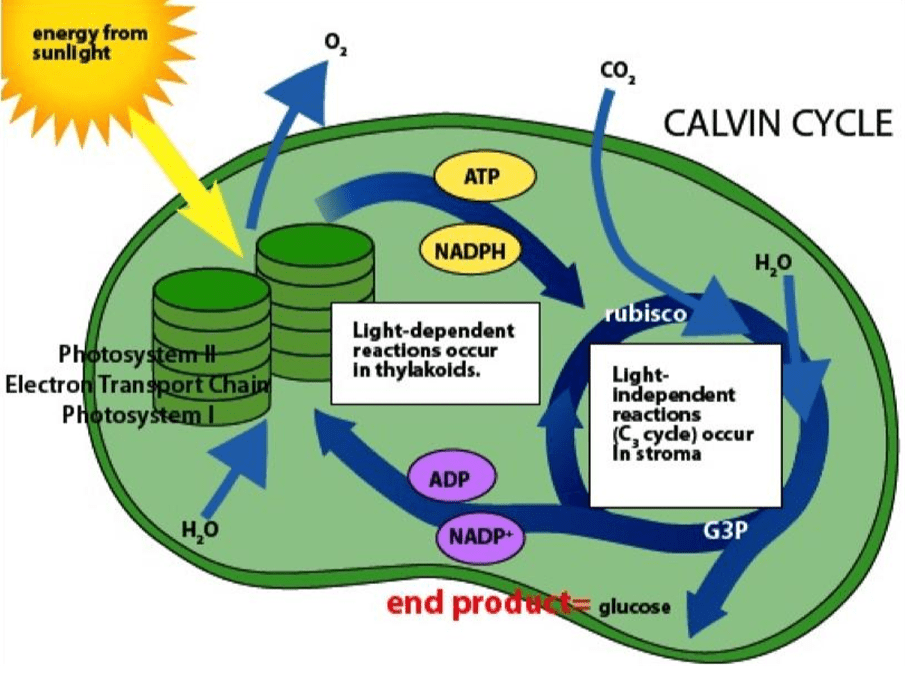
the making of complex carbohydrates (i.e. glucose) from carbon dioxide and water; occurs in autotrophic organisms such as algae
What is photosynthesis?
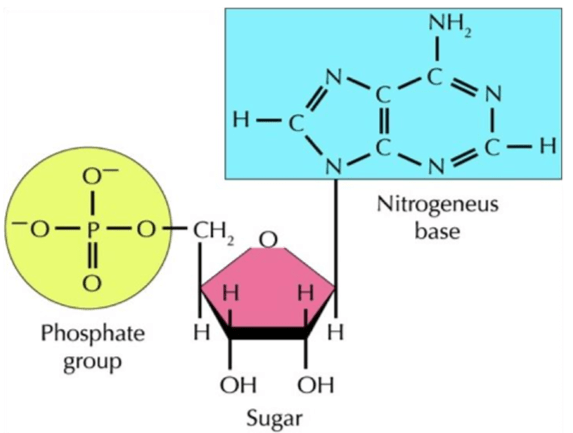
the part of a nucleotide / DNA molecule that stores genetic information; if this code is changed, it may lead to differences in the organism's proteins, and even their physical body
What is a nitrogenous base? (note: will accept nitrogenous base pair, base pairings - A=T; C=G)
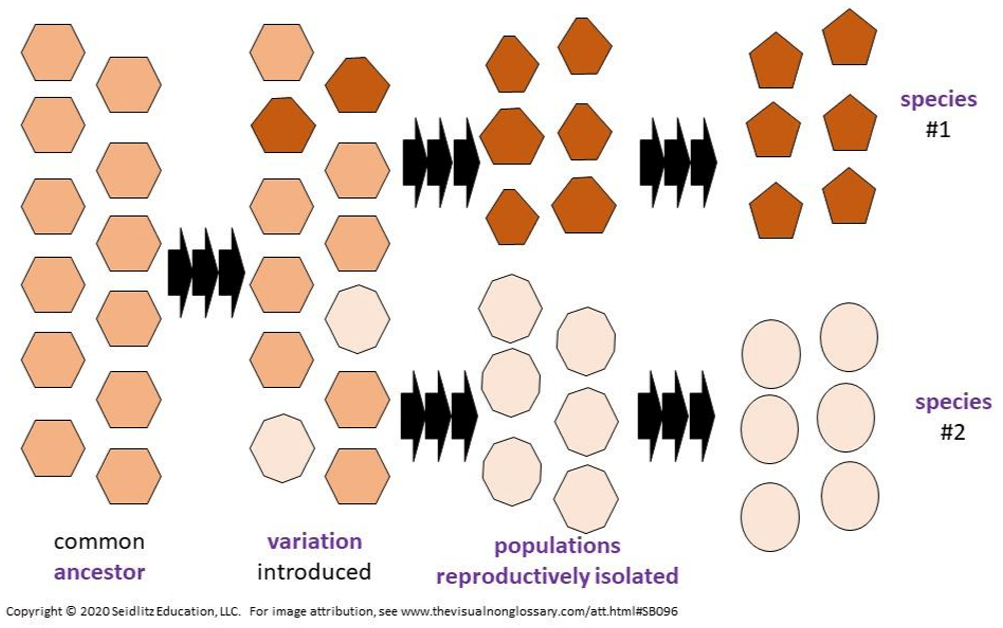
a change in the gene pool over time that results in populations of organisms becoming more closely adapted to their environment, to outcompete other organisms for resources (such as food or shelter)
What is Darwin's theory of evolution? (note: will accept evolution or theory of evolution)
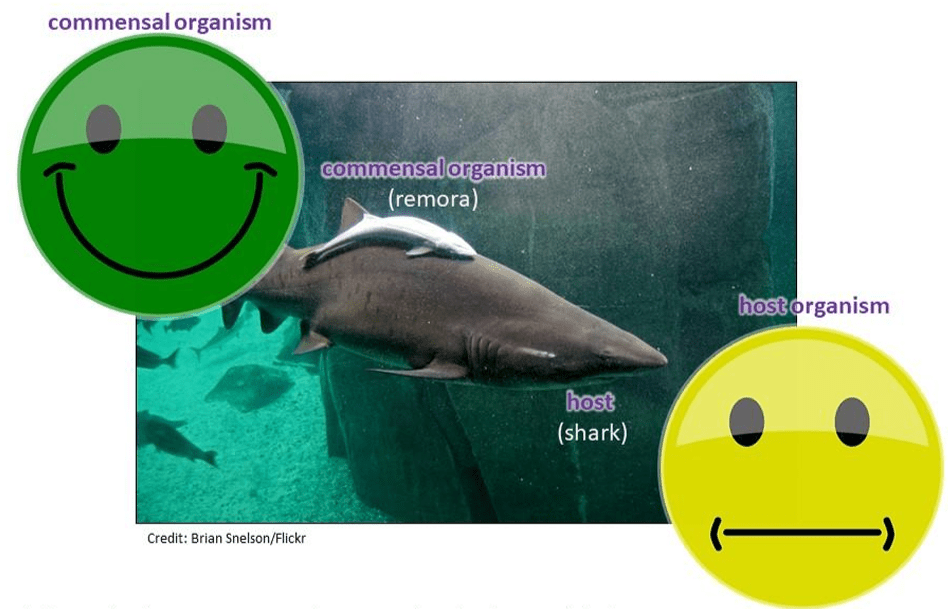
a squirrel lives inside the hole of a tree for shelter during the winter; the tree grows normally
What is commensalism?
