Standard of care is the ____ and considers these circumstances:
Objective standard: the reasonable, prudent person who knows (Vaughan v. Menlove):
Only those risks that a reasonable person would have known or are reasonably foreseeable to a person of ordinary intelligence and prudence, regardless of the actual knowledge of the defendant. (Parrot v. Wells, Fargo & Co.)
1) Extraordinary Knowledge and Skill
2) Physical Disability (same/similar condition)
3) Sudden emergencies, IF not caused by negligence.
**Children's duty may be considered accordingly to age, intelligence, and experience UNLESS DOING ADULT ACTIVITIES.
What is the eggshell plaintiff rule and shabby millionaire rule:
Eggshell plaintiff rule: holds that a D is liable for the full extent of a plaintiff's injuries, even if the victim was especially vulnerable due to a pre-existing condition
Shabby millionaire rule: a D is liable for a P's full loss of income, regardless of their high income or wealth.
What does intent mean in the context of the intentional tort of battery?
Intent means either that the defendant acted with the purpose of causing a harmful/offensive contact, or that the defendant knew with substantial certainty that harmful or offensive contact would result from her actions.
General Jurisdiction exisits when:
The Defendant has continuous and sytematic contacts with the forum state that are so substantial that the defendant is essentially "at home" (i.e. domiciled) there.
What is the Well-Pleaded Complaint Rule?
For the court to have this type of jurisdiction, the federal law issue MUST appear in the plaintiff's complaint, without relying on an anticipated defense.
3 ways property may be transferred?
What is:
1) Intervivos
2) Will
3) Death
The level of control required over a wild animal, typically met by mortal wounding or actual trapping, to establish first possession.
Dominion and Control
The factor the jury considers when applying the reasonably prudent person standard to a defendant acting in a sudden, unforeseen, and terrifying situation not of their own making.
The Emergency Doctrine.
Applicable if D is not the cause of the emergency.
What kind of proximate cause relieves the D from liability:
Superseding cause:
1) 3rd party's intervening act (occurring after D's negligence) that was not reasonably foreseeable by D. (harm is unforseeable)
2) Puts fatal kind in the chain of causation (chain of causation is broken)
3) Although it’s true that criminal or tortious third-party conduct typically severs the chain of proximate causation between P and D, that is not the case when the third
party’s intervening act was foreseeable.
Under what circumstances will a contact be deemed offensive?
Offensive contact occurs if the contact offends a reasonable sense of personal dignity.
Due Process requires that:
1) the plaintiff's claim arise from or closely relate to the defendant's minimum contacts with the foum state and;
2) the exercise of jurisdiction comply with the notions of fair play and substantial justice.
What is the amount in controversy a plaintiff must allege in good faith in a diversity case?
$75,000.01
Two characteristics of a fee simple absolute?
Alienable: Transfer by will
Heritability: Ability to pass property down to heirs
The three requirements necessary to make an irrevocable gift during the donor's lifetime:
Donative Intent, Delivery (physical, symbolic or constructive) and Acceptance.
The highest level of duty owed by a possessor of land, requiring inspection and warning against both known and reasonably discoverable dangers.
Duty owed to an Invitee
3-step analysis for causation?
What is:
1) Is there actual but-for cause (or one of the alternatives if but-for doesn't work?)
2) Is there a proximate cause using the court's primary test (for our purposes, that's the foreseeability test, unless you're told otherwise)
3) Are there any superseding cause?
Elements of a tresspass [to land] claim?
P owns or has exclusive possessory interest in the land.
D intetionally acts causing a phyiscal invasion, or faith to leave P's land.
A defendant's voluntary appearance in court automatically subjects the Defendant to personal jurisdiction unless:
He/she appears to challenge personal jurisdiction.
How does a corporation and LLC differ in the way they establish domicile in a diversity case?
INC: State where its Principle place of business is and where its incorporated.
LLC: Where all its members are domiciled.
What is escheat?
The transfer of property from a person who dies without heirs and intestate to their lord...or in present times, to their state.
