This event is caused by an underwater earthquake that can rapidly change Earth's surface.
What is a tsunami?
A wave of energy that travels through the Earth, away from an earthquake in all directions.
What is a seismic wave?
True or false. Only transform boundaries have earthquakes.
False.
What could occur at point x in this diagram?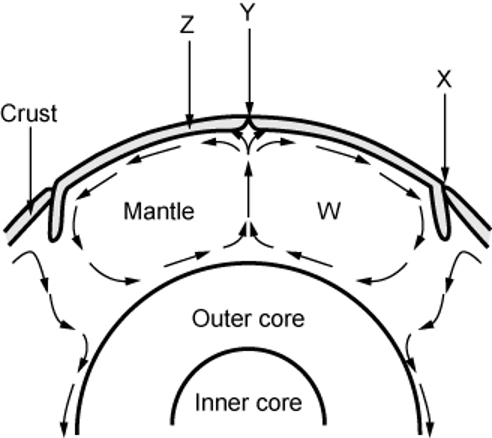
What is an earthquake and a volcano?
Tectonic plates move in opposite but parallel directions along boundaries at ____________. Fill in the blank.
This type of fault is caused due to two blocks of rock sliding past each other in opposite directions.
What is a strike-slip fault?
This type of seismic waves does the greatest damage.
What are surface waves?
This movement causes earthquakes to occur.
What are convection currents?
This type of fault is where the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.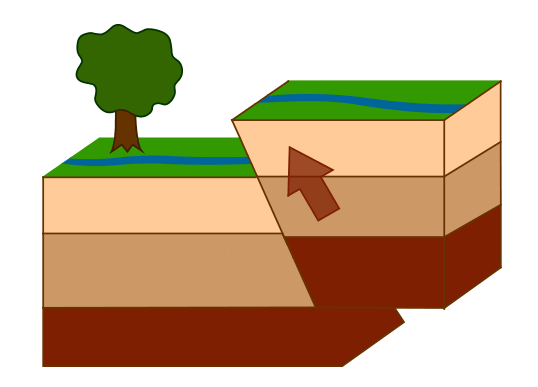
What is a reverse fault?
Earthquakes occur due to the ______________ of tectonic plates that release _________________. (fill in the two blanks in order)
This fault is where the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
What is a normal fault?
The three *main* types of seismic waves.
What are P Waves, S Waves, and Surface Waves?
True or False. Earthquakes can form at any point in the plate under stress from the mantle convections.
True
What type of fault is shown?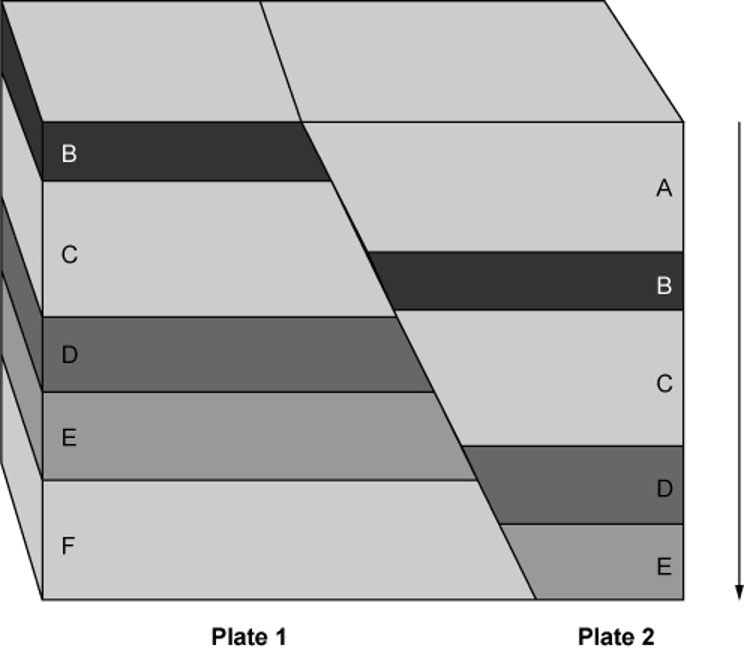
A normal fault
A ___________ is a break in the earth's crust.
What is a fault?
This region is known for having volcanoes and earthquakes due to its numerous tectonic plate boundaries. Name that region.
What is Ring of Fire?
What could be a reason for an increase of speed in seismic waves?
The waves travel from a less dense material into a more dense material.
What is an earthquake?
Explain what is happening in this picture. Make sure to use science vocabulary!
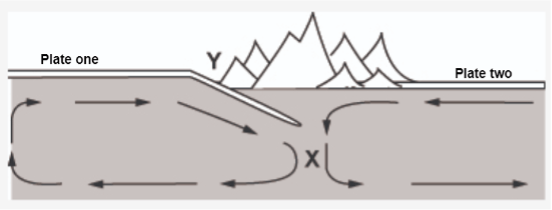
This is a convergent boundary. Plate one is more dense so it is subducting underneath plate two. At point X, Plate one is melting into magma (molten rock). Magma is melting through plate two causing a volcano to form at point Y.
____________ is the point inside the earth, along a fault, at which an earthquake begins.
What is a focus?
Where do we mostly find earthquakes?
Close to a plate boundary.
The fastest seismic waves.
What are P waves (primary waves).
Where do most earthquakes take place?
Where do we most likely find volcanoes?
Close to a plate boundary.
Seismic waves generate from earthquakes help provide evidence of liquid layers of earth's interior. Why? Because ________ waves only travel through _______ matter.
Secondary, solid