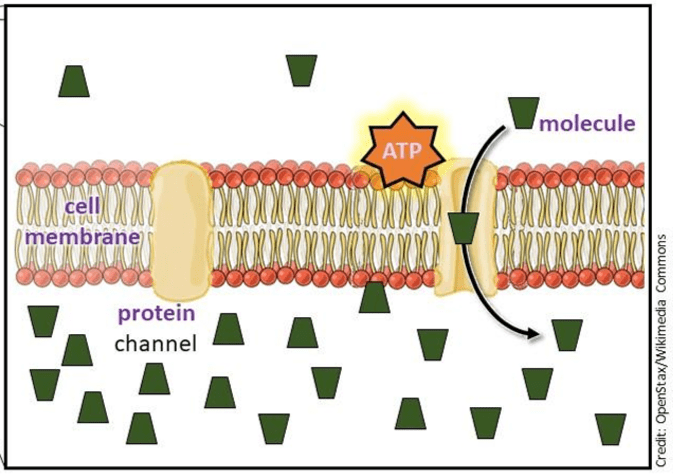
the movement of substances across the membrane against the concentration gradient; requires the use of a protein pump and ATP energy
What is active transport?
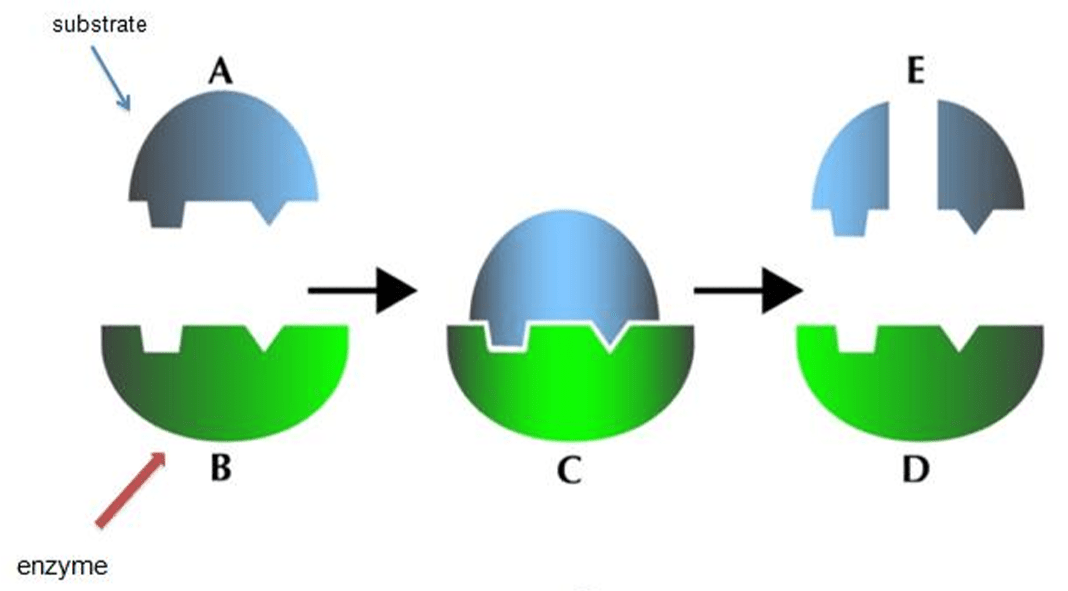
a protein molecule that lowers the activation energy of essential chemical processes within the body to speed up metabolic reactions, allowing organisms to survive
What is an enzyme?
ORIGINAL DNA SEQUENCE:
ATG ACG TAT CGA CGT CAG
MUTATED DNA SEQUENCE:
ATG ACT ATC GAC GTC AGC
What is a frameshift deletion mutation?
ORIGINAL DNA SEQUENCE:
ATG ACG TAT CGA CGT CAG
MUTATED DNA SEQUENCE:
ATG ACT ATC GAC GTC AGC
the most reliable method scientists use when determining similarities between organisms, and the strongest evidence for evolution so far
What are biochemical properties? (note: will accept DNA / comparing DNA sequences)
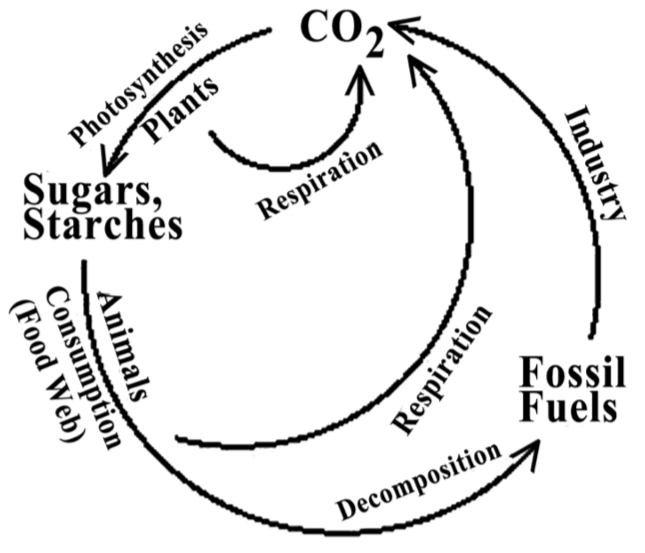
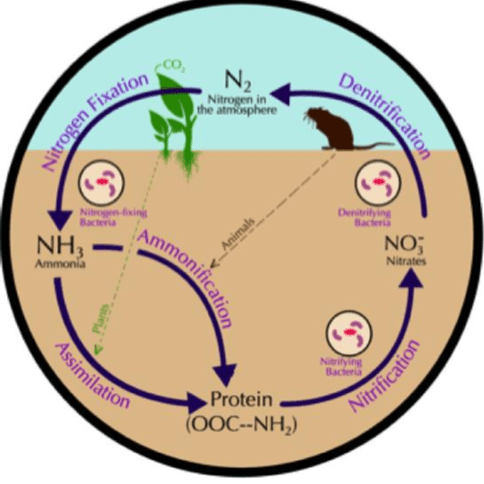
living things that help cycle nutrients like carbon and nitrogen back into the soil; too small to see without the use of microscopes
What are micro-organisms? (note: will accept bacteria for 100pts)
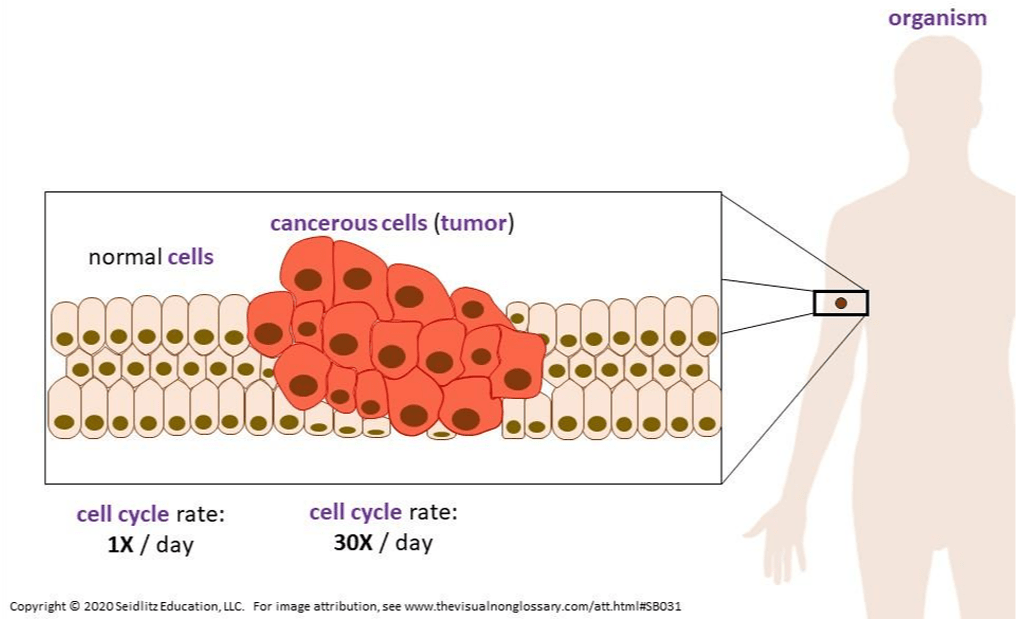
a disease that occurs as a result of mutations in the DNA, leading to uncontrolled mitosis
What is cancer?