A wallet found on a bank counter, intentionally placed there and forgotten, is classified this way, giving the landowner superior title against the finder:
Mislaid Property
The Good Samaritan Statute will shield:
The legal action filed by family members to recover for their own losses sustained after the death of the victim, such as loss of consortium or loss of support.
Wrongful Death Action.
What are the defenses for intentional torts?
1) Express consent, implied consent
2) Self Defense.
3) Defense of others
4) Defense of property
A type of jurisdiction based on the defendants contacts that allow the plaintiff to sue on any claim, even one unrelated to those contacts.
General Jurisdiction
Diversity Cases, Federal questions cases
O owns Blackacre. O is unmarried and has two children, A and B. B has two children, B1 and B2. B dies intestate, then O dies intestate.
What is:
A owns 1/2, B1 and B2 each own 1/4
A gift made in contemplation of impending death is revoked automatically if the donor does this.
Recovers from the illness/peril.
To prevail on a prima facie negligence claim:
The plaintiff must demonstrate that the defendant owed a duty of care and breached it, was the factual and proximate cause of the injury to the plaintiff's person, or property. To completely prevail in court, there should be no successful affirmative defenses.
n an NIED claim, this is the strongest argument a plaintiff can make if they were not physically injured, but were close enough to an immediate accident to have been placed at risk of physical impact.
Being in the Zone of Danger.
What must P prove in order for D to be liable for the trespass to chattel?
D intentionally interfered with P's rightof possession of the chattel by ether:
1) dispossessing P of the chattel; or
2) using or intermeddling with P's chattel (an thereby damaging the chattel or harming P
The three main factors assessed to determine if Specific Personal Jurisdiction is constitutional, beginning with the defendant's purposeful direction of activity toward the forum
Purposeful Availment, Claim Arises From/Relates To Contacts, and Reasonableness (Fair Play and Substantial Justice)
In contrast to diversity cases, there is no time limit on removal based on Federal Question Jurisdiction, except that removal must be made:
within 30 days of this initial pleading.*
*initial pleading (or service of the complaint)*
To Hartford School Board but if it ceases to use the land as a school, to the City Library”
What is a FEE SIMPLE SUBJECT TO EXECUTORY LIMITATION
This type of minor, physical trespass across a boundary line, often involving a fence or a small structure, is the most common situation where courts apply the mistaken boundary rule for adverse possession.
Encroachment
Proving breach through negligence per se:
1) D violated the statute prohibiting certain conduct.
2) The statute was intended to protect against harm when recovery is sought.
3) persons harmed were part of the class of persons for whom the statute was intended to protect.
Proximate Cause: What is the foreseeability test:
A question of whether the type of accident is within the scope of the risk of D's negligent conduct?
a) Was the type of accident within the scope of risk?
*The breach of duty does not necessarily prove proximate cause.*
What are the elements of a Prima Facie Claim of IIED?
What is:
1) D intentionally or recklessly;
2) through outrageous conduct;
3) causes P severe emotional distress
What are the requirements for Specific Personal Jurisdiction?
Long-arm statute: Forum state statute must authorize jurisdiction under specific circumstances
Due Process:
1) Minimum contacts: Purposeful availment of forum state's law so suit is foreseeable AND;
2) Fair play and substantial justice: Using the reasonableness factors-
-Burden on defendant to appear and defend in forum state
-Plaintiff's interest in obtaining relief in forum state
-Forum State's interest
-Interstate judicial system's interest in obtaining most efficient resolution of disputes
-Interest of several states in furthering fundumental substantive social policies.
This is required for a single plaintiff who sues a single defendant to meet the amount in controversy requirement by combining all their claims, even if the claims are factually unrelated.
Aggregation
What langauge creates a Fee simple determinable language:
What is:
1) To Hartford School Board
2) So long as the property is used for school purposes
3) During the continuance of said school
3) Until the Board no longer uses the property for a school.
A gift causa mortis is invalid if this subjective element, relating to the transferor's condition, is not satisfied at the time of delivery.
