Parkinson disease is characterized by a lack of dopamine produced in this brain area
Substantia Nigra
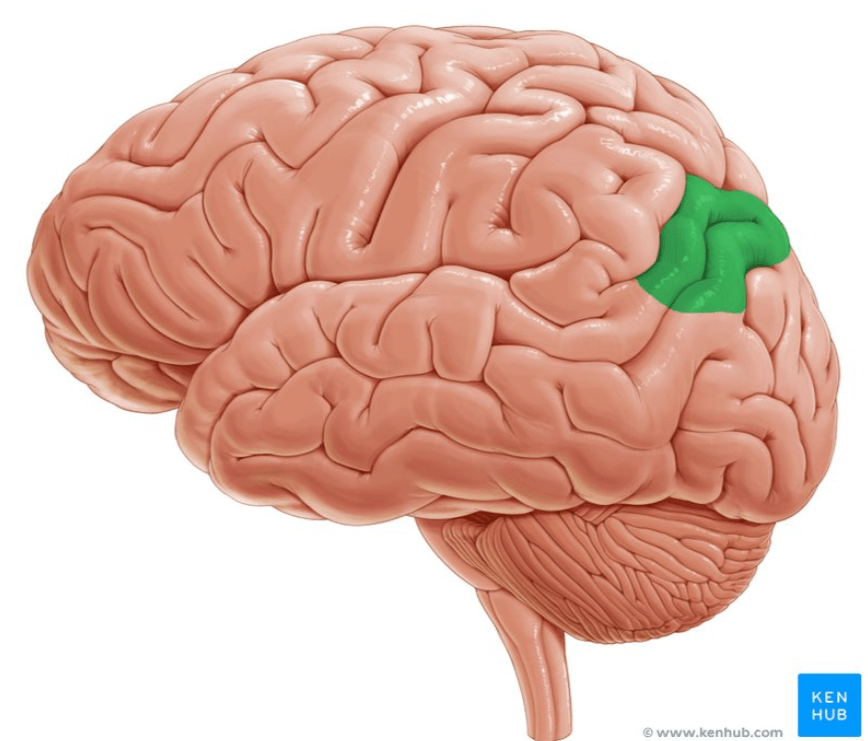
1. Name the gyri anterior to the central sulcus
2. Name the gyri posterior to the central sulcus
2. Describe their GENERAL function. Be vague.
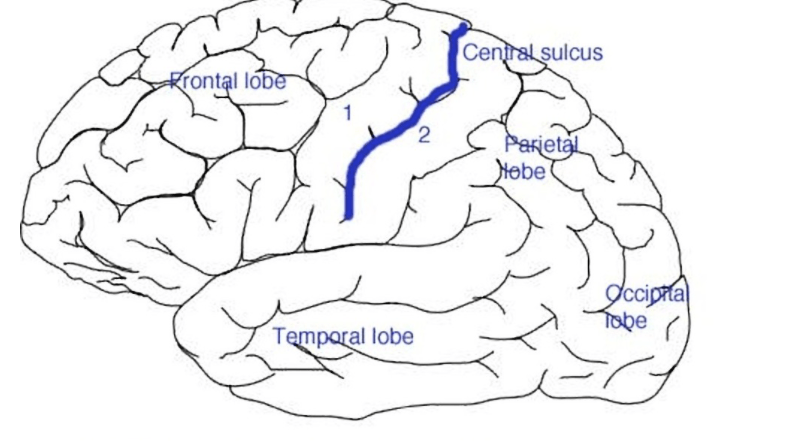
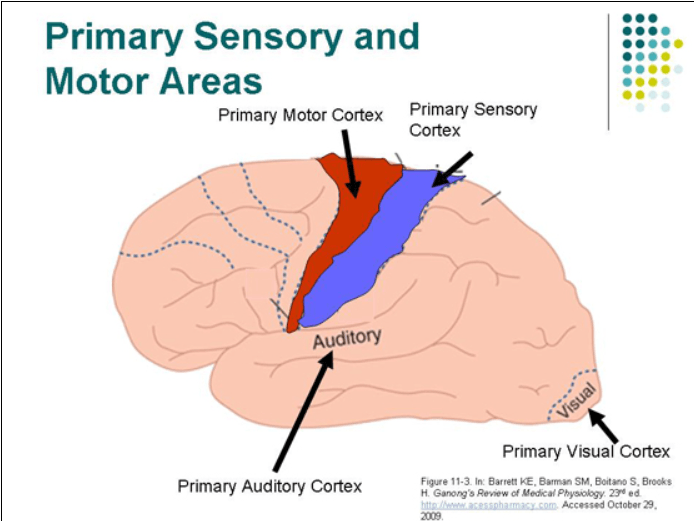
1. Precentral Gyrus.
2. Postcentral Gyrus
3. Precentral is the Primary Motor Area. Postcentral gyrus is the Primary Somatosensory Area.
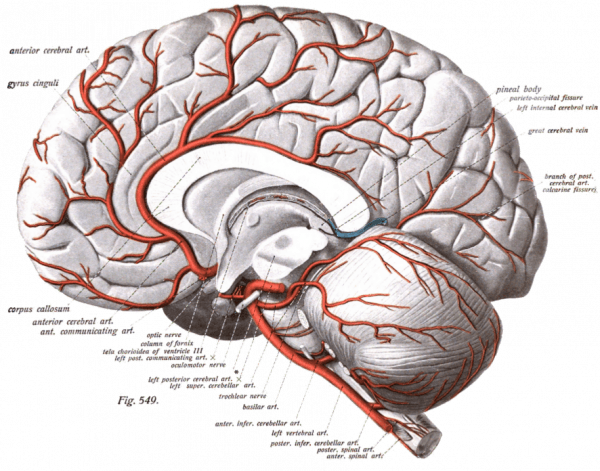
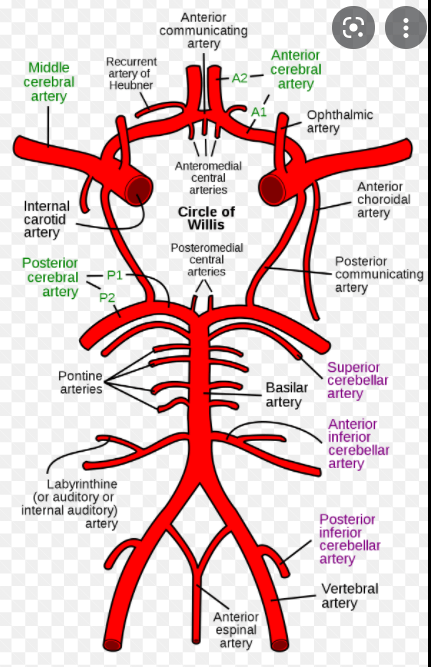
1. These are all infarcts in different regions of this vessel off the Circle of Willis.
2. Patient would have trouble moving this extremity
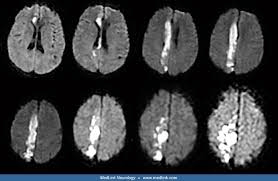
1. Anterior Cerebral Artery