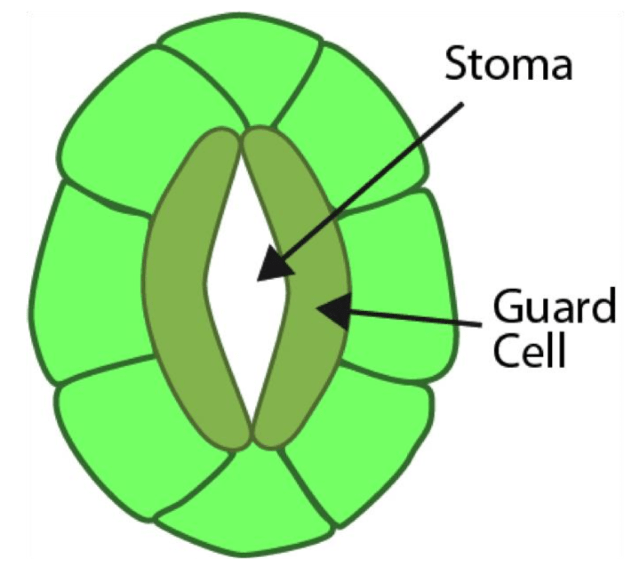
a tiny pore in the epidermis of a leaf used for gas exchange in plants; site of water leaving through the leaves through the transpiration stream
What is a stomata?
the FULL (unabbreviated) name of a nucleic acid molecule created in transcription and used in translation as the code for making polypeptide chains (proteins)
What is messenger ribonucleic acid? (note: will accept messenger RNA)
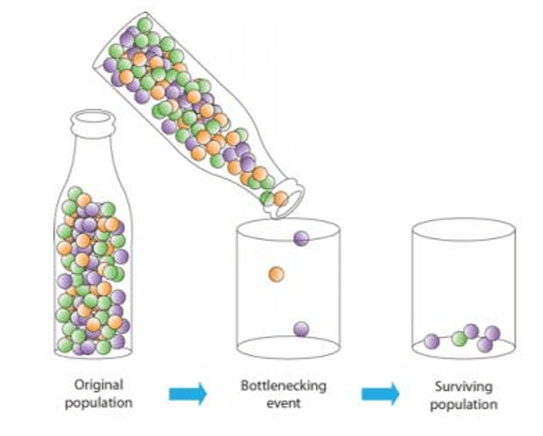
A small group of ten (10) otters manage to survive a tsunami by riding on a raft to a distant island. In the original population, 80% of the otters had white ears; nine of the otters that arrived on the new island have black ears, altering the genetic makeup of the otter population
What is genetic drift? (note: will accept bottleneck effect)
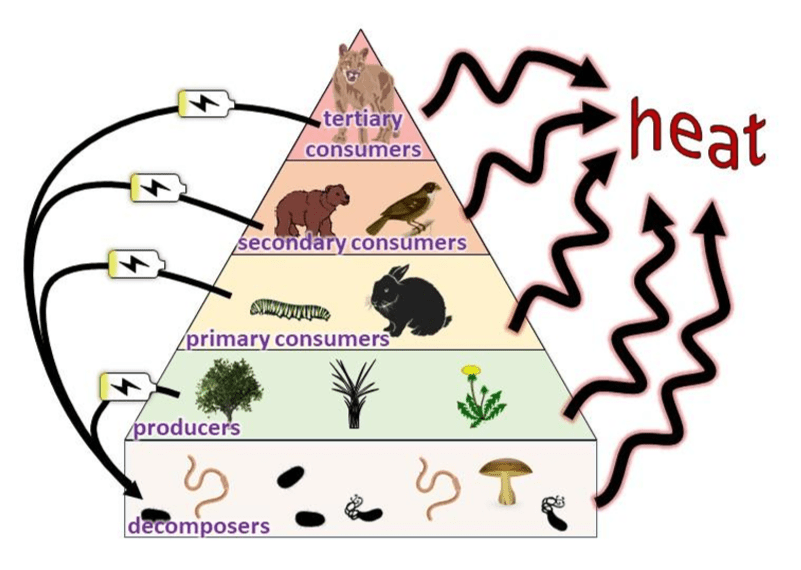
a model showing the various types of relationships that occur between trophic levels of an ecological community; can be used to calculate how much energy is left at certain trophic levels
What is an energy pyramid?