Apprehension of imminent death.
Res Ipsa Loquitor allows the jury to infer negligence because:
1)The accident is the kind that does not ordinarily occur in the absence of negligence;
2) The instrument or cause of injury was within the D's exclusive control and;
3) The plaintiff did not contribute to their own injury
**Remember in an issue of Res Ipsa Loquitor, a plaintiff cannot prove breach but is allowed to move foward with an inference of negligence on the defendant's part.
What is a proximate cause of that may not relieve you the D from liability?
Intervening cause:
1) an event that happens after the initial negligence and contributes to or worsens the injury.
2) The original D may still be liable if the intervening cause was a foreseeable consequence of their negligence.
What is Battery?
Harmful/offensive contact with another.
Harmful:contact that causes injury,
Offensive: to a reasonable sense of dignity (exception: known sensitivity)
Contact: anything connected to the person; can be direct or indirect e.g. blowing smoke/bubbles.
SPJ: Minimum contacts for a defendant and defendant-manufacturer exsists when:
The defendant purposefully avails itself of the state's protection and benefits so that the defendant should reasonably foresee being sued there.
A defendant-manufacturer has minimum contacts with the forum state if it places a product in the stream of commerce PLUS purposefully targets the forum state (e.g., by adversiting there).
(Purposeful availment by manufacturer: stream of commerce + purposeflly target forum state)
What is the Forum Defendant Rule?
This is the general rule that prevents a defendant from removing a case from state court to federal court based on diversity jurisdiction if any defendant is a citizen of the forum state.
What language creates a Fee simple subject to condition subsequent:
What is:
1) BUT if the property is not used for school purposes, the grantor has the right to reenter and retake the property”
2) PROVIDED HOWEVER, if the property is not used for school purposes, the grantor has the right to reenter and retake the property”
3) ON THE CONDITION THAT, if the property is not used for school purposes, the grantor has the right to reenter and retake the property”
The crucial point in time when the true owner's disability must exist in order for the statute of limitations to be tolled.
When Adverse Possession first begins.
Duty of Common Carriers and Innkeepers:
Utmost care due to the special relationship of trust and dependence between the parties. They must take affirmative steps to protect patrons from dangers once the danger becomes foreseeable. Such as carrying basic medical tools, duty to protect from third parties, etc.
The specific type of legal action filed by the deceased victim's estate to recover for the victim's losses before death, such as pain and suffering or medical expenses.
Survival Action
What is assualt?
Voluntary act causing reasonable apprehendion of imminent harmful or offensive contact.
Intent: act with intent to cause apprehension or the contact itself.
Harm: concern of contact must be objectively reasonable; awareness required;
Imminent: Future harm not enough; words and circumstances may suffice. ("I will jump the straddle")
When can a court exercise specific jurisdiction over a defendant that is not domiciled in the U.S.?
When the requirements for specific jurisdiction are satisfied.
The Mottley Rule holds that under the Well-Pleaded Complaint Rule:
The federal law issue must be part of the plaintiff's cause of action itself, not merely a federal defense or a preliminary matter.
Future interest of Fee Simple Absolute
None.
The fee simple absolute is the present interest. The Grantor retains nothing.
Giving the keys may be symbolic of the delivery of the furniture but could be constructive delivery of the contents of the dresser found in the drawers.
The Firefighter Rule is doctrine that limits the duty of care oweed by a property owner...the general rule states:
A professional rescuer who is injured while performing the duties inherent to their job (the "accepted risks") cannot recover in tort from the person whose negligence created the emergency that necessitated the response.
The Firefighter's Rule is not absolute and has several important limitations. Recovery is generally allowed if the injury stems from a danger that is separate and apart from the risk that caused the initial emergency.
What does Multiple Sufficient Causes refer to? What test do you use?
The element: factual causation.
Subtantial Factor Test:
Multiple sufficient causes are two or more independent factors, each of which could have caused an outcome on its own.
What is the doctrine of transferred intent?
Intent to commit an intentional tort transfers across people and across torts.
