The invention that lead to the discovery of cells.
What is the microscope?
The type of cell in the picture below:
Image in the public domain via LadyofHats on Wikimedia Commons
What is a plant cell?
Name of this organelle:
Image in the public domain via LadyofHats on Wikimedia Commons.
What is the cell membrane?
The kind of particles that move across the membrane during osmosis.
What is water molecules?
What energy process is shown in the equation below:
oxygen + glucose --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
What is cellular respiration?
Definition of biogenesis.
What is the fact that all living things come from other living things?
True or False: Animal, Plant, and Bacteria cells all have cell walls.
Job of the mitochondria.
What is to make energy for the cell?
Explain why a cell membrane has to be semipermeable.
What is: semipermeable means the cell membrane lets some thing in and keeps some things out. The job of the cell membrane is to control what goes in and out of the cell, acting like a barrier.
The location where photosynthesis and cellular respiration take place.
- Photosynthesis: chloroplast
- Cellular Respiration: mitochondria
Definition of abiogenesis.
What is the idea that living things grew spontaneously from nonliving things?
Job of the nucleus.
What is to control the cell?
Job of the vacuole.
What is: to store nutrients and keep water levels balanced?
What type of transport is shown in the image below:
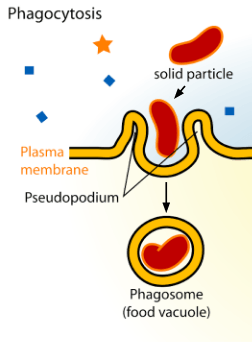
Image in the public domain via LadyofHats on Wikimedia Commons (image was cropped to remove title and show only one process)
What is endocytosis?
2 differences between anaerobic and aerobic respiration.
What is:
- Anaerobic Respiration is less efficient and only creates 2 ATP. Aerobic Respiration creates 36 ATP.
- Anaerobic Respiration does not require oxygen.
The 3 parts of the cell theory.
What is:
- All living things are made of cells.
- Cells are the basic unit of life.
- All cells come from preexisting cells.
Job of ribosomes.
What is: to make protein?
What is: to transport fluids and chemicals around the cell?
T or F: Water leaving a lettuce leaf that has been left on the counter is an example of hypotonicity.
What is: false? This is an example of hypertonicity because water leaves the cell and the cells shrivel (wilt the lettuce leaves).
Explain how humans benefit from photosynthesis.
What is:
- Humans need oxygen which is the product of photosynthesis.
- Humans need to eat plants which need photosynthesis to survive.
Explain why the cell theory is a paradigm shift.
What is: because we did not know that cells existed and made up all life. We used to think that living things came from nonliving things but our understanding shifted over time. We now know that all things are made of cells and all living things come from other living things.
Name 4 organelles on this diagram (you must point to or describe the ones you name):
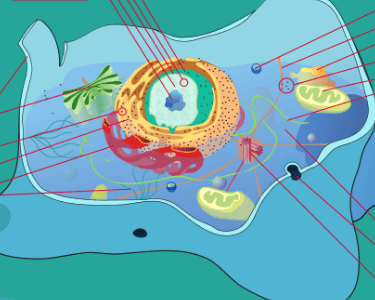
Image in the public domain via LadyofHats on Wikimedia Commons. Image was cropped to remove labels.
What is:
- nucleus
- nucleolus
- mitochondria
- rough endoplasmic reticulum
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- ribosome
- vacuole
- golgi apparatus
- cytoplasm
Job of the flagellum.
What is: to propel the cell forward?
What is:
- both are a type of passive transport (no energy)
- diffusion is when small particles pass over the cell membrane
- facilitated diffusion is when protein channels or carrier proteins help larger particles pass through the membrane
The 3 parts of the cellular respiration cycle.
What is:
- Glycolysis
- Krebs Cycle
- Electron Transport Chain