2. Contralateral leg/foot.
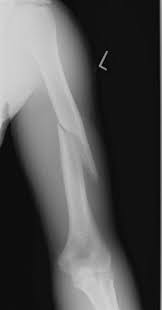
Slitting your wrist can damage 1) this nerve
Ouch they probably damaged 2) this nerve in the picture below. 3) Weakening their ability to do this.
 +
+
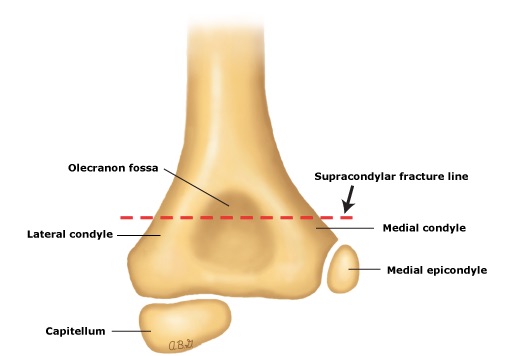
1. Median Nerve
2. Radial Nerve
3. Extend wrist/elbow
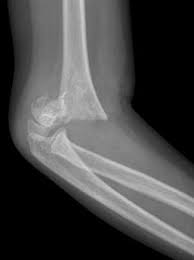
What fracture is this and what nerve is damaged?
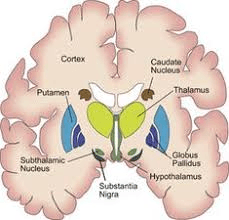
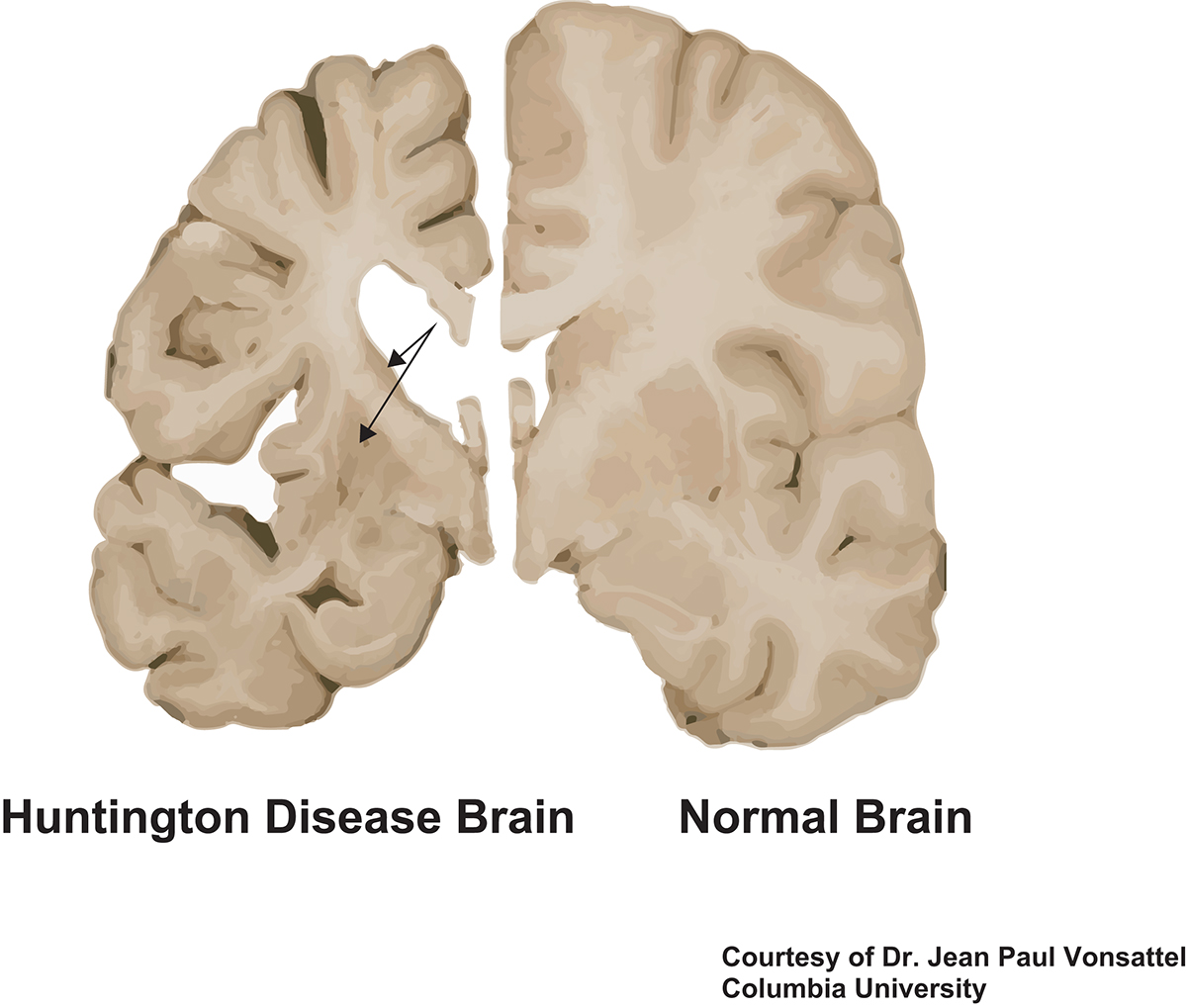
1. Damage to the top structure on the right side of this picture is implicated in this disease. 2. This Neurotransmitter is decreased.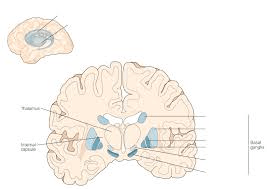
1. Caudate/Putamen Atrophy in Huntington’s Disease
2. GABA we talked about last week, but ACh as well.
CAG repeat. Caudate loses Ach and Gaba

