Define the term ‘classification’.
Classification is the grouping of organisms in terms of similarities in morphology, anatomy and biochemistry.
Distinguish between abiotic and biotic
Abiotic factors are the non-living factors that affect an organism’s ability to survive. Biotic factors are the living components of an environment.
Define and give an example of a food chain.
A food chain is a simple linear arrangement between organisms that shows the flow of matter and energy from one organism to another through feeding relationships. An example of a food chain from a grassland ecosystem would be:
grass à rabbit à snake à eagle
A population is made up of:
A all individuals of any species
B groups of individuals of any species in an area
C all groups of organisms in an area at a given time
D individuals of the same species in an area at a given time
D
Define Primary succession
Primary succession is ecological succession that begins in essentially lifeless areas, such as regions in which there is no soil or where the soil is incapable of sustaining life (because of recent lava flows, newly formed sand dunes, or rocks left from a retreating glacier).
Identify the three components of a nucleotide.
Phosphate group, sugar (deoxyribose) and a nitrogen base
Describe what would occur during sexual reproduction in animals if meiosis had not occurred.
If meiosis had not occurred, there would be no gametes (egg and sperm); hence, during sexual reproduction there would be no fertilisation of an egg.
Define the epigenome.
The epigenome is a set of factors that affect which part of the DNA is activated.
Define allele
Alleles are the forms of a gene located in the same position on homologous chromosomes.
Define the term biotechnology.
Biotechnology is the application of biological knowledge to the production of organisms useful to humankind.
Describe what is meant by biological evolution.
Biological evolution is a unifying theory that attempts to provide an explanation of the changes that have occurred over time in a population, based on scientific evidence.
Define the term ‘coevolution’.
Coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other’s environment.
Explain why the classification system for organisms needed to be modified following the ability to sequence DNA.
Scientists are now able to sequence DNA and compare molecule sequences of different organisms. This has enabled them to discover previously unknown relationships between different species. The classification system had to be modified to fit with the updated information.
Describe why ecosystems are considered to be self-sustaining.
Ecosystems are considered self-sustaining because each organism in the community has a niche. Autotrophs are able to produce energy, consumers have particular feeding relationships to transfer energy, and detritivores and decomposers help to recycle matter.
Explain why simple food chains are rare, and how food webs provide greater stability in ecosystems.
A simple food chain is rare due to an organism generally having more than one food source. There is greater stability in a complex food web, as most organisms have a variety of food sources to compensate for seasonal fluctuations.
The highest rate of reproduction of a population under ideal conditions is called the:
A biotic potential
B environmental resistance
C carrying capacity
D birth rate
A
Using a specific example, explain how species composition in any particular ecosystem can change seasonally.
Student answers may vary. Seasonal changes include factors such as temperature, rainfall and light intensity. An example would be a bird species migrating during the winter months to a location that is warmer. This would change the species composition in the ecosystem they departed from as well as the ecosystem they migrate towards.
Describe a nucleosome.
A nucleosome is a length of DNA coiled around a core of eight histone protein molecules.
Explain what happens to homologous pairs of chromosomes during meiosis.
At the beginning of meiosis, chromosomes are in homologous pairs (diploid) and metaphase I. These homologous chromosomes line up along the equator and separate. During metaphase II, chromosomes are no longer in homologous pairs, instead lining up along the equator singly.
Explain how a genetic mutation can occur without the amino acid being changed.
A mutation in a single nucleotide may not change the amino acid since more than one codon can code for the same amino acid. This is called a silent mutation.
In pea plants, tallness is dominant to shortness and purple flower colour is dominant to white. If two heterozygous tall purple pea plants were crossed, determine what the expected ratio of the offspring will be.
Explain, with examples, why many microorganisms have played an important role in biotechnology.
Microorganisms are used in food processing, waste reduction and the production of medicines. Possible examples include bacteria used to produce vinegar from alcohol, butter from milk and acetone from molasses.
Define the terms viability and fecundity.
Viability is the ability to survive and reproduce. Fecundity is the natural capability to produce offspring.