DOES NOT APPLY TO IIED.
Types: person to person, tort to tort, tort and person.
Merely sending the product into the stream of commerce with the awareness that it is marketed and sold in the forum state is insufficient.Rather, the defendant has to direct some activity to the forum state, must intend to serve the forum State:
Justice O'Conner Approach (stream of commerce approach)
The maximum number of years after a case is commenced in state court that a defendant can remove that case to federal court on the basis of diversity jurisdiction, regardless of how many non-diverse defendants are dropped.
1 year.
Ex. if a the party making the case non-diverse is dropped at 360 days- D has only 5 days to remove to federal court.
Future interest of Fee Simple Determinable:
What is: Possibility of reverter, automatically gets the future interest attached to the possessory estate.
The three most common legal conditions recognized by statute that typically qualify as a disability sufficient to toll the adverse possession period.
Minority, disbility, and imprisonment.
In order to invoke the Rescue Doctrine, a rescuer (plaintiff) typically must prove these four elements to hold the negligent party (defendant) liable for the rescuer's injuries:
1) Negligence by the Defendant: The defendant's negligent conduct created a peril (danger) to the victim (or sometimes, to the victim's property).
2) Imminent Peril: The victim was in actual or apparent imminent peril. The rescuer must have a reasonable belief that the victim is in danger.
3) Rescue Attempt: The plaintiff (rescuer) must have acted with the purpose of rescuing the person or property from the imminent peril.
4) Reasonable Care: The rescuer must have acted with reasonable care in effecting the rescue under the emergency circumstances (i.e., the rescue attempt itself was not rash or reckless).
Proximate Cause: What is the direct cause test?
A question of whether there is a "direct connection" between D's negligent act and harm to P without too many intervening causes.
Brisboy v. Fibreboard Paper Products Corp.: evidence was sufficient to
support jury’s finding that D’s negligent failure to warn P about dangers of
asbestos was a substantial factor in causing P’s death, even though P was a
heavy smoker; so D’s negligence was a proximate cause of P’s death
What is False Imprisonment?
Act with intent to confine/restrin another within fixed boundaries, resulting in confinement such that plaintiff is conscious of or harmed by the confinement.
Confined/restrained: freedom of movement limited in all directions; no reaosnable means of escape
By: physical barriers, force, threat of force, invalid invoation of authority, duress, coercion, refusal to set free (failure to provide safe means of escape).
As long as a defendant places the product into the stream of commerce with the knowledge that the final product is being marketed in the forum State, the defendant has sufficient minimum contacts.
Justice Brennan's Approach (foreseeability approach)
Two traditional, narrow categories of state-law cases over which federal courts will abstain from exercising diversity jurisdiction, even if the parties are completely diverse.
Domestic Relations (divorce, child custody) and Probate (wills, estates)
Future interest of Fee simple Subject to Condition:
Right of entry, when the condition is violated and the guarantor must enter the property to reclaim the possessory estate.
The specific legal action, often running concurrent with conversion, that a true owner uses to recover the physical possession of a specific piece of personal property from a wrongful possessor.
Replevin
A legal concept that holds that, absent certain exceptions, a defendant generally owes no duty to a plaintiff who suffers emotional distress alone, without any accompanying physical injury unless:
(a) Impact Rule to Zone of Danger
(b) from the Zone of Danger to the Dillon Rule of Foreseeability
(c) Is there a general duty not to cause emotional distress
A legal doctrine legal doctrine where a plaintiff can sue multiple manufacturers of a defective product to recover damages:
This can help meet factual cause.
Modified Alternative Liability: Market Share
A legal doctrine legal doctrine where a plaintiff can sue multiple manufacturers of a defective product to recover damages- this can help meet factual cause.
Key elements:
- The product must be fungible, meaning the products from different manufacturers were essentially identical.
- Each defendant must have sold the product in an unreasonably dangerous manner.
- The plaintiff must have been unable to identify the specific manufacturer of the product that caused the injury, through no fault of their own.
