Why is the routine for a lateral CXR performed with the left side up against the IR versus the right?
A. The heart will be magnified/larger if performed with a right lateral
B. The heart and chest will not be rotated in a left lateral
C. The routine is a right lateral, not a left lateral.
what is A. The heart will be magnified/larger if performed with a right lateral
How can you tell if a KUB is rotated?
a. Spinous process's are not centered
b. iliac wings are not supinated
c. the obturator foramina are not symmetrical
D. All of the above
What is D. all of the above
Decreasing radiation dose to the patient includes which of the following:
A. Collimating to the part being examined
B. Using grids for all upper extremity exams
C. Exposing more than what is needed for the part being examined
What is A. Collimating the part being examined
Which term describes the medial end of the clavicle?
a. Acromial extremity
b. Acromion
c. Acromial tuberosity
d. Sternal extremity
What is D. Sternal Extremity
What is A
1. trachea 2.Apices 3. carina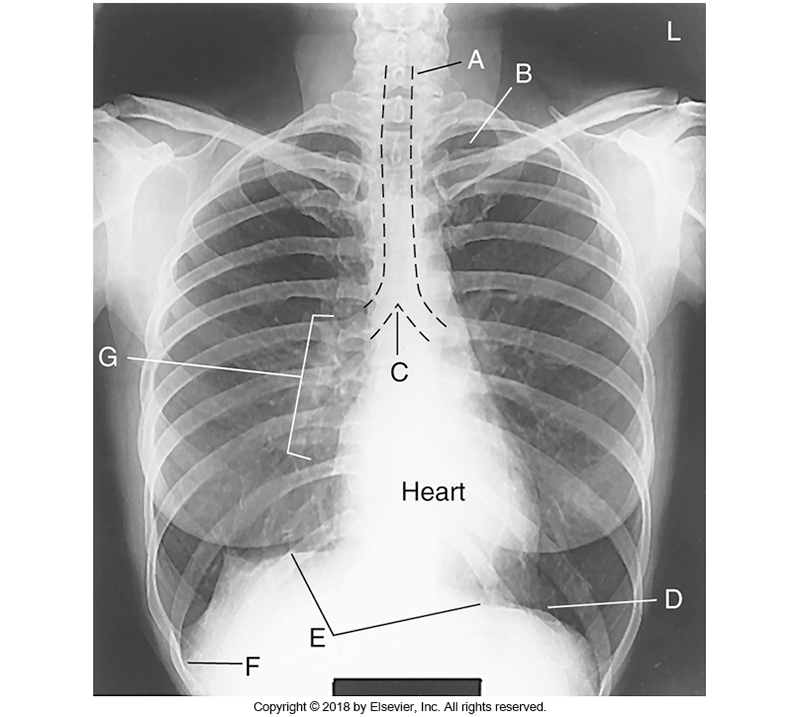
what is 1. Trachea
Which one of the following is a clinical indication for a KUB?
A. Bowel Obstruction
B. All of the above answers are correct
C. Kidney stones
D. Foreign Body
What positioning consideration is crucial when imaging a lateral forearm or lateral elbow?
A. The elbow and shoulder should be in the same plane
B. The elbow is bent at a 90 degree angle
C. The epicondyles are perpendicular to the IR
D. All of these are correct
What is D. All of these are correct
Visualizes the glenoid cavity but with an additional 45 degree caudad angle directed towards the scapulohumeral joint?
a. Grashy
b. Garth
c. Fisk
What is B. Garth
What is B
1. Carina 2. Costophrenic angle 3. Apices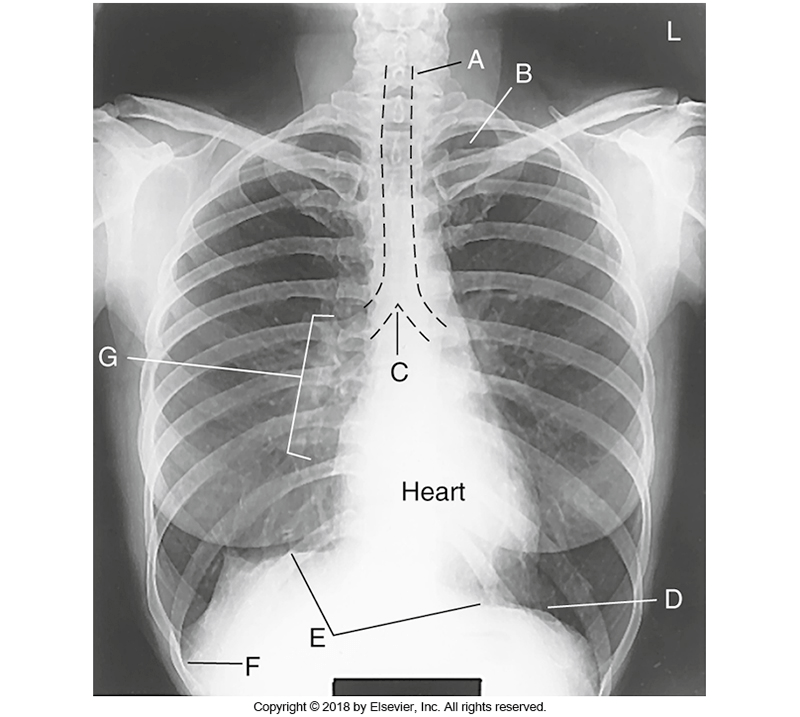
what is 3. Apices
What vertebral level is the xiphoid process?
A. T2
B. T6
C. T10
D. T11
What is C. T10
Why do we perform an AP forearm in the AP position versus the PA position?
