What is "nature" in nature vs. nurture?
DNA/genetics
1. Which psychological perspective would think that a child acts out because neurochemicals in the brain are not at the correct levels?
2. Which psychological perspective would think that a child acts out because a person does not feel fulfilled with their relationships?
1. Biological
2. Humanism
1. Describe a naturalistic observation.
1. Observe subjects in their natural habitat.
State 3 ethical standards that should be present in every research study.
1. Informed consent
2. Confidentiality
3. Debriefing
Which trait most likely has a higher heredity coefficient: Novelty-seeking or Eye color?
Eye color
What is "nurture" in nature vs. nurture?
Environment/How you were raised
1. Which psychological perspective would think that a child acts out because he has learned that if he throws a fit, his mother will let him have a cookie?
2. Which psychological perspective would think that a teenager acts out in class because, deep down, the teacher reminds her of her mother?
1. Behavioral
2. Pshychoanalytical
1. Describe a case study.
1. A single subject is studied in depth over time.
A researcher wants to determine if eating chocolate before a race makes people run faster. The researcher designs an experiment in which the control group does not eat chocolate before a race and the experimental group does. All participants then race 1 mile.
1. What is the operational definition of the independent variable?
2. What is the operational definition of the dependent variable?
1. The amount of chocolate eaten. (i.e. Each participant in the control group eats 0 grams of chocolate and each participant in the control group eats 8 grams of chocolate).
2. The amount of time to run 1 mile.
Which type of trait is influenced by genes and the environment: Discrete or Multifactorial?
Multifactorial
Which perspective deals with stimulus and response?
Behavioral psychology
1. Describe a correlational study.
1. Determines if there is a correlation (relationship) between two things.
A researcher is testing the effects of a new drug on patients who have drug addictions. What experimental method will ensure that the researcher does not insert any observer-expectancy bias into the study?
Double-blind experiment
According to ultimate reasoning, why would a mother save her nephew rather than a stranger if they were both in a life-threatening situation?
To pass on her own genes
Which perspective deals with thinking, memory, and perception?
Cognitive psychology
1. Describe an experiment.
1. The researcher manipulates everything. Everything is that same between the control and experimental groups except for the independent variable.
A researcher wants to determine if a brand of sunscreen really works. She develops an experiment in which the control group does not wear the sunscreen on a sunny day for 2 hours and the experimental group does wear the sunscreen on a sunny day for 2 hours. She then determines how much UV radiation from the sun reached their skin.
1. What is the operational definition of the dependent variable?
1. The level/measurement of UV radiation that reached their skin.
A researcher wants to determine if a brand of sunscreen really works. She develops an experiment in which the control group does not wear the sunscreen on a sunny day for 2 hours and the experimental group does wear the sunscreen on a sunny day for 2 hours. She then determines how much UV radiation from the sun reached their skin.
1. What can the researcher do so that the participants do not know whether they are in the experimental group or the control group?
1. Provide the control group with a placebo sunscreen.
A twin study on novelty-seeking found the following results.
- For monozygotic (identical) twins, if one twin is a novelty-seeker, there is an 70% chance the other twin is a novelty-seeker.
- For dizygotic (fraternal) twins, if one twin is a novelty-seeker there is a 42% chance the other twin is a novelty-seeker.
Is this trait determined by the environment, genetics, or both? Explain why.
Both
What do all of the psychological perspectives have in common?
They are all used to analyze behavior
What is the only type of research method that can determine a cause-and-effect relationship?
Experiment
In an experiment, why is random sampling necessary?
To ensure that the sample is representative of the larger population.
A researcher wants to determine if eating lettuce, rather than pellets, causes rabbits to gain weight. She sets up an experiment in which the control group eats pellets and the experimental group eats lettuce. After 2 weeks, the control group weighs 12 pounds (on average) and the experimental group weighs 10 pounds (on average).
The researcher wants to determine if the difference between the two groups is statistically significant.
What is "statistical significance"?
The difference between the control group and the experimental group is due to the independent variable, rather than random chance.
(Ex: The rabbits in the experimental group weighed less because they ate lettuce. Eating lettuce caused them to weigh less).
After the twin study, scientists performed an association study to determine which genes are associated with novelty-seeking. They looked at genes for high novelty-seekers and low novelty-seekers and got the following data.
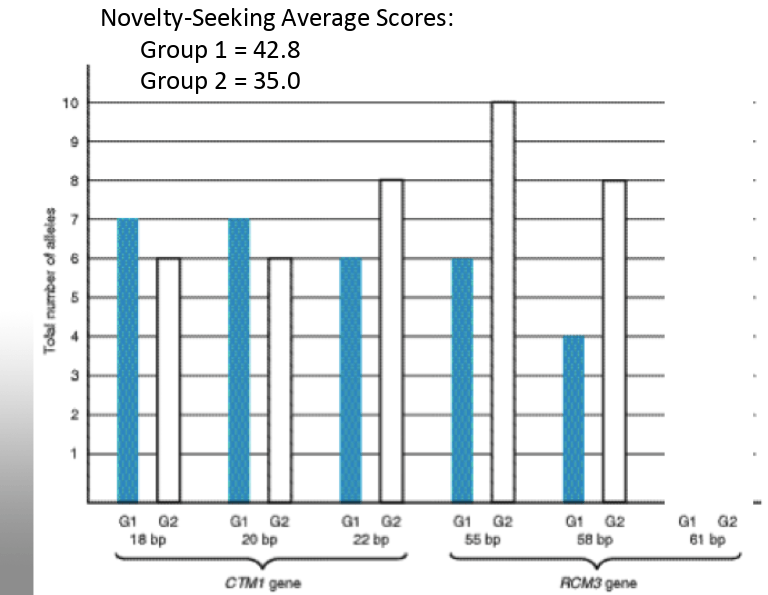
Which genes are associated with novelty seeking? CTM1, RCM3, or both?
Maybe both. RCM3 moreso.
Which perspective tells us that we act differently because we are products of different environments?
Sociocultural
What are key features of an experiment.
Answers vary.
1. The researcher manipulates the independent variable.
2. The control group and experimental group are exactly the same except for the independent variable.
3. Random sample
4. Random assignment
1. In an experiment, what is assignment?
2. Why is random assignment necessary?
1. Assigning subjects to the control group or experimental group.
2. To account for pre-existing differences between the participants in the experimental and control groups.
A researcher wants to determine if eating lettuce, rather than pellets, causes rabbits to gain weight. She sets up an experiment in which the control group eats pellets and the experimental group eats lettuce. After 2 weeks, the control group weighs 12 pounds (on average) and the experimental group weighs 10 pounds (on average).
The researcher wants to determine if the difference between the two groups is statistically significant. What statistical test would she perform to determine statistical significance?
P-test
The following correlations exist between monozygotic and dizygotic twins for a trait.
Monozygotic twins: 1
Dizygotic twins: 0.6
Is the trait influenced by genetics only, the environment only, or both?
Genetics only