- Enough manufacturers must be joined in the lawsuit to account for a substantial share of the market.
What is shopkeeper's privilege?
(In some jurisdictions) the ability to detain a suspected shoplifter for reasonale time/manner.
Remember, reasonableness measured against an objective standard.
The focus of the minimum contact analysis in the stream of commerce cases should be: the volume of the activity; the value of the products, and; the hazardous nature of the components being sold.
Justice Steven's Approach (Volume approach)
The _____ refers to the narrow circumstance where a plaintiff's state-law claim can still be removed to federal court because it embeds a disputed and substantial federal issue.
The Smith Exception
Typical order of preference in intestacy statutes
1) Decendent's Spouse
2) Surviving Issues
3) Parents
4) Ancestors/Collateral
The legal effect a qualifying disability has on the adverse possession statute of limitations, causing it to stop running until the disability is removed.
Tolling
The attractive nuisance doctrine holds that:
A property owner or possessor is liable for injuries to trespassing children if the injury is caused by a hazardous object or condition on the land that is likely to attract children.
1) Foreseeable Trespass: The possessor knows or has reason to know that children are likely to trespass on the place where the condition exists.
2) Known/Should Be Known Danger: The possessor knows or has reason to know that the condition involves an unreasonable risk of death or serious bodily harm to children.
3) Child's Inability to Appreciate Risk: The children, because of their youth, do not discover the condition or realize the risk involved in intermeddling with it or coming within the area made dangerous by it.
4) Utility vs. Risk: The utility to the possessor of maintaining the condition and the burden of eliminating the danger are slight compared to the risk to the children. In other words, the possessor could have easily made the condition safe
5) Failure to Exercise Reasonable Care: The possessor fails to exercise reasonable care to eliminate the danger or otherwise protect the children.
It essentially lowers the typical duty owed to a trespasser (which is usually minimal) when the trespasser is a child drawn by an attractive, dangerous condition.
The doctrine applied when two or more defendants are negligent, but the plaintiff cannot prove which one actually caused the injury, leading the burden of proof on causation to shift to the defendants.