Damage to this structure causes this symptom
Unconsciousness
19 year old CF with broad based gait. Derived from glial cells. Benign
I call it

Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Benign. Typically found in Kids 10-20. Most common in cerebellum. Appears solid or cystic on imaging
Other tumors.
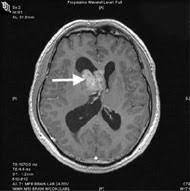
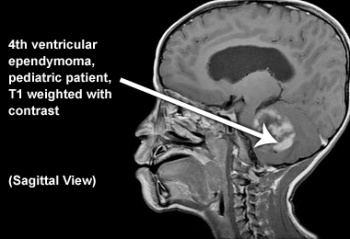
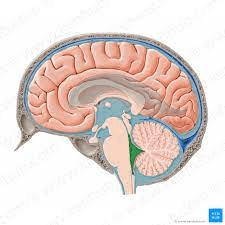
Associated with ventrical. Ependymoma. Ependyma is the cells that line ventricles usually the 4th. Vignette: 25 y/o pt with severe headache, visual loss, vomiting, bilateral babinski, and then becomes drowsy, hitting brain/stem and reticular formation
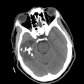
Usually calcified and found in frontal lobe. Oligodendrocytoma
1) ______ is characterized by large amplitude movements of one side of the upper and lower extremities are caused by an ipsilateral lesion of this 2) basal ganglia nuclei.
1. Hemibalismus
2. Subthalamic Nuclei

