The energy an object has due to motion.
What is Kinetic Energy?
The sum of Kinetic and Potential Energy.
What is Mechanical Energy?
Energy can be converted from one form into
another, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
The transfer of thermal energy from a warmer object to a cooler object.
What is heat?
A material that transfers heat well.
What is a conductor?
The formula for calculating an object's Kinetic Energy.
What is KE = 1/2mv2?
The Potential Energy that is stored in the nucleus of an atom.
What is Nuclear Energy?
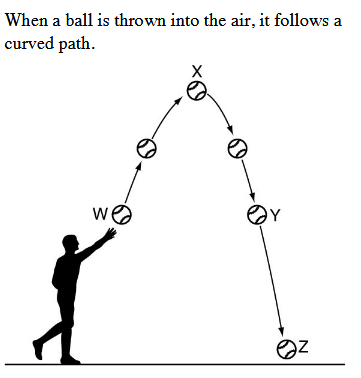
The position in which the ball has the greatest Potential Energy.
What is Position X?
The measure of the average Kinetic Energy of the particles in an object.
What is temperature?
A material that does not transfer heat well.
What is an insulator?
Energy that results from the position or shape of an object.
What is Potential Energy?
A nuclear reaction in which the nuclei of atoms join together.
What is Nuclear Fusion?
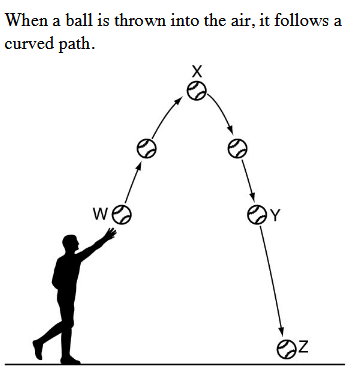
The position at which the ball has the greatest Kinetic Energy.
What is Position Z?
The type of heat transfer that occurs from one particle of a matter to another within an object or between two objects.
What is conduction?
The amount of energy that is required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of material by 1 Kelvin.
What is specific heat?
The two types of potential energy.
What are Elastic and Gravitational Potential Energy?
The total energy (Kinetic and Potential) of all the particles in an object.
What is Thermal Energy?
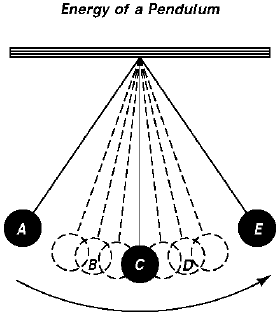
The position at which the Potential Energy is greatest.
What is Position A and E?
The process in which heated air rises and cooler air sinks, causing a circular motion.
What is a convection current?
The expanding of matter as it is heated.
What is thermal expansion?
The formula to calculate Gravitational Potential Energy.
What is PE = mgh?
Name two types of energy associated with a lamp (ignore Thermal Energy).
What are Electrical and Electromagnetic Energy?

The position at which the sum of the Kinetic and Potential Energy is the greatest (ignore friction).
What is neither?
The only type of heat transfer that does not require matter.
What is radiation?
Gold has a specific heat of 126 J/(kgK). A sculptor increased the temperature of 0.5 kg of gold by 10o C. The sculptor added this much energy to the gold.
What is 630 Joules of energy?