Alternative Liabiliy (Summer v. Tice)
Ex. Imagine two hunters, Fred and Kazoo, negligently fire their rifles at the same time. Barney is injured but cannot determine if Fred's or Kazoo's shot caused the injury. Under the alternative liability doctrine, Barney can sue both Fred and Kazoo. If Barney proves they were both negligent, the burden shifts to Fred and Kazoo to prove that their specific actions did not injure Barney. If neither can prove this, they may both be held jointly and severally liable for Barney's injuries.
A statute that allows a court to exercise personal jurisdiction over out-of-state defendant's in specified circumstances:
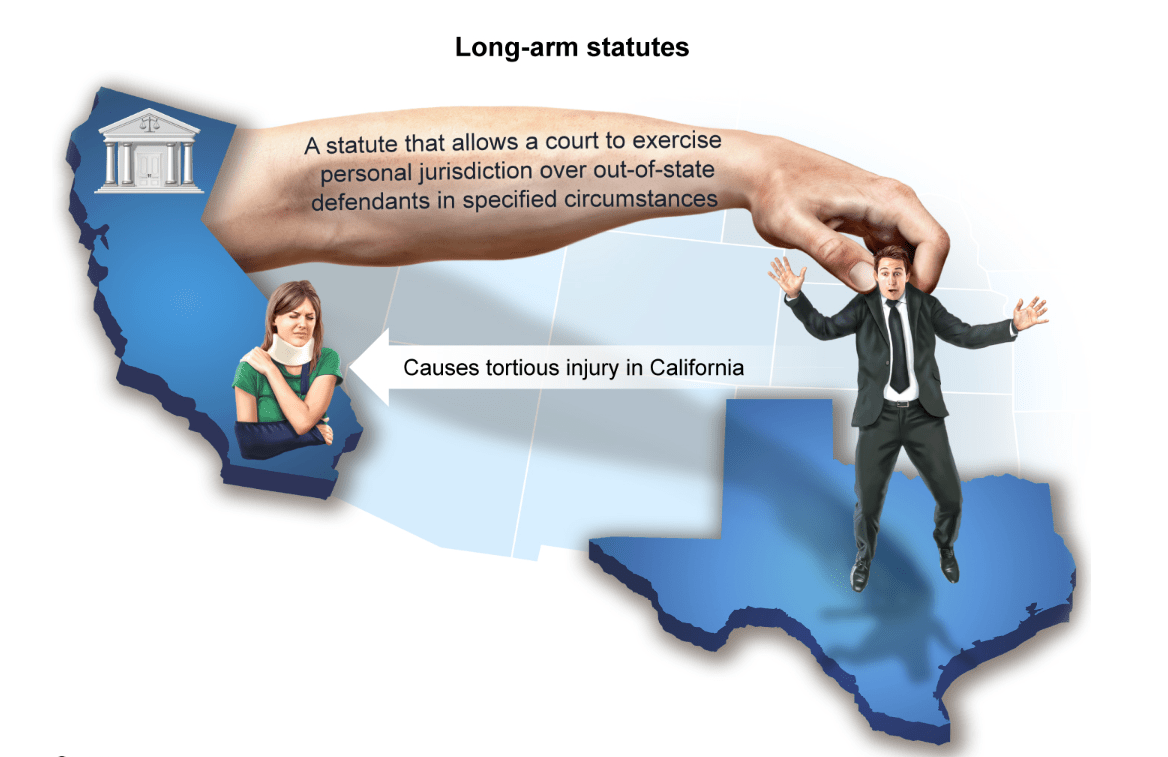
In many states, the long-arm statute authorizes jurisdiction to the extent contitutionally permissible BUT when a long-arm statute does not permit jurisdiction to this extent, the court must interpret the scope of the statute.
This is the specific U.S. Code section that grants federal district courts original jurisdiction over civil actions "arising under the Constitution, laws, or treaties of the United States."
28 U.S.C. Section 1331
If O owns Blackacre. O is married to W and they have two children, A and B. O dies intestate. What percentage does W, A, and B get of the land?
W, A, and B each own 1/3
If the adverse possessor enters the property after the ownership has been divided in time between the life tenant and the remainder, he can divest:
Ex. O leaves blackacre to A for life, then to B when A dies.
Only the life estate, and the statute does not begin to run against the remainderman (B).
The Learned Hand Formula is a way to prove:
Liability for negligence due to failure to take safety precautions exists if the burden of taking such precautions is less than the
probability of injury multiplied by the gravity of any resulting loss.
Burden of taking precaution against an accident < Probability that an accident will occur x Loss (seriousness/magnitude of damages or injury)
Under Pure Comparative Fault, if a plaintiff is found 70% at fault and suffers $100,000 in damages, this is the amount of money they can recover.
30k.
The plaintiff can recover damages regardless of their percentage of fault.
The plaintiff's recovery is simply reduced by their percentage of fault.
Factors: Severity, Duration, Intent
Trespass to chattel: less serious, shorter duration, intent is just messing- less harm.
Conversion: more serous, longer duration, intent is claiming right- greater harm, more expensive, less convenient.