Damage to the Angular Gyrus can cause Gerstman Syndrome
1-3) Name 3x symptoms of Gerstman Syndrome
4) What Lobe does this occur
1-3) Acalculi, Agraphia (can't write), Finger agnosia, Alexia (can't read), Right to left confusion. Speech is intact.
4. Dominant (So usually left) Parietal Lobe
1-3) Name the vessels
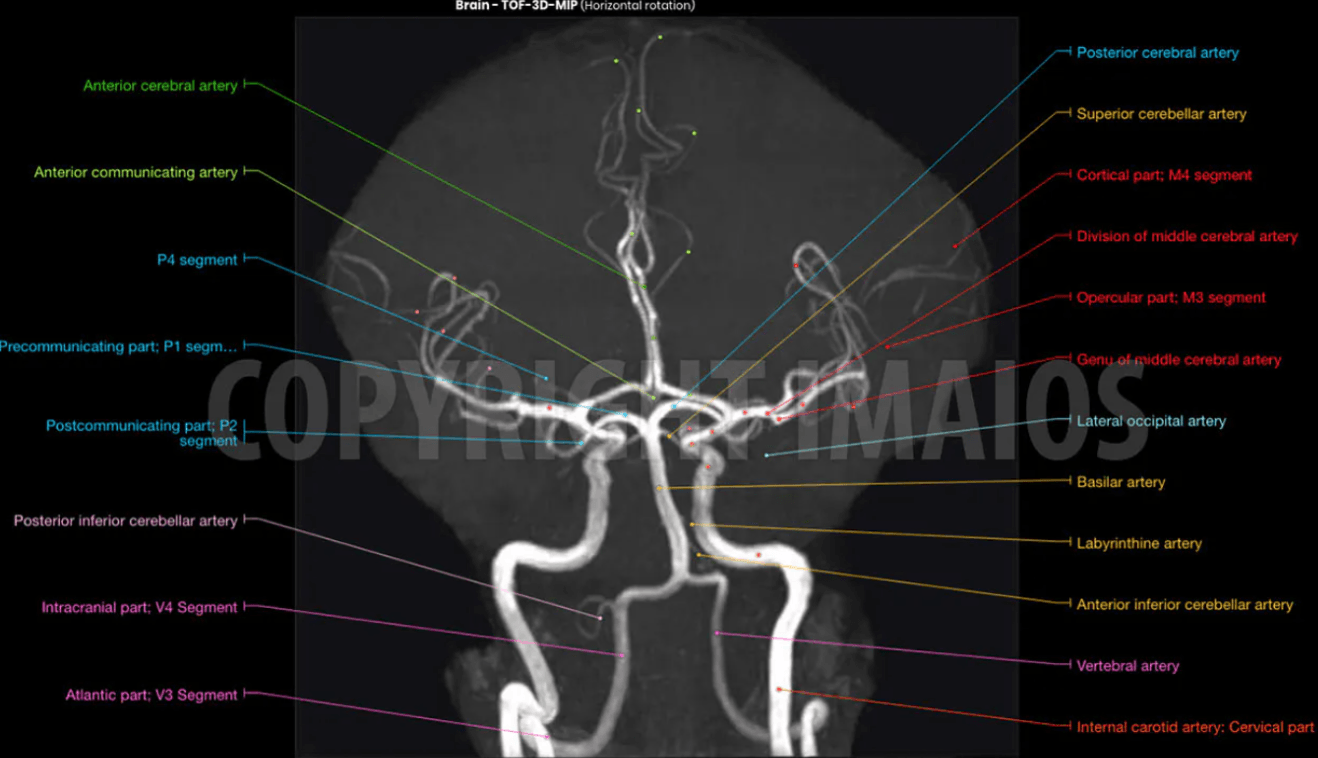
1. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
2. Vertebral Artery
3. Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
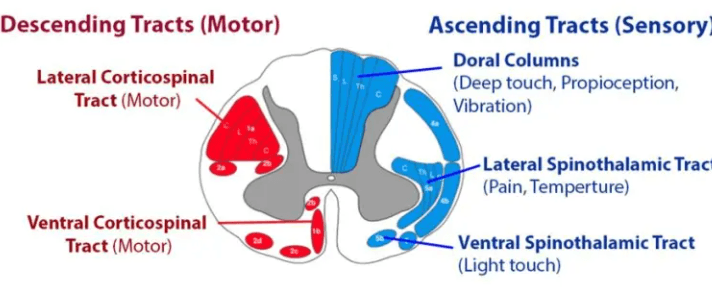
Name the tracts as shown below and describe their function. (Hint divide into anterior and lateral)
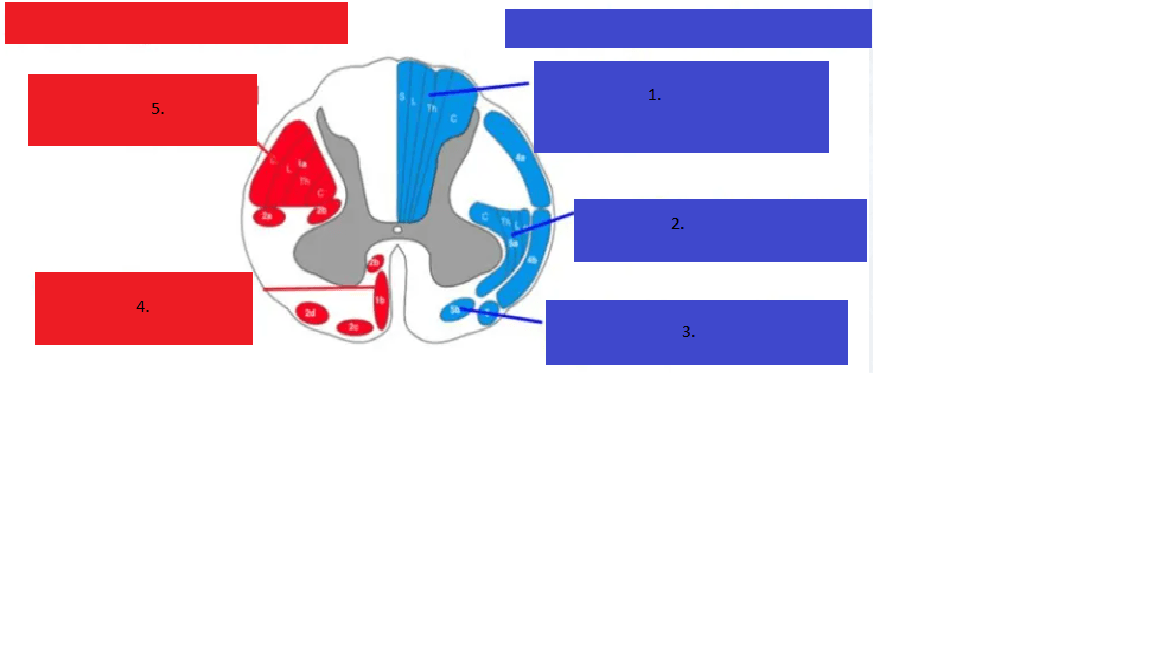
1. Dorsal Column, vibe/prop
2. Lateral Spinothalamic, pain/temp
3. Anterior Spinothalamic, light touch
4. Lateral Corticospinal, motor
5. Anterior Corticospinal, motor
Patients afflicted with 1) this syndrome typically can have phenotypic features such as a Big Chin and Giant Gonads (macroorchidism) in addition to large ears, mental retardation. Due to a mutation in 2) this gene on this 3) chromosome

