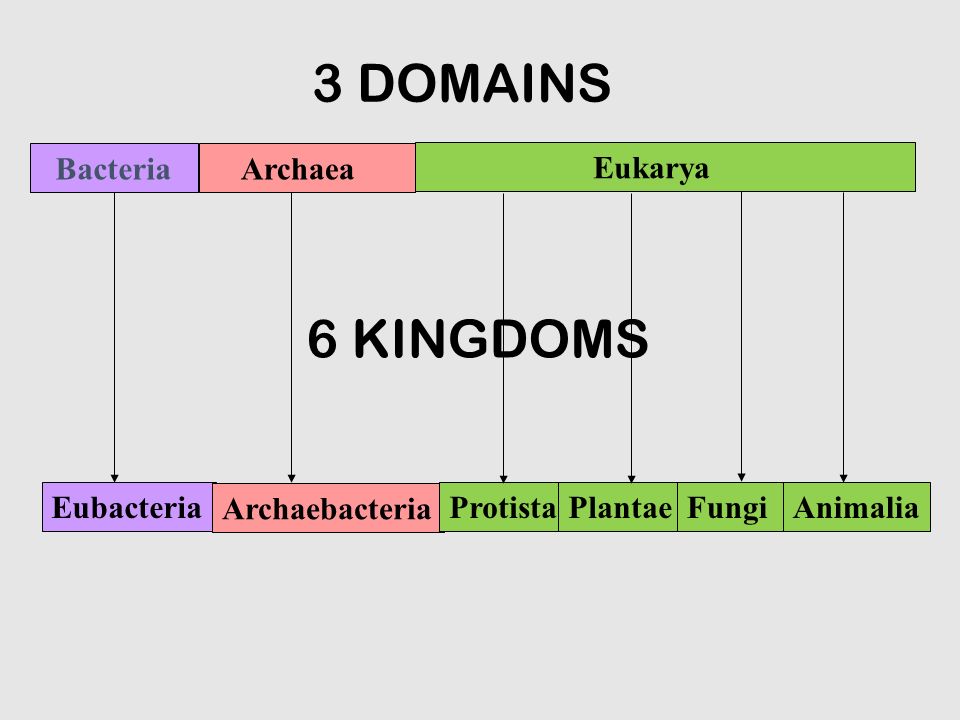
Which of them are in humans/plants, and which in animals?
animals: eukaryote
humans: prokaryote
/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478-v41-5b69b4c546e0fb0025628d06.png)
how do cells reproduce?
they replicate
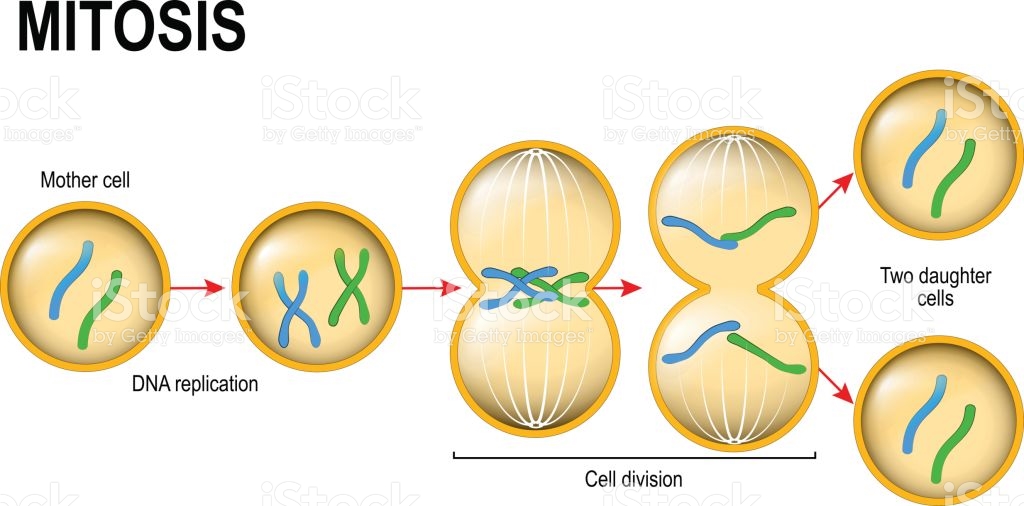
what is mitosis?
the process of cell replication

Why do some ribosomes need to be free-floating?
So they can communicate with all other parts of the cell
FREE
FREE
To which domains do both correlate?
prokaryote: domain bacteria
eukaryote: domain eukarya
Which structures are found in all types of living cells?
ribosomes, and cell membranes
what is cell-death called?
aptosis
Aside from emergency room, what does ER stand for, and what is its function?
endoplasmic reticulum; helps transport things (specifically ribosomes)
What happens if a lysosome explodes within the membrane?
It takes whole cell down with it, as well as many others
Which category is the more complex one and which is more experienced?
complex: eukaryotes
experienced: prokaryotes

What are the principles of the Cell Theory?
Cells are the smallest unit of living things, living things are made of one or more cells, and cells come from pre-existing cells.
/TC_373300-cell-theory-5ac78460ff1b78003704db92.png)
what is the function of a lysosome?
It eats up all the trash and self-sacrifices outside the membrane
What is special, and super essential about the cell membrane?
It is semi-permeable meaning it allows for things to come in and out
What are the two different types of vesicles, and what is their function?
cis - receives vesicles
trans - ships vesicles
which one lacks a nucleus and organelles?
prokaryotes
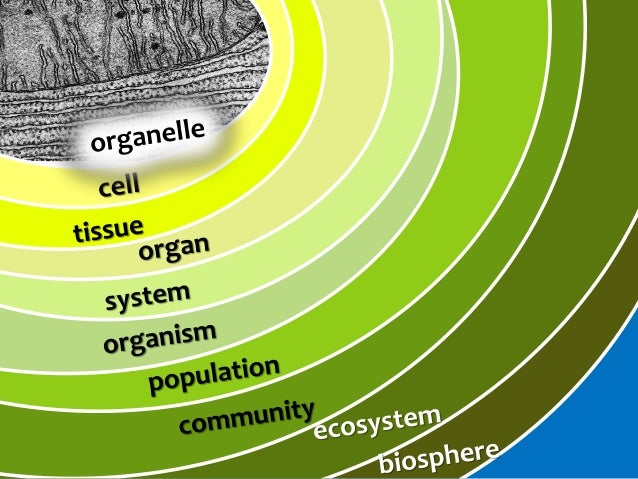
What is the hierarchy of life?
cells --> tissues --> organs --> organ systems --> organism
what is the hydrolytic enzyme's job within the lysosome?
it sorts out the trash and reuses what can be reused; the recycler
What happens if cells spot other cells acting weird?
they are programmed to immediately kill it
**Critical Thinking: What would occur if the cell membrane was NOT semi-permeable?
The cell would get "sick" and most probably die always leading to its death because it cannot gain the healthy good stuff and remove the bad stuff
Flashback: What is hydrolysis?
it's when water is incorporated in a bond, therefore causing it to break

**Critical Thinking: Cells must be small to maintain a large surface area to volume ratio. What happens when the cell expands?
it decreases the efficiency of the cell and can greatly affect humans

**Bonus: how many hemoglobin proteins are there in one red blood cell?
280 million
**Critical Thinking: Why do the shape of chromosomes matter?
it matters for the sake of organization and enables the cell to fit stuff in the nucleus
Riddle: What serves as a wrapping paper for proteins before they enter the Golgi apparatus, and leaves as soon as the protein gets there?
vesicles