I say '--otomy'
A 7 yo patient presents with pain reported while eating, especially sugary foods. Radiograph shows deep caries on #T(MO). What is the likely pulpal diagnosis?
What is reversible pulpitis?
Thermal, chemical, mechanical and intermittent pain suggests reversible pulpitis
Name 3 differences in primary and permanent pulp anatomy
What are (features noted in primary pulp anatomy):
Mesial pulp horns closer to the surface
Flat ribbon shaped canals in the anterior teeth
Increased number of accessory canals
Name three indications for doing a pulpotomy on primary teeth
Mechanical or carious exposure
Absence of spontaneous pain
Inflammation limited to coronal pulp
Absence of swelling or alveolar abscess formation
Restorable tooth
An 11yo male, healthy, behavior F4- Presents with spontaneous pain at night in his upper right quadrant. What type of treatment would you provide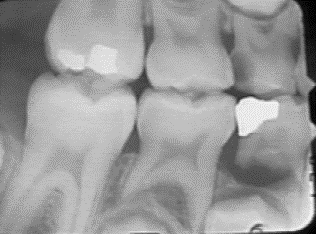 ?
?
What is Extraction? - to remove source of pain. Pulpectomy and SSC are not a viable option since tooth #B will be exfoliating soon
A 5 yo patient presents for an emergency appointment with complaint of ‘constant tooth pain’ on the upper right side. What other information would you like and possible diagnosis.
What is irreversible pulpitis?
Nature, frequency, intensity of the pain
Spontaneous, nocturnal, and constant pain suggests irreversible pulpitis
What does this picture indicate? Treatment options?
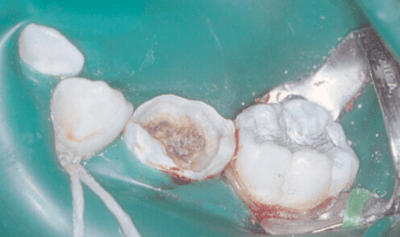
What is Affected carious dentin; Indirect pulp cap
What are the objectives of performing a pulpectomy on a primary tooth?
Maintain tooth free of infection
Biomechanical cleansing and canal obturation
Promote physiologic resorption
Maintain space eg. (E’s until 6’s erupt)
Esthetics
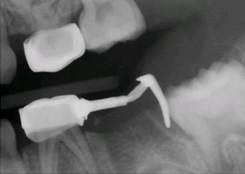
Describe what you see for treatment on tooth L. What are the possible sequelae?
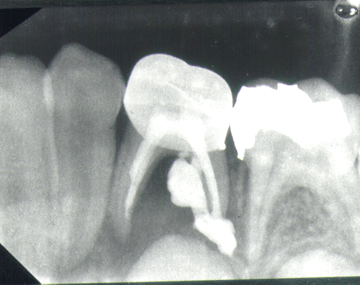
WHat is Furcation involvement; iatrogenic perforation. Medicament through furcation and apical overfill.
Ectopic eruption
Delayed eruption
Why are these diagnostic tests not reliable for testing primary teeth:Electric pulp test; Thermal test; Mobility
What is questionable reliability of child’s response?
Mobility may be present normally due to physiologic resorption; many pulpally involved teeth have no mobility
The most important action of Formocresol is bactericidal. True/False?
What is True
The best treatment option for asymptomatic tooth #T with a large carious lesion approximating the pulp, in a child with a h/o a heart transplant
What is Extraction?
This patient is symptomatic when eating. How would you treatment plan this quadrant?
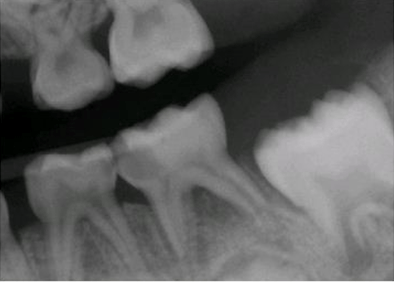
Extract K (possibly a candidate for pulpectomy). SSC on L. Place distal shoe space maintainer until 19 erupts
What are 4 clinical signs or symptoms that would suggest a tooth has irreversible pulpitis/ is non-vital?
Hyperemic pulp
History of unprovoked pain
Presence of fistula or swelling
Necrotic pulp
What are the indications for a Direct Pulp capping procedure in a young permanent tooth?
A small mechanical, traumatic exposure
Absence of significant hemorrhage
No evidence of suppuration
You are performing a pulpotomy on a primary second molar. After unroofing the pulp chamber, you see that the pulp is not actively bleeding. Treatment options include-
What is. Pulpectomy/extraction?
The tooth is necrotic
Upon initial exam, you observe a 6 yr old child with several clinically visible posterior carious lesions Behavior- F2. The child is asymptomatic, caries are firm to explorer and there is no radiographic pathology. Treatment options?
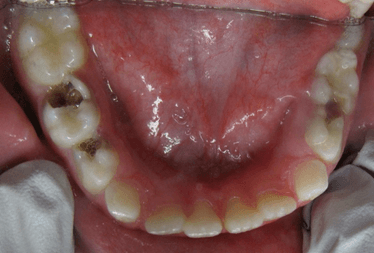
ITR; Monitor; SDF
Restorative, N2O
Sedation
GA
Radiographically, pathologic changes in primary anterior teeth are often seen at the ___, whereas pathologic changes in primary posterior teeth are seen at the ___
Root apices and bifurcation area
What are the steps in a pulpotomy procedure in a primary molar?
Local anesthesia; RD isolation
Caries excavation
Unroof pulp chamber
Pulp extirpation- spoon excavator/ low speed large round bur
Hemostasis with a moist cotton pellet
Treat radicular pulp with medicament
ZOE fill in pulp chamber and SSC restoration
Which medicament has the highest success rates in pulpotomies?
What medicament is most commonly used in primary molar pulpotomy?
What s Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Formocresol
Carcinogen, but toxicity from usage in minimal doses in pediatric dentistry has not been proven
Tooth #S has a history of intermittent pain, while eating. What would be your treatment options?
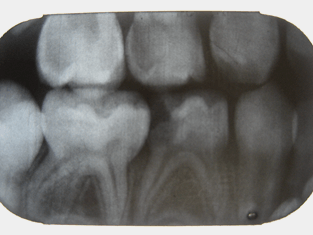
Evaluate the restorability clinically. If not restorable, extract; Space maintainer.