1. Fragile X
2. FMRP (Fragile X Mental Retardation Gene)
3. X-chromosome
70 y/o develops flaccid paralysis severe water intoxication is hospitalized. Several days later develops dysphagia and dysarthria without other cranial nerve involvement. Sensory exam is limited but grossly normal, DTR’s are symmetric, and cognition is intact. Likely dx
Central Pontine Myelinolysis
8 year old CF, family history of colon cancer found to have this fast growing mass.
I call it

1. Medulloblastoma
Malignant. Most common in cerebellum. Appears heterogenous in imaging with light and dark areas. Associated with Turcot Syndrome. FAP/HNPCC (Lynch Syndrome)
1. This brain area in the limbic system is related to motivation and reward processing. It is specifically connected to addiction.
2. Neurotransmitter associated with it?
3. Beginning of pathway is where?
1. Nucleus accumbens
2. Dopamine
3. Ventral Tegmental Area

87 yo AAF with occlusion of distal L MCA
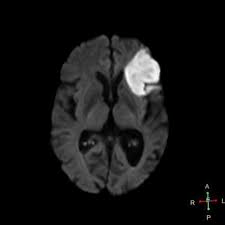
1. Describe language deficit (more than one word)
2. Name area affected
3. Name the Gyrus

1. Expressive aphasia, non-fluent aphasia (frontal think motor)
2. Broca's Area
3. Inferior Frontal Gyrus
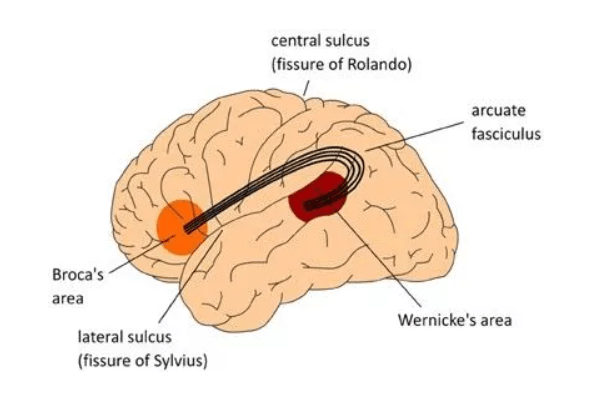
A small stroke to 1) this structure in green can cause allodynia and chronic pain known as 2)
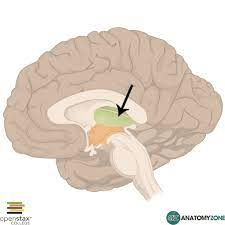
1) Thalamus
2) Central Pain Syndrome or Thalamic Pain Syndrome
A shoulder dystocia and being pulled out of the birth canal caused 1) this condition due to damage to 2) which nerve roots

1. Erb's Palsy. Neonatal Brachial Plexus Paralysis (NBPP)
2. Damage to C5-C6. Brachial Plexus Upper Trunk
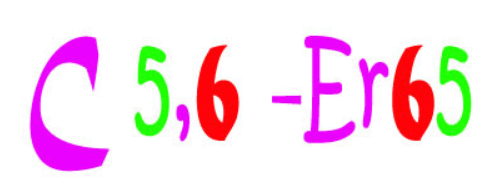
GAA Friedreich! You are only 10 years old why do you keep falling like that? Friedreich has 1) this neurodegenerative condition resulting in 2) this change in his spine and is more at risk for 3) this heart condition

1. Friedreich Ataxia, trinucleotide disease with GAA
2. Kyphoscoliosis
2. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy

Trinucleotide repeat of GAA.
Lesion of this structure in the brainstem leads to INO in MS.
Describe INO
1. Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
2. Horizontal Gaze Palsy