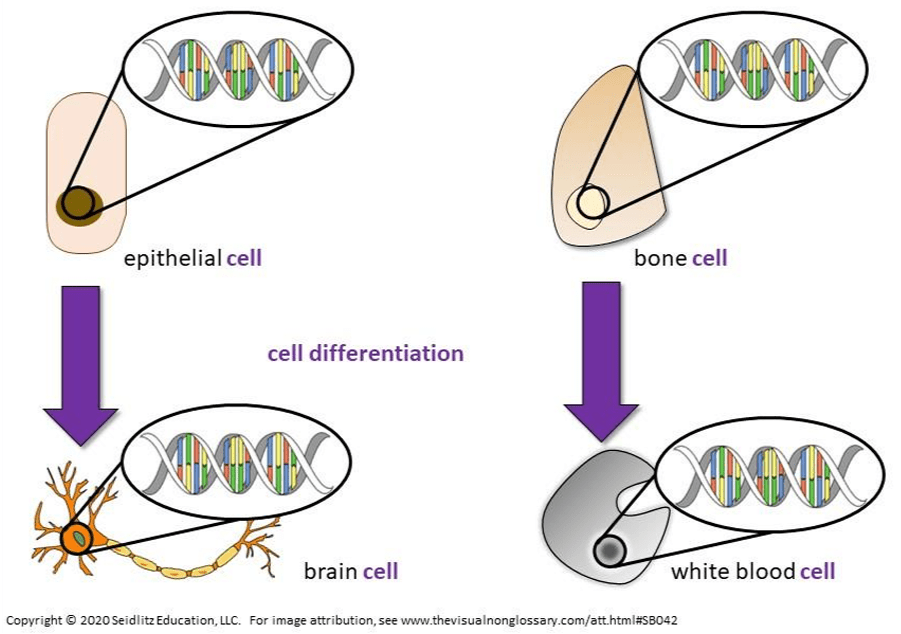
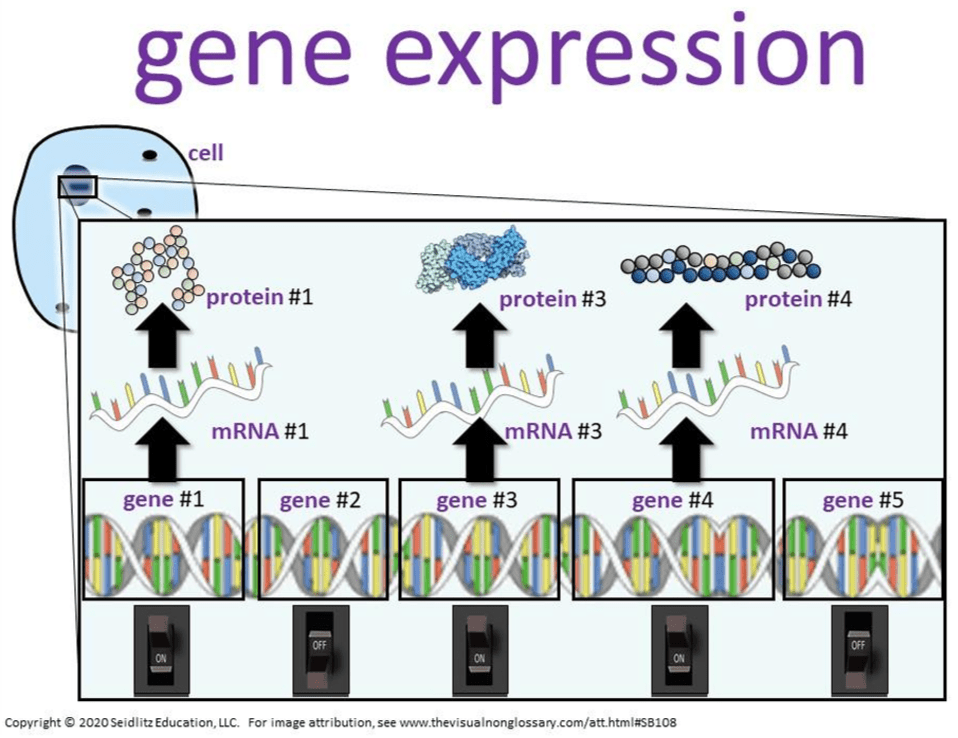
the biological term to explain why cell can be genetically identical and still perform different functions, by making different proteins (i.e. expressing different genes)
What is cell differentiation? (note: will accept gene expression for 100 pts)
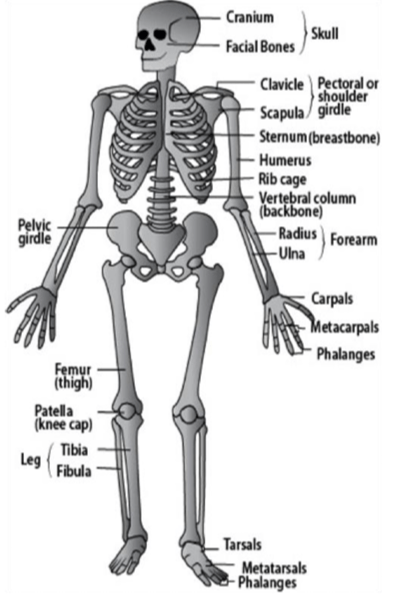
three (3) organ systems involved during puberty, when hormones signal to the bones in a teenager's body to replicate through mitosis and grow bigger and denser
What are the skeletal, endocrine, and reproductive systems? (+200 pts for each system)
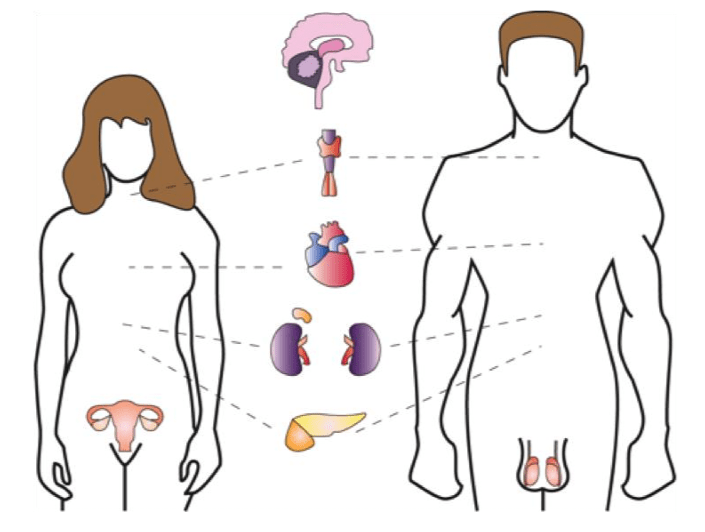
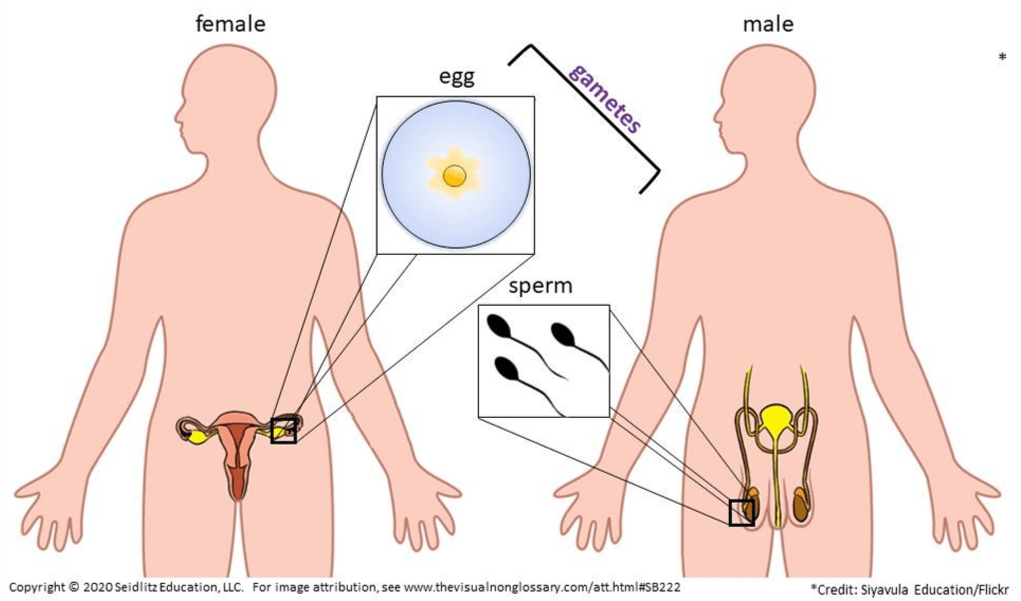
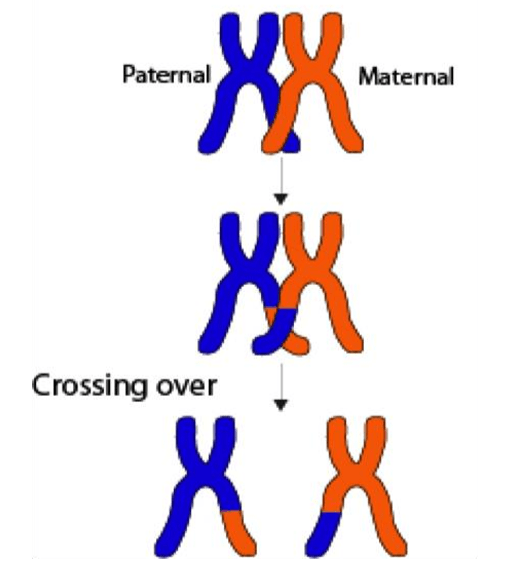
the process of exchanging genetic material between homologous chromosome pairs during meiosis; contributes to genetic variation
What is crossing over?
