Long-term self-renewal, unspecialized cell type, generates multiple differentiated cell types
What are the unique properties of stem cells?
Two populations of adult stem cells?
What are the shoot and root apical meristems?
The organ outlined in red.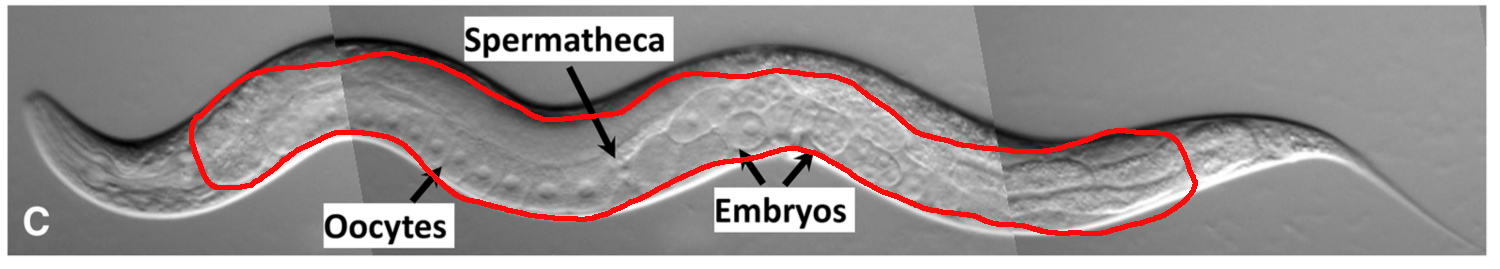
What is the gonad?
Neoblasts
What are stem cells in Planaria?
Ovary, testis, intestine
What are tissues supported by adult stem cells?
This technique allows visual detection of cells in S-phase.
What is BrdU/EdU labeling?
A group in an experiment that receives a treatment known to produce results.
What is a positive control?
The embryonic stage from which embryonic stem cells arise.
What is the blastocyst?
Two populations of adult stem cells?
In the gonad, self-renewal is to differentiation as ____ is to ___.
What is mitosis and meiosis?
Large nucleus and little cytoplasm
What are two cellular features of neoblasts?
In the germarium, the cells shown in yellow are a component of the stem cell niche in the ovary.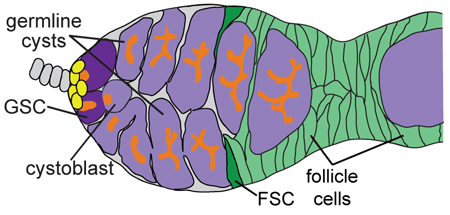
What are cap cells?
Using antibodies to visualize proteins within cells and tissues.
What is immunofluorescence?
A group in an experiment that uses a treatment expected to not produce any results.
What is a negative control?
The cells outlined in red.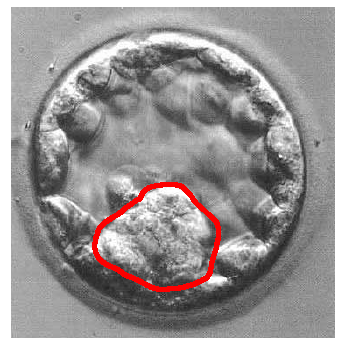
What is the inner cell mass?
SAM stem cells are located in the _____.
What is the central zone?
Mitotic zone
What is the location of GSCs?
Neoblasts are more sensitive to radiation because they are _____.
What is mitotic?
The developmental potential of GSCs.
What is unipotent?
Amplifying cDNA to measure gene expression.
What is RT-PCR?
Non-numerical data that describes a result.
What is qualitative?
Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc
What are the Yamanaka factors?
Organizing center and Quiescent Center
What are stem cell niches in plants?
Distal Tip Cell
What is the stem cell niche?
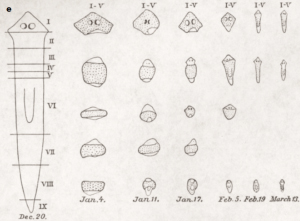 The picture below demonstrates what property of Planaria?
The picture below demonstrates what property of Planaria?
What is the ability to regenerate?
Enteroblasts, daughters of intestinal stem cells, generate ____ and ____.
What are enteroendocrine cells and enterocytes.
Introducing genes not normally expressed into cells.
What is transduction?
Data whose value is measured in the form of numbers or counts.
What is quantitative?
A measure of how many cell types a stem cell can generate?
What is developmental potential?
Stele initials, endodermis initials, lateral root cap initials, columella initials
What are stem cells in the RAM?
_____ signaling is important for stem cell maintenance.
What is notch?
The type of study conducted that showed neoblasts support survival and regeneration.
What is transplantation?
The fully differentiated cell type generated by GSCs in the testis.
What are sperm?
Grouping different cell types together based on labeling specific proteins with fluorescent antibodies.
What is FACS or Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting?
Minimum number of times an experiment needs to be completed in order to do statistics.
What is three?
Stem cells that can generate cell types from more than one germ layer.
WUS only becomes active in the correct cell because of _____.
What is post-translational modification?
What is promotes and suppresses?
What is 25-30%?
The fully differentiated cell type generated by GSCs in the ovary.
What are oocytes?
A technique used to visualizing RNA in in tissues.
What is in situ hybridization?
The number of units (cells, organisms, etc) in a population to be studied.
What is sample size?
Stem cells that can generate cell types from one germ layer.
What is multipotent?
WUS and WOX5 are ____ in the signaling pathways important for stem cell maintenance.
What are ligands?
This feature makes the Notch ligand special.
What is being membrane-bound?
The region along the anterior-posterior axis where neoblasts do not reside.
What is the anterior?
Two physiological factors that affect ovarian GSCs.
What are age and nutrition?
Labeling a cell and all of its progeny.
What is lineage tracing?
Three types of stem cells based on their origin?
What are embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, and adult stem cells?
WUS and WOX5 move through _____ to signal to nearby cells.
What are plasmodesmata?
The range of GSC number.
What is 50-75?