12 yo CM with tunnel vision, breast development, peeing all the time.
I call it

Craniopharyngioma. Has Diabetes Insipidus. Prolactinemia.
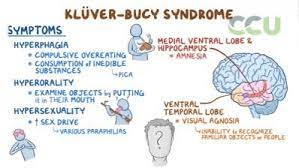
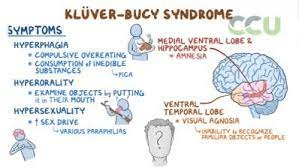
1. Name four symptoms of Kluver Bucy Syndrome. 2. What limbic structure(s) is affected.
1. Hyperphagia, hyperorality, hypersexuality, visual agnosia, hypermetamorphosis, decreased emotional reaction, amnesia.
2. Amygdala primarily, hippocampus as well.
1. This gyrus is marked in red.
2. If lesioned you would have difficulty with the following.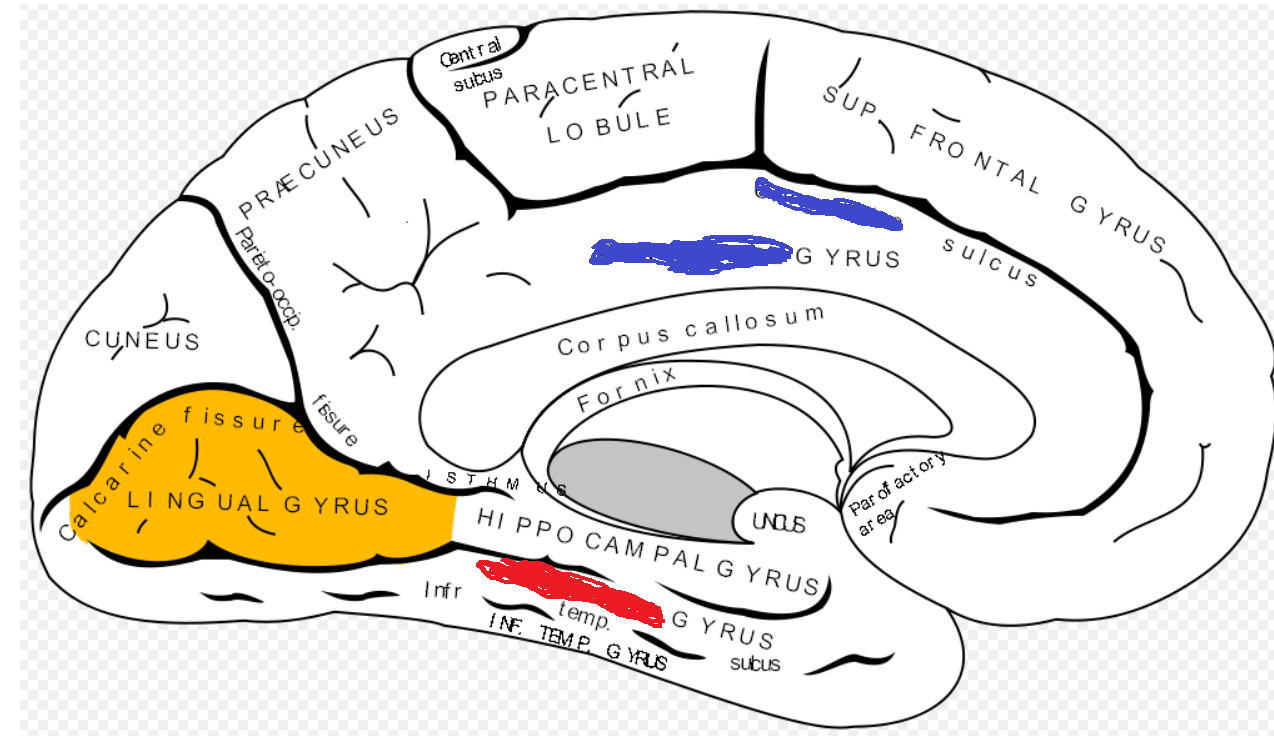
1. Fusiform Gyrus
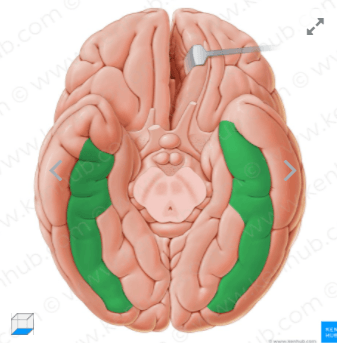
On the bottom of the brain. Composed of medial and lateral occiptotemporal gyri.
2. Facial Recognition
Jean Dominique Bauby wrote the Diving Bell and the Butterfly after he had a stroke of 1) this vessel leaving him with 2) _____ syndrome rendering him with flaccid quadriplegic paralysis and unable to speak and with a gaze palsy. The book was written by his blinks and by eye movements he was able to make in 3) _____ direction

