Part of the brain that controls balance, posture, and voluntary muscle movements.
What is the Cerebellum?
(Multi-part question) Identify each lobe: 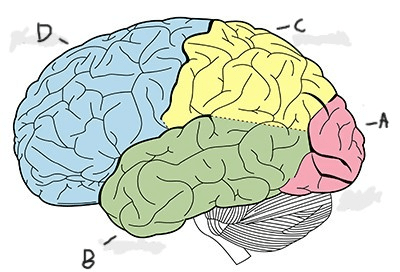
A: Occipital Lobe
B: Temporal Lobe
C: Parietal Lobe
D: Frontal Lobe
A sleep disorder that involves persistent difficulty falling or staying asleep:
What is insomnia?
The minimum amount by which a stimulus needs to change in order for a person to detect a difference:
What is just noticeable difference?
The process of sensing information, processing the information and storing it to be retrieved later.
What is Encoding?
Part of the brain that is severed when a patient has a split brain.
(The bundle of nerve fibers connecting the brain's left and right hemispheres.)
What is the Corpus Callosum?
Caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and methamphetamine:
What are stimulants?
A disorder that impacts the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles/stay awake:
What is narcolepsy?
LSD and psilocybin (mushrooms) are examples of this type of drug.
What are hallucinogenics?
Conscious recollection of information vs. unconscious recollection of information. (2 different answers)
What is Explicit and Implicit memory?
Part of the brain that processes emotions.
What is the Amygdala?
(Multi-part question) Identify the parts of a neuron:
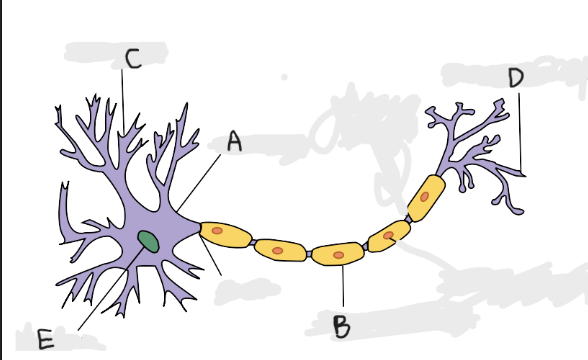
A: Cell Body
B: Myelin Sheath
C: Dendrites
D: Axon Terminal
E: Nucleus
A sleep disorder that causes a person to repeatedly stop breathing while sleeping:
The process of transforming new information into a format that can be stored and later retrieved by the brain:
What is Encoding?
The ability to recall specific past events, including the details of when and where they happened as if viewing it.
What is Episodic Memory?
A research method where neither the participants nor the experimenters know which group (treatment or control) each participant is assigned to, ensuring that neither party can influence the results based on this knowledge, thus minimizing bias in the study.
What is a Double-Blind Experiment/Procedure?
Parts of the body responsible for secreting hormones:
What are glands?
State of sleep when dreams occur:
What is REM sleep?
(Multi-part question) Identify the parts of the eye: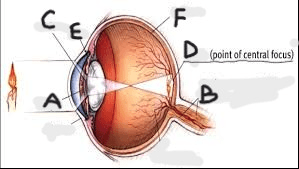
A: Pupil
B: Optic Nerve
C: Iris
D: Fovea
E: Lens
F: Retina
When people are more likely to remember the first and last items in a list.
What is the Serial Position Effect?
Variables that have an unwanted influence on the outcome of an experiment. Also known as extraneous variables.
What is a Confounding Variable?
This neurotransmitter is responsible for calming down neural activity/regulating the sleep-wake cycle and is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter.
What is GABA?
24 hour internal clock:
What is Circadian Rhythm?
(Multi-part question) Identify the names of the middle ear bones:
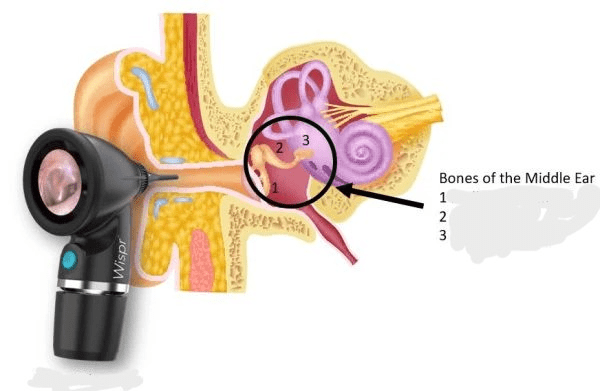
1: Malleus (Hammer)
2: Incus (Anvil)
3: Stapes (Stirrup)
A mental representation of the best example ofsomething.
What is a Prototype?