When analyzing minimum conacts, "purposeful availment" can occur even if the defendant never physically enters the forum state because:
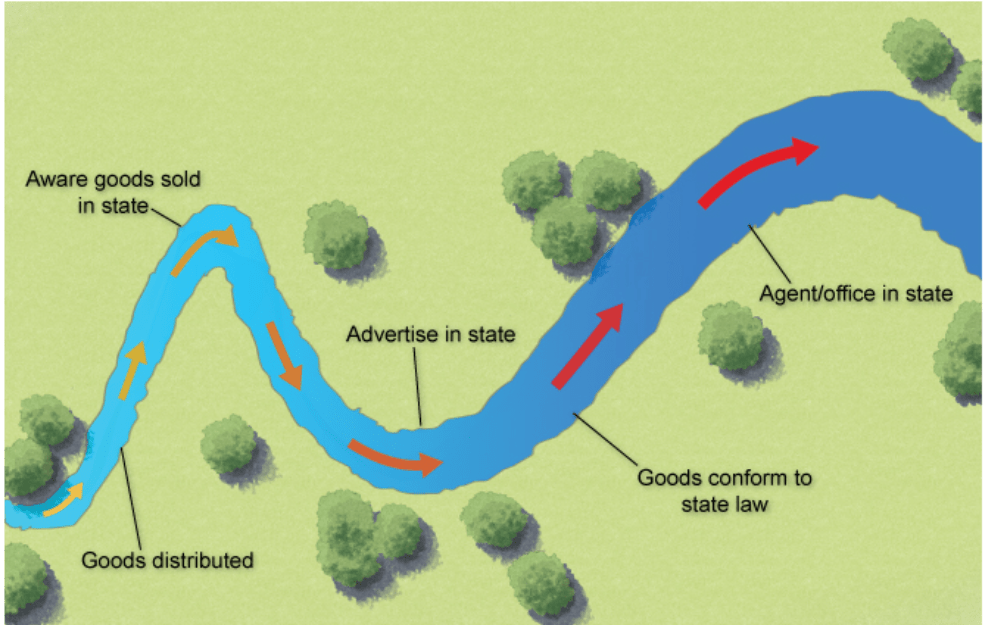 The defendant can commit a wrongful act with the intent that the effects will be felt in the forum state (e.g. defamation.).
The defendant can commit a wrongful act with the intent that the effects will be felt in the forum state (e.g. defamation.).
However, minimum contacts are ABSENT when the defendant does not target the state or its residents.
The state of the previous domicile is presumed to continue until the party proves a simultaneous physical presence in the new state and....
The intent to remain indefinitely.
What is a vested remainder?
The future interest held by a third-party grantee that is CERTAIN to become possessory when a preceding life estate naturally ends, as in the conveyance "to A for life, then to B."
NOT subject to RAP.
If the adverse possessor enters the property before O, the original owner, makes the transfer of property to A and B the SOL:
Generally, there is no duty to act. However, when there is a_____________, one must act like a reasonably prudent person:
*Hint: 5 general categories.
When there is a:
1) Special relationship: (Carriers, Inkeepers, Employer, Parent, Healthcare worker);
2) Landowners: (Invitee, Licensee, Trespasser, Child trespasser);
3) a statute, or contract;
4) If you assume the risk of rescue;
5) Creation of the Peril;
This liability rule, often abolished or modified in states that adopt comparative fault, held that any one of the negligent defendants could be made to pay the plaintiff the entire amount of the damages.
Joint and Several Liability.
When does a defendant commit conversion?
When D intentionally commis an act:
1) depriving P of the possession of his chattel
2) interfering with P's chattel in a manner so serious as to deprive P of the use of the chattel.
"Intentional exercise of dominion over a chattel which so seriously interferes with the right of another to control it that the actor may justly be required to pay the other the full value of the chattel.” Restatement (Second) of Torts
DAMAGES: full value of chattel at time of conversion.
A defendant's ownership of property in the forum state establishes minimum contacts in an action related to that property. What types of actions are they?
In order for a state-law claim to be heard in federal court:
1) P must Necessarily Raise a Federal Issue;
2) A federal question must be Actually Disputed;
3) The federal issue must be Substantial to the federal system as a whole..and;
4) Granting federal jurisdiction must not disrupt the congressionally approved balance of federal and state judicial responsibilities. The federal court must find that this category of cases is rare and won't suddenly flood the federal docket with state tort or contract claims.
What is a Contingent Remainder (Or Executory Interest) and what is the rule it is subject to?
A complex future interest that vests in a 3rd party and is subject to the Rule Against Perpetuities (RAP) because its vesting depends on a condition being met by someone who is NOT identifiable at the time of the conveyence.
The legal relationship between successive adverse possessors that must be established to permit tacking of their periods of possession.
Privity of estate: is a voluntary transfer through a deed or will between the successive adverse possessions.