1. Pontine or Basilary Artery
2. Locked-in Syndrome
3. Vertical direction. (d/t horizontal gaze palsy)
This brachial plexus injury is called 1) ______ . spinal levels of the brachial plexus were damaged. Describe most common cause..
1. Klumpke's Palsy
2. C6-C8
3. Grabbing on an outstretched branch.]
40 yo CF presents with intermittent headache and tingling in her hands. this sagittal MRI. When shining a light into each eye the left dilates while the right constricts.
1. Name the physical exam finding.
2. Describe the finding in Sagittal MRI
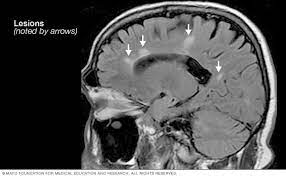
3. What is found in the CSF
1. L Marcus Gunn Pupil, positive swinging light test
2. Dawson's fingers
3. Oligoclonal bands
Marie-Foix Syndrome is an infarction of 1) this vessel, causing loss of taste to the anterior 2/3rds of the tongue, paralysis of the face, ipsilateral Horner's syndrome, contralateral loss of pain temperature sensation, ataxia, dysmetria. It is also called Lateral 2) ______ syndrome, because it affects the largest part of the brainstem.
1. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery OR Basilar Artery
2. Lateral Pontine Syndrome
Pons is the biggest part of the brainstem. Also affects cerebellum causing ataxia.
PICA/AICA infarction only differ by the bold symptoms. In PICA it causes swallowing difficulty and dysphagia by affecting the Medulla. 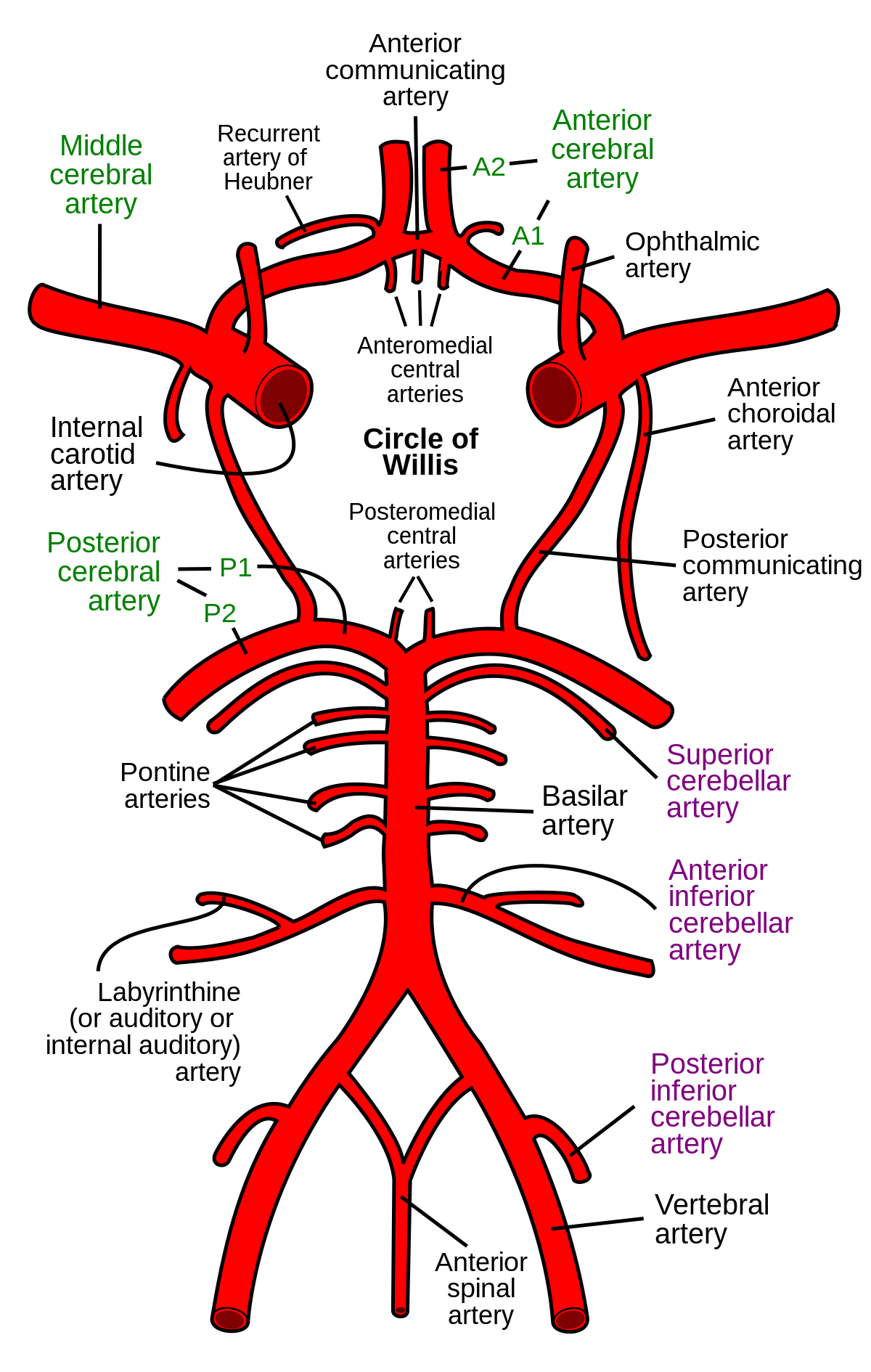
81 yom CM from Arizona found to have this fast growing brain lesion
I call it
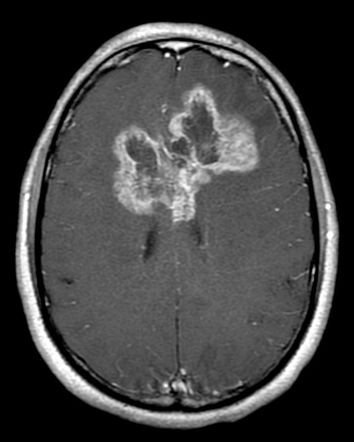
Glioblastoma Multiforme.
John Mccain. Died from it. Malignant. Found in Cerebral White Matter. Butterfly shape. Older adults
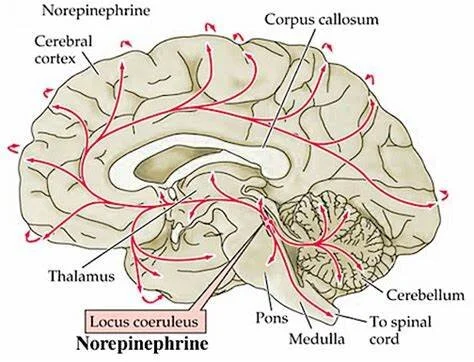
The following neurotransmitters originate from which brain structure/nuclei/area.
1. Dopamine
2. Serotonin
3. Norepinephrine
4. Acetylcholine
1. VTA, Substantia Nigra, Hypothalamus (Arcuate Nucleus/Preoptic Nucleus)
2. Raphe Nucleus
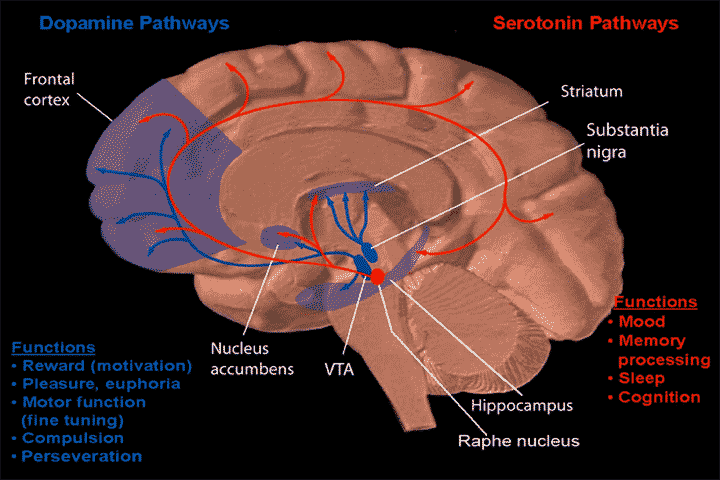
3. Locus Coeruleus
4. Basal Nucleus of Meynert