(Remember: "crossing over increases genetic variation"!)
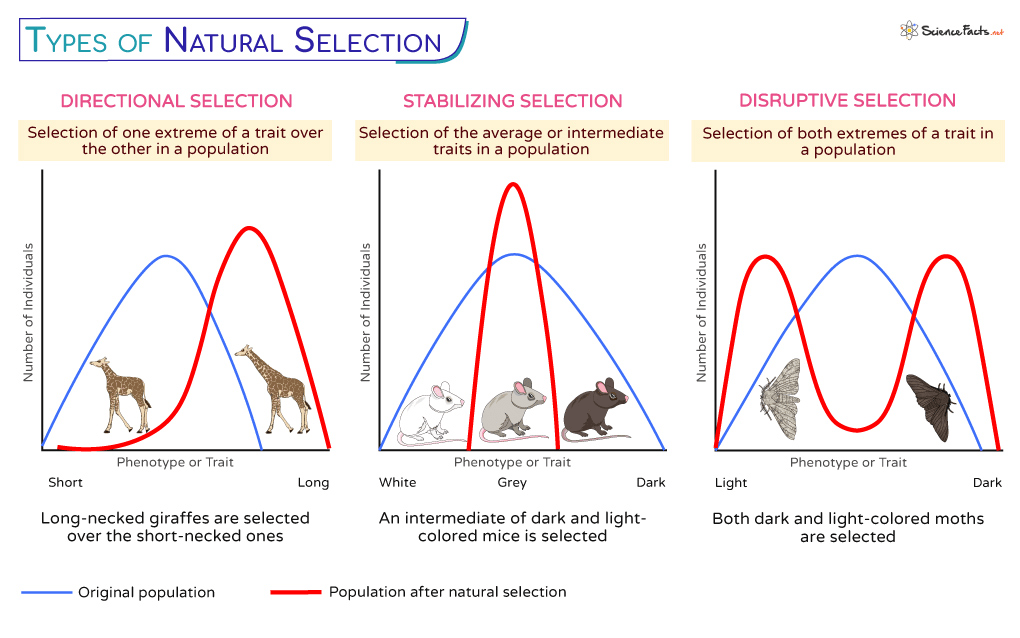
a type of natural selection that favors either extreme of a genetic trait, diversifying the population into two distinct groups. Over time, this type of selection is the most likely to result in speciation
What is disruptive selection?
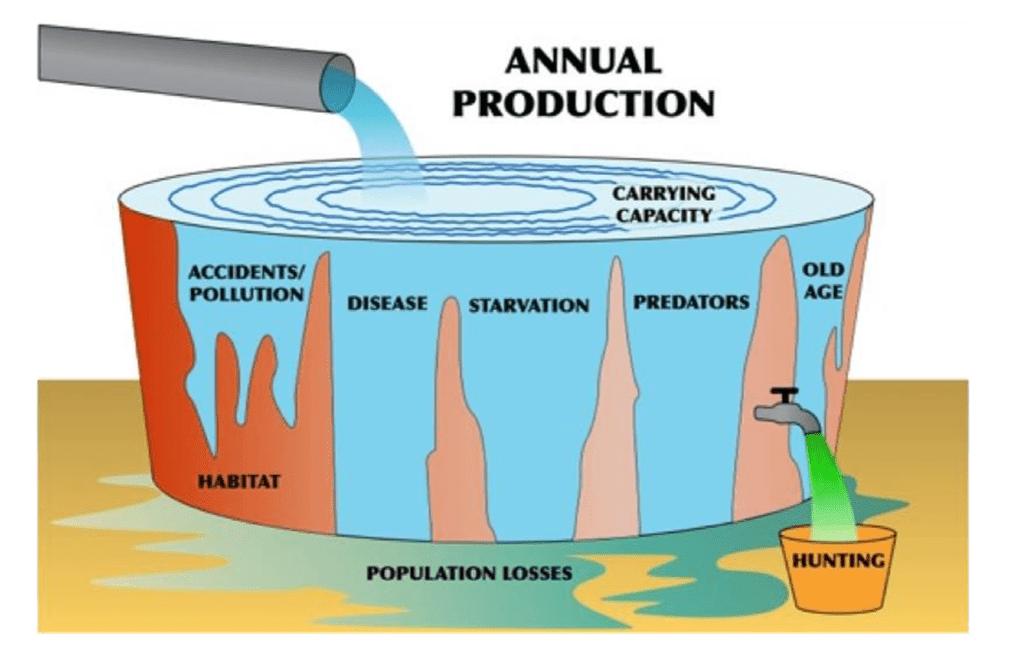
the maximum number of species an ecosystem can support; influenced by many factors, including emigration, immigration, predation, birth rate, and lifespan.
What is carrying capacity?
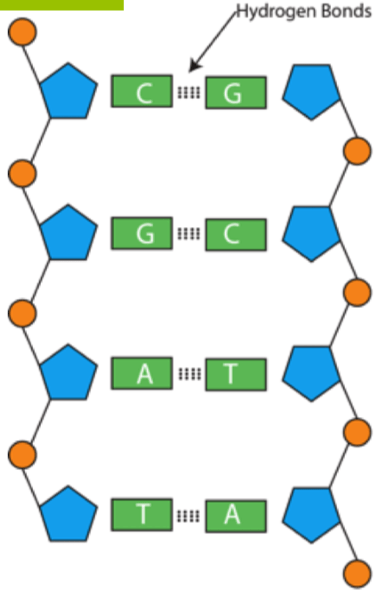
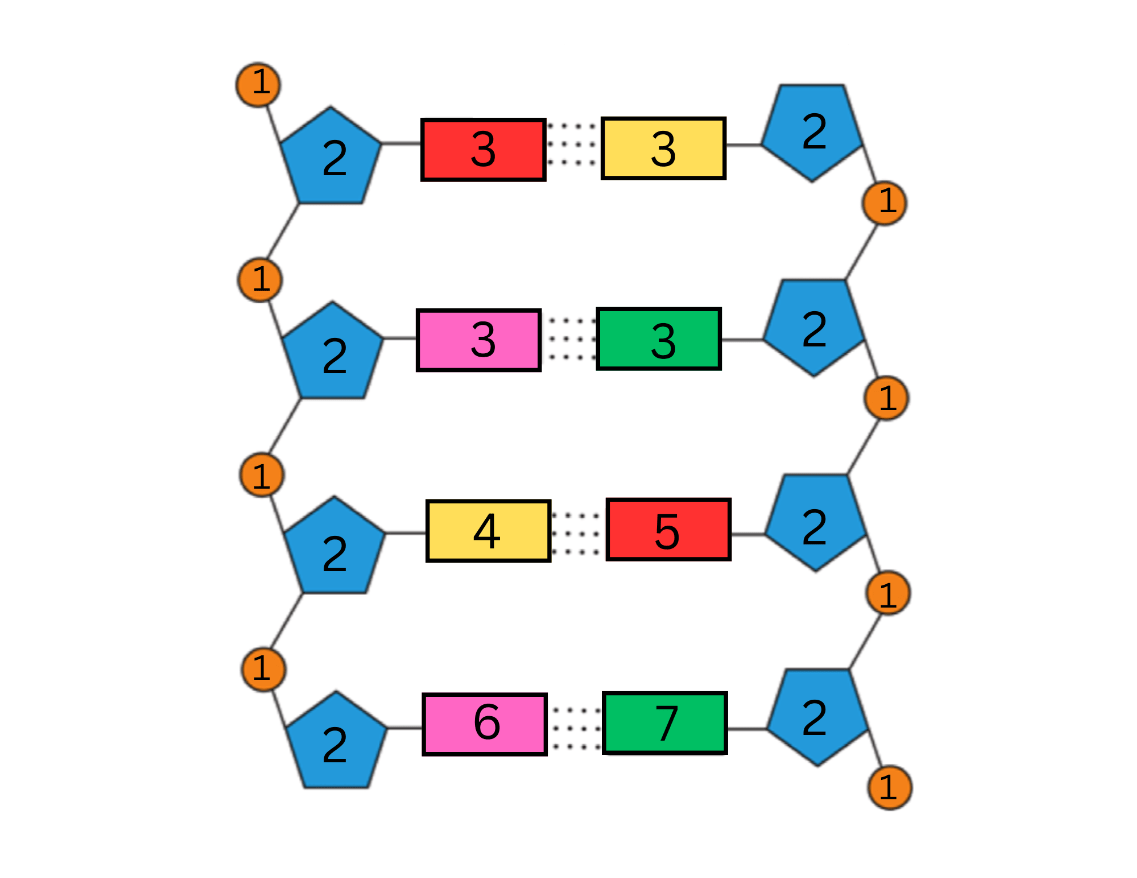
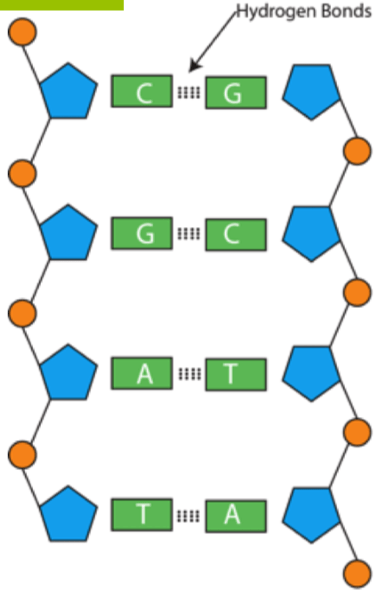
List all seven (7) labels for the parts of a DNA chain shown in the diagram below, AND the term to describe the shape of a DNA molecule:
