What molecule contains Fe within a red blood cell contains.
Heme.
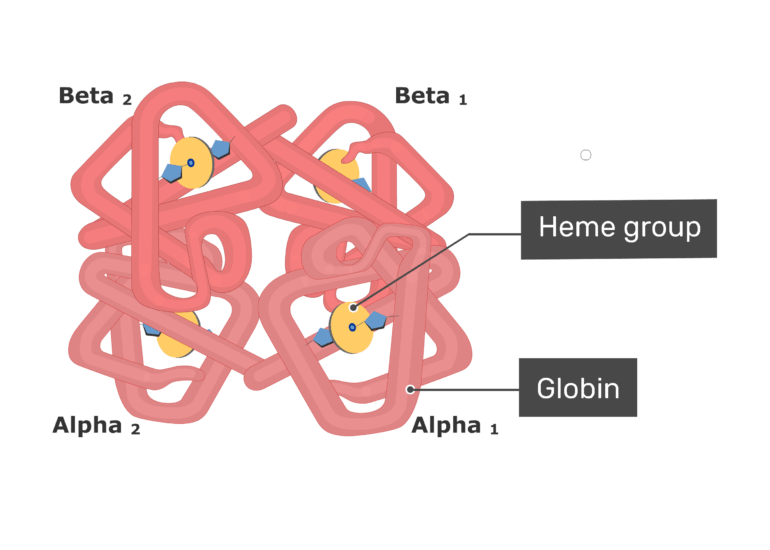
Haemoglobin: "heme" + "globin"
What does hemolytic anaemia mean?
Haemolytic anaemia is rapid breakdown of red blood cell.
Can you die from aplastic anaemia? Is there a cure for aplastic anaemia.
Why does iron deficiency lead to anaemia?
It is the iron that binds to the oxygen molecule. Iron deficiency leads to insufficient oxygen delivery to vital organs.

Gives one example of hemolytic anaemia.
(1) Autoimmune hemolytic anaemia-> self-antiobdies start attacking the red blood cells
(2) sickle cell anaemia -> sickle cell-shaped red cells prone to hemolysis
(3)Thalassemia
What is aplastic anemia:
(A) RBCs in an abnormal shape
(B) rapid depletion of RBCs
(C) failure of RBCs production
(C)
What's the first-line therapy in treating iron deficiency?
(A) blood transfusion
(B) iron therapy
(C) bone marrow transplant
Oral or intravenous iron replacement therapy.
First-line therapeutic management of autoimmune hemolytic anaemia.
Corticosteroid
Can aplastic anaemia develop over one's life?
Yes. chemotherapy
Why do we check for signs of anaemia in the renal examination?
Anaemia is associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It presents as at the early stage of CKD (patients with 20-50% of normal kidney function).
(1) Kidney produces erythropoietin which stimulates bone marrow for red blood cell production.
(2) blood loss from haemodialysis
(3)inadequate nutrient intake (ie. iron, folic acid, B12 which is necessary for haemoglobin production)
Multiple blood transfusion can lead to haemachromatosis, true or false?
True
Immunosupressant is contraindicated to aplastic anaemia.
False.
A long-term blood transfusion will cause the development of antibodies against the blood product
What are the common causes of iron-deficiency.
common cause of iron deficiency:
(1) malabsorption of iron (e.g. coeliac disease),
(2) decreased dietary intake of iron and
(3) increased need of consumption of iron (eg. Gastrointestinal haemorrhage)
someting about celiac disease:
- Celiac disease can cause damage to the small intestinal lining where iron, folate, and vitamin B12 are absorbed.
- The most common sign of celiac disease in adults is iron-deficiency anemia that is unresponsive to iron therapy.
Which is the most approrpriate treatment for haemolytic anaemia:
(A) iron therapy
(B) blood transfusion
(C) cephalosporin
(A) In hemolytic anemia, the iron released from red blood cells is often reused, and the iron stores are not reduced
(B) mechanism of action of transfusion involves in quick replenishment of healthy red blood cells to replace the hemolytic red blood cells in the bloodstream.
(C) antibiotics (ie, cephalosporin, penicillin) can cause autoimmune hemolytic anemia. The antibodies binds to membrane of RBCs and get broken down too early via the formation of immunogen or clearance by macrophage.
What is the mechanism of action of haematopoietic stem cell in treating aplastic anemia?
(A) replace/repair damaged or diseased Haematopoietic system.
(B) potential use of innate immune system of non-identical donor as a immunotherapy.
(C) allow use of high does (otherwise lethal) chemotherapy or radiation therapy against disease.
(D) genetic modification of stem cell to "correct" disease haemopoietic stem cell.
(A)
but we can actually use D to treate thalassemic and sickle cell anemia (single gene disease)
Fanconi anemia is a type of aplastic anemia. Mutations in at least 15 genes can cause Fanconi anemia. proteins encoded by these genes invovles in a cellular process call Fanconi Anemia pathway which involves DNA replication and DNA repair.