1. This gyrus is marked in blue
2. Describe the symptoms when lesioned

1. Cingulate Gyrus
2. Akinetic Mutism
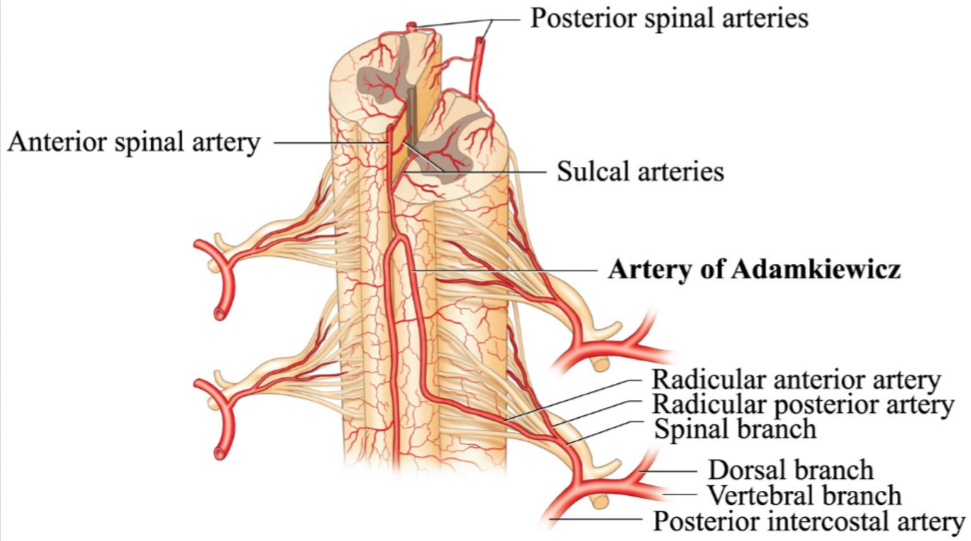
65 yo CM with 30 pack year smoking history is treated for AAA s/p endovascular repair develops bladder/bowel incontinence, loss of temperature sensation below the umbilicus, flaccid paralysis of lower extremities also known as 1) _________ syndrome due to disruption of artery of 2) _______
1. Anterior Cord Syndrome/Anterior Spinal Artery Syndrome
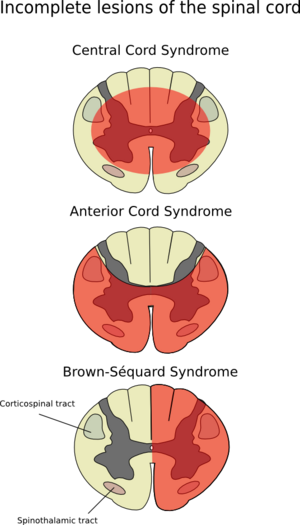
2. Disruption of Artery of Adamkiewciz

38 yo CF w/h/o hashimoto's thyroiditis presents with blurred vision that worsens in the evening. Is treated for 1) ______ she is later found to have. CT chest shows 2) _____ . If she had an acute exacerbation of her condition she should be treated with 3) ________
1. Myasthenia Gravis due to Post-synaptic AChR abx
2. Thymoma
3. Acute exacerbation treat with IVIg. Plasmapheresis. Endotracheal Intubation.
Stable condition not in exacerbation treat with: pyridostigmine/glucocorticoids.
46 yo CF AIDS patient with memory problems, R hemiparesis, L limb ataxia, BL visual field deficits, and normal CSF. MRI showed.
1) Name that disorder
2) Cause
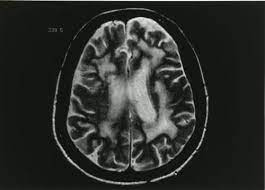
1. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
2. JC Virus Reactivation
Baroreceptor reflex occurs in this nucleus. We also mentioned it for a different reason last week.
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
67 year old with a headache and focal deficits, found to have antibodies to presynaptic voltage gated calcium channels

1. Lung Cancer Metastasis, with Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome.
SCLC 40-50% of cases have or will have a met to the brain.
Occurs in watershed area