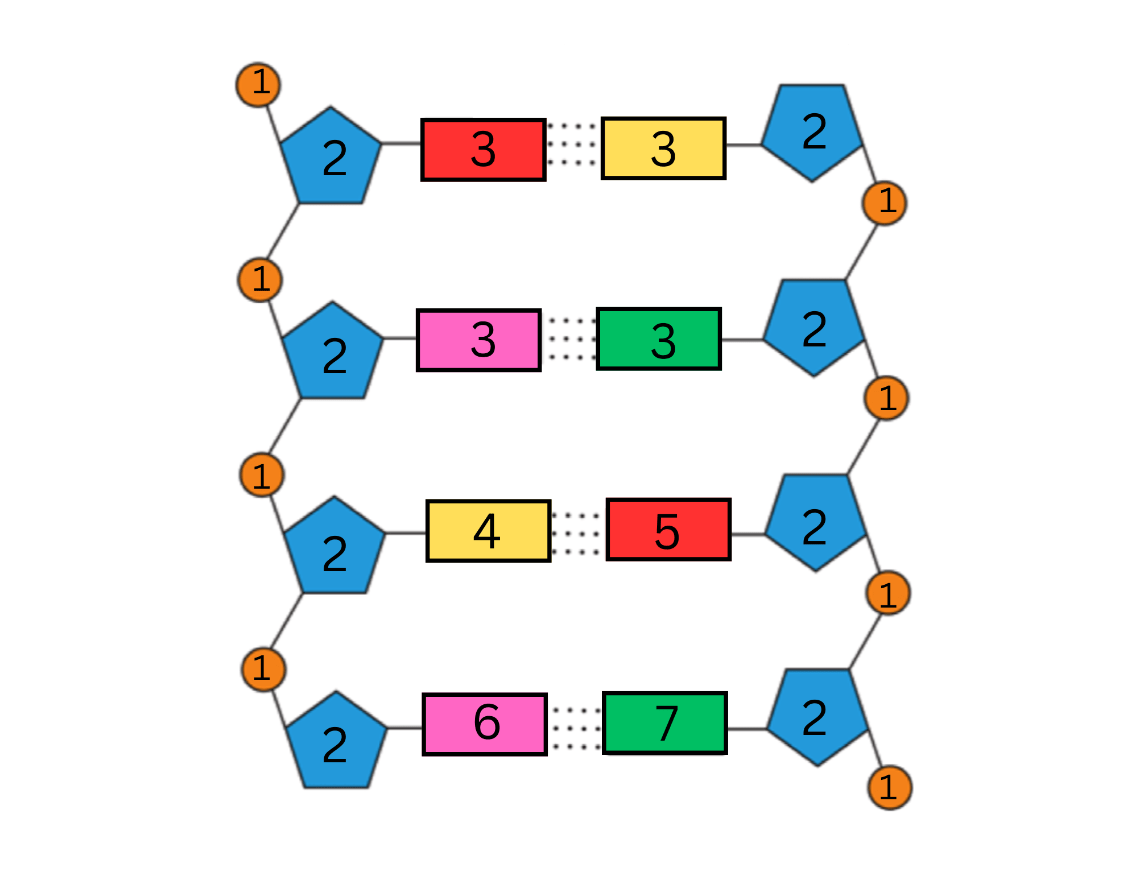
1. What is a phosphate group? (+100)
2. What is a (deoxyribose) sugar? (+100)
3. What is a nitrogenous base? (+100)
4. What is adenine (A)? (+100)
5. What is thymine (T)? (+100)
6. What is guanine (G)? (+100)
7. What is cytosine (C)? (+100)
8. What is a double helix? (+100)
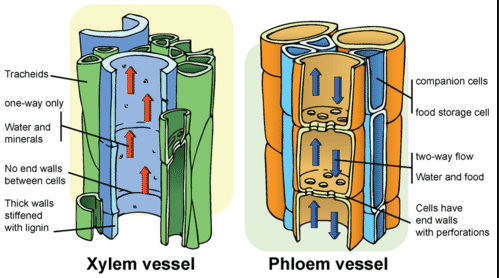
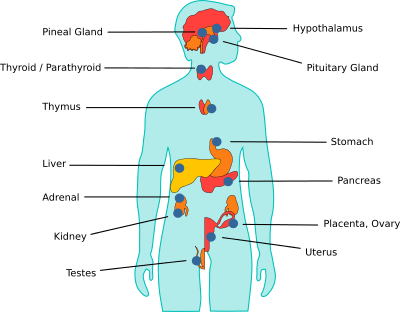
List four (4) similarities between animals and plants; including body systems + plant structures, metabolic processes, and methods of maintaining homeostasis
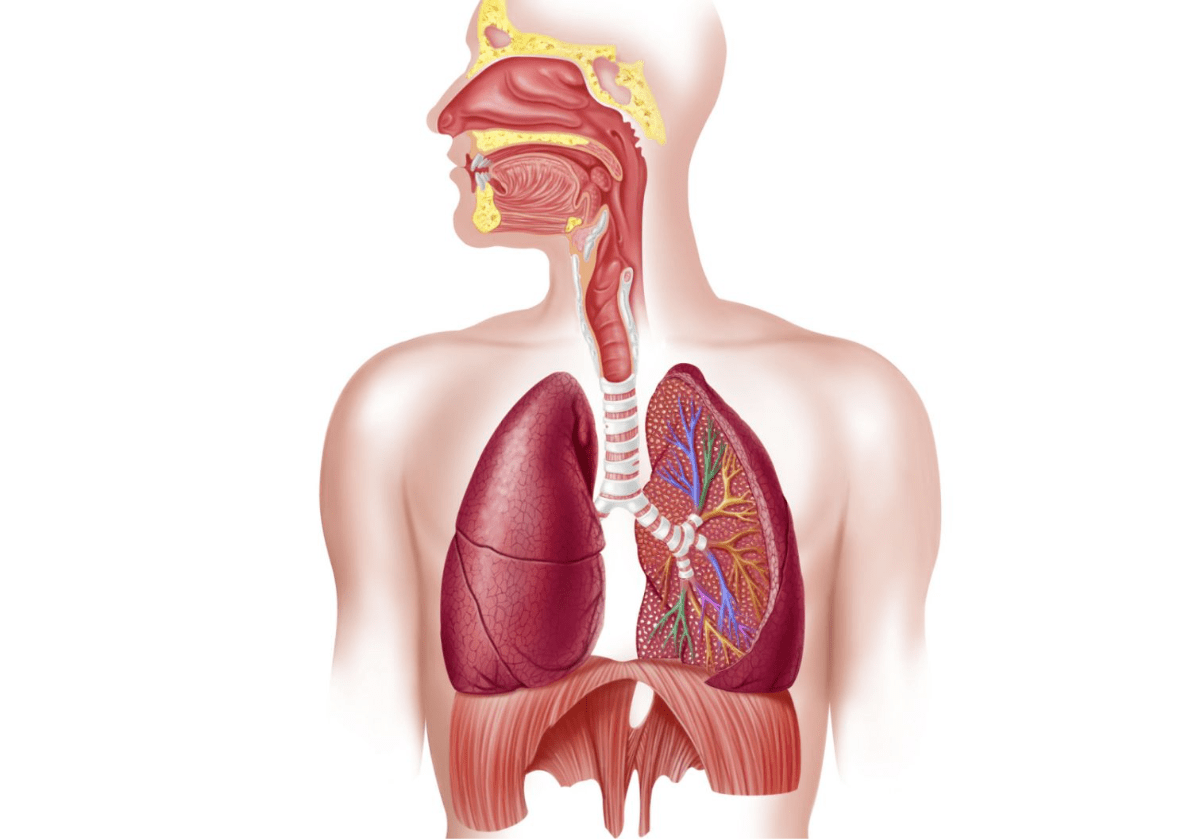
What is the stomata and the respiratory system? +200 (note: will accept lungs for 100pts)
What is the vascular and circulatory system? +200 (note: will accept arteries and veins for 100pts)