A. It is more comfortable for the patient
B. The radius and ulna are crossing or overlapping in the PA position
C. The forearm is not performed in the AP position
Match anatomy:
Greater tubercle is lateral in profile
a. internal
b. neutral
c. external
what is c external rotation
What is C
1.Trachea 2. Carina 3. Costophrenic Angle
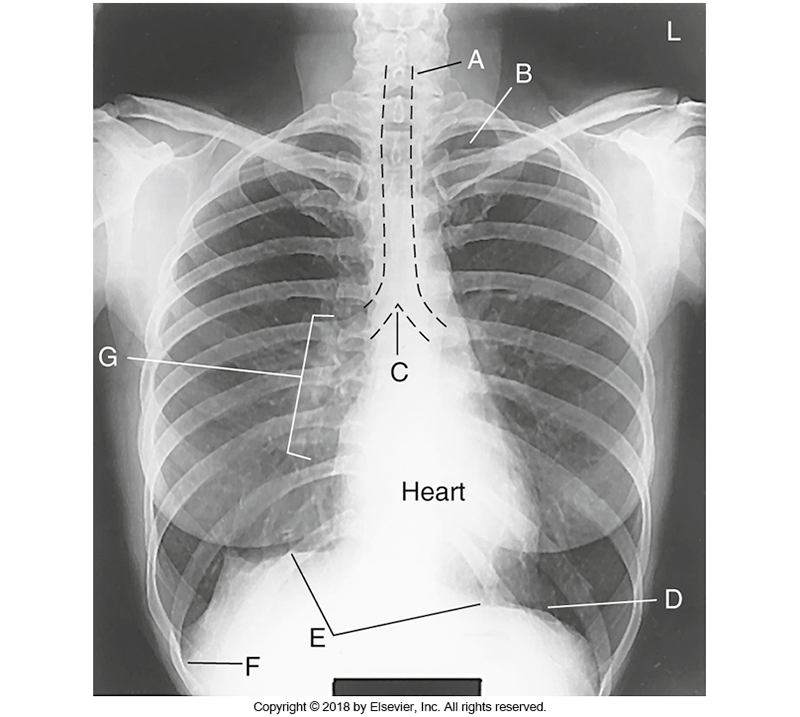
what is 2. Carina
What region is the bladder located?
a. Epigastric
b. Umbilical
c. Hypogastric
What special wrist projection would best demonstrate the posterior (or dorsal) aspect of the carpal bones?
A. Carpal Bridge (Tangential projection)
B. Carpal Canal (Tunnel, Gaynor-Hart Method)
C. PA
D. Lateral
What is A. Carpal Bridge (tangential projection)
Match anatomy:
Lesser tubercle is medial profile
a. internal
b. external
c. neutral
what is a. internal
What is D
1. Costophrenic angle 2. Costaphrenic Angel 3. Castophrenic angle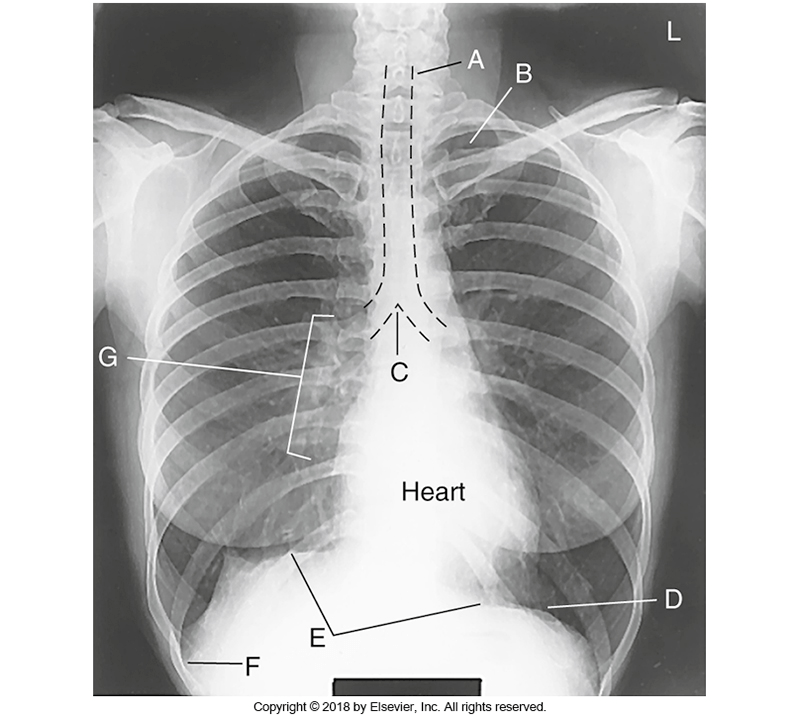
What is 1. Costophrenic angle
Why is the right kidney usually lower in the abdomen than the left kidney?
A. Presence of right suprarenal gland
B. Presence of the liver
C. Presence of right colic flexure
D. Presence of the stomach
What is B. presence of the liver
You have an order for a forearm on a 2 year old and the father is staying in the room to help immobilize the arm. What should you consider before making the exposure?
A. Position the father’s hands so that they are not exposed in the image when immobilizing the arm
B. Leave the light open, its okay that the father’s hands are in the image.
C. Ensure there is a long exposure time
What is A. Position the fathers hands so that they are not exposed in the image when immobilizing the arm
match the anatomy:
Greater tubercle is anterior but still lateral to lesser tubercle
a. external
b. neutral
c. internal
what is a. neutral