What is cell respiration? +200
What are hormones? +200
Determine the expected phenotypic ratio of this cross: In a fish, gold skin color (G) is dominant to black skin color (g) and split tail fin (F) is dominant to single tail fin (f). A breeder crosses a male fish having GgFf genotype with a female fish having ggFf genotype.
Genetic Cross: GgFf x ggFf
GgFf (+200 for FOIL) ggFf (+200 for FOIL)
F: GF F: gF
O: Gf O: gf
I: gF I: gF
L: gf L: gf
4 unique combinations 2 unique combinations
(+200 for the table)
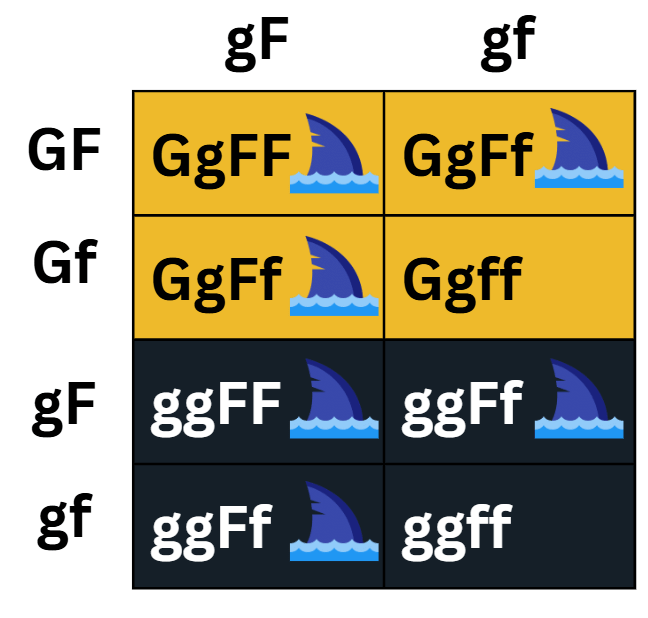
3 gold + split fin; 1 gold + single fin; 3 black + split fin; 1 black + single fin
(+200 for correct final answer)
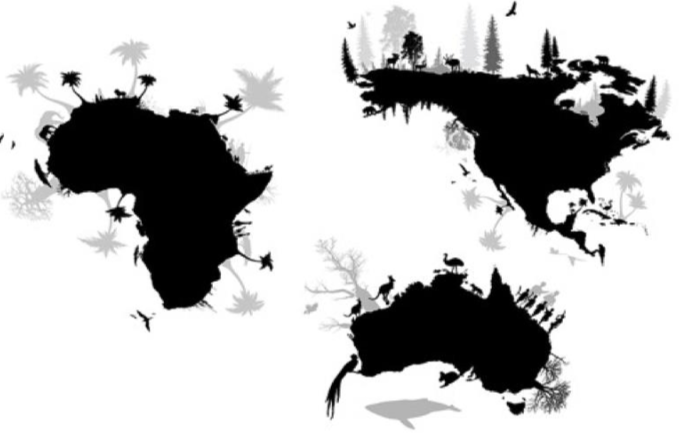
List the six (6) major pieces of evidence for the theory of evolution.
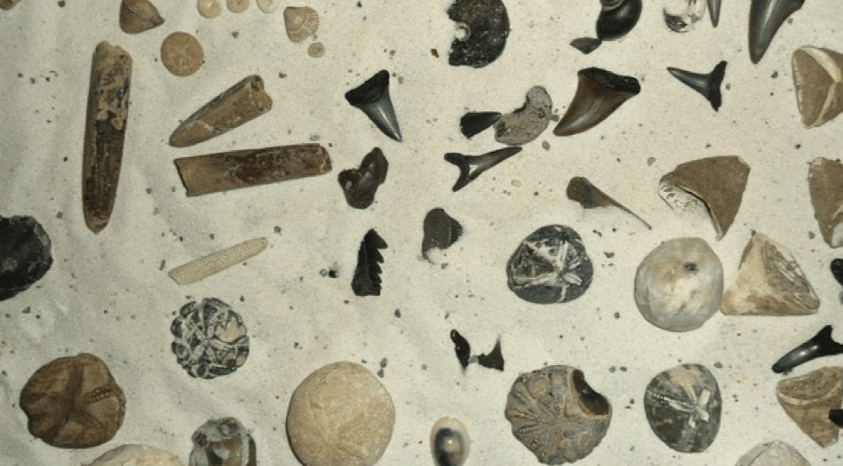
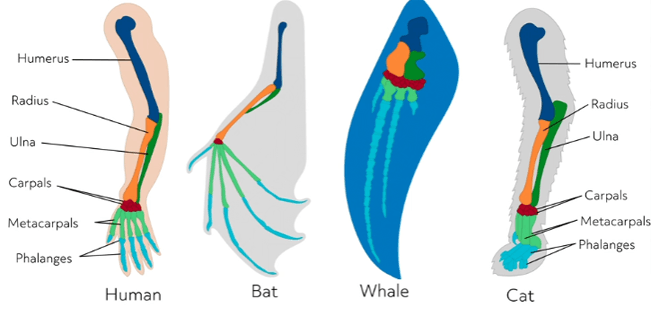

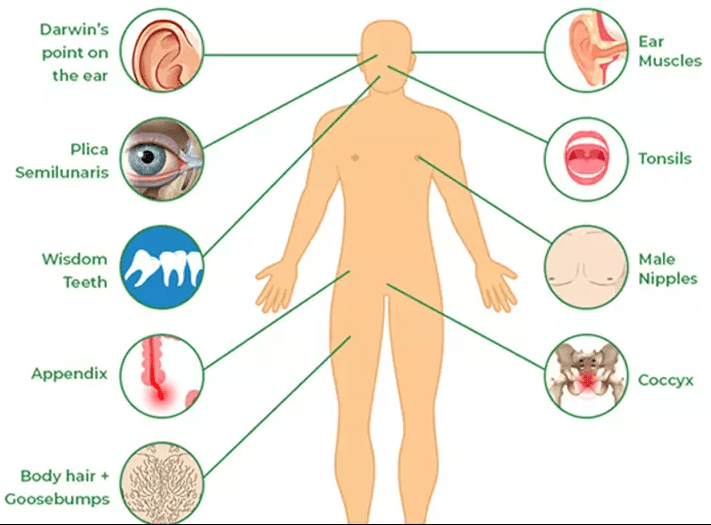
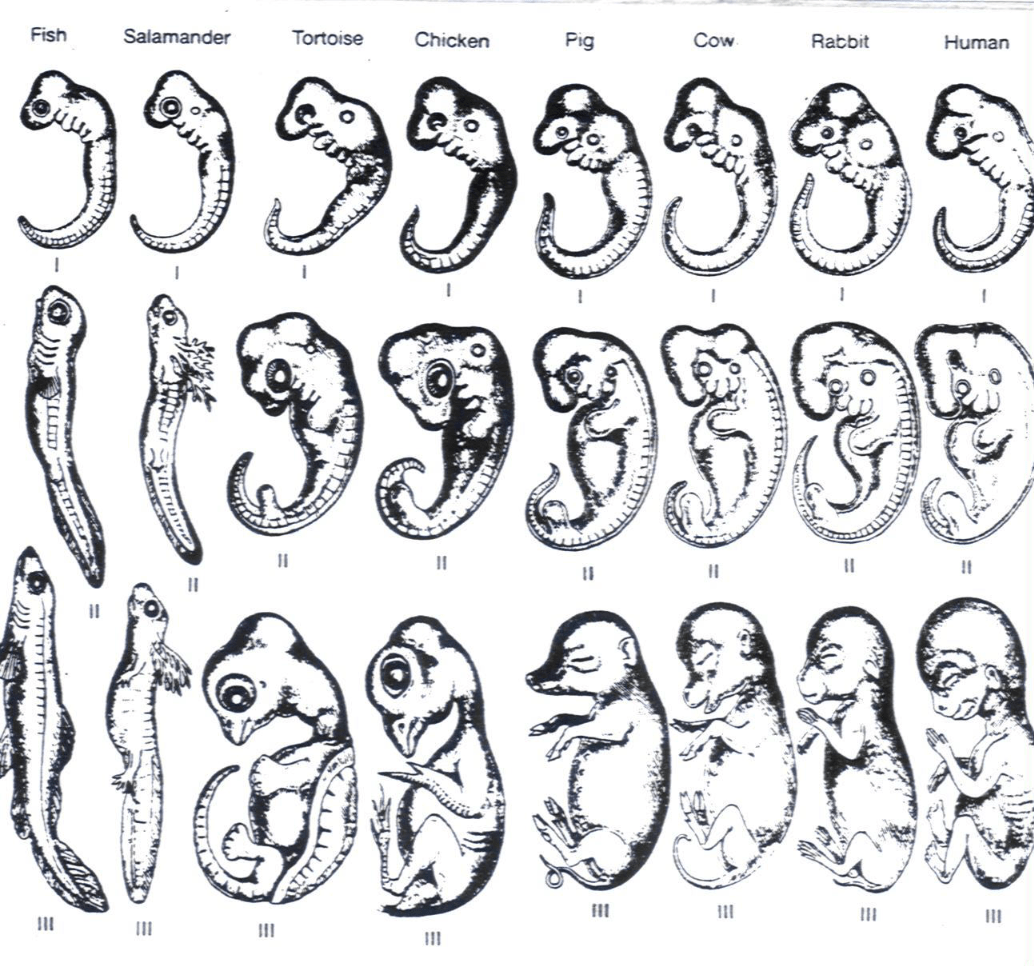
What are molecular homologies? (note: will accept biochemical similarities or DNA sequences)
What is the fossil record?
What is biogeographical distribution? (note: will accept biogeography)
What are homologous structures?
What are vestigial organs?
What are embryological homologies? (note: will accept embryology)
List all seven (7) possible terms that could be used to label the organisms shown in this food web; Calculate the amount of energy left (in kJ) at the fourth trophic level.
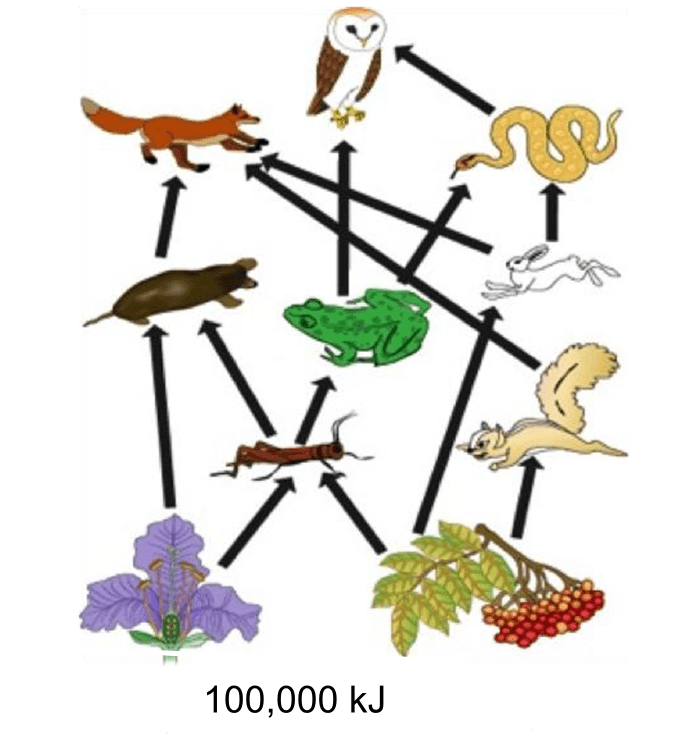
What is an autotroph? (+100)
What is a heterotroph? (+100)
What is a producer? (+100)
What is a primary consumer? (+100)
What is a secondary consumer? (+100)
What is a tertiary consumer? (+100)
What is a quaternary consumer? (+100)
What is 100 kJ? (+100)