Describe the means by which divergent speciation may occur.
Divergent speciation can occur when there is competition for a particular resource or when a new niche becomes available in a single environment. Environmental pressure acts upon the population and certain variations are selected for and become increasingly dissimilar. This occurs when the two or more groups of organisms will become so different that they will no longer be able to breed together. They become reproductively isolated.
Describe some of the problems associated with a transition from living in water to living on land.
The terrestrial environment is hostile in many ways and organisms faced many problems transitioning from water to land. They needed to prevent loss of water by evaporation, maintain a moist surface for gas exchange, transport water and dissolved substances around their bodies, support their bodies against the pull of gravity, reproduce without water and survive with changing environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, wind and light.
The vast majority of Australian plants are sclerophylls – woody plants with evergreen leaves that are narrow and thick to reduce water loss. Identify what primary environmental factor these plants are adapted for.
These plants have adaptations to reduce water loss and are therefore able to survive in dry environmental conditions. The primary environmental factor is water.
Some species in an ecosystem are ‘specialists’ and some are ‘generalists’. Define these two terms and explain which of the two types has greater survival potential.
Specialists are consumers that eat only a limited range of things, and generalists are consumers that eat a wide variety of food. Generalists have a survival advantage as they eat a wide variety of food so, if one food choice is limited, they have other options to obtain their energy requirements.
The capture–recapture method of measuring a population would be most likely be used for measuring the population of:
A wedge-tailed eagles
B soil bacteria
C Eucalyptus maculata
D dairy cattle
A
Describe some of the adaptations that are an advantage to pioneer species.
A pioneer species needs to survive in harsh areas, which includes environments with high light intensity and low water holding capacity of the soil due to lack of organic matter. Some adaptations would include the ability to photosynthesise, rapid spore or seed germination, wind pollination capability, nitrogen fixing from the air, and r-strategists that disperse rapidly and are tolerant of extreme conditions.
Describe a replication bubble.
A replication bubble is an unwound and open region of DNA in which DNA replication occurs.
Distinguish between an autosome and a sex chromosome.
An autosome is a chromosome that is not sex determining, and sex chromosomes carry the information that determines the sex of an individual.
Compare histone modification and DNA methylation.
Histone modification is the addition of a chemical tag that varies the width between nucleosomes and therefore determines whether or not a gene can be transcribed. They are often transitory and can be reserved according to the chemical environment of the cell. DNA methylation is also the addition of a chemical tag; however, its role is at the start of the structural gene that blocks transcription.
A homozygous rough black guinea pig (RRBB) is mated with a smooth white one (rrbb). Describe what the F1 generation will look like.
The F1 generation will be heterozygous for both traits (hybrids) and will be rough and black (dominant traits).
Distinguish between DNA polymerases, restriction enzymes and DNA ligase.
DNA polymerase is a type of enzyme responsible for assembling nucleotides to form new copies of DNA. Restriction enzymes are enzymes that cleave DNA at specific recognition sites. DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together.
Describe the three main observations or ideas on which the theory of natural selection is based.
The theory of natural selection is based on three main observations:
1 – The numbers of individuals in a population remain approximately constant.
2 – Variation exists within all populations.
3 – Over many generations, new variations gradually accumulate, possibly resulting in new species.
Define the term ‘cline’.
A cline refers to a specific characteristic such as colour or size, rather than describing the entire appearance of the species.
Describe how scientists name a species.
Scientists use the Linnaean system to give a species a scientific name. Every species has a genus name that is a classification group, followed by a specific name that indicates the particular species within that genus. Well-known organisms also have common names. The person who first discovers a species has the right to name it. They may name the species after a person (not necessarily themselves) or the place it was observed.
A particular, humid locality has a potential evapotranspiration ratio of 1, an annual precipitation of 9000 mm and biotemperature of 20°C. Using Holdridge’s classification to identify what type of plant community should be present.

wet forest or rain forest (PET of 0.25)
Define the terms ‘biomass’, ‘productivity’ and ‘standing crop’.
Biomass is the mass of all the organic matter in an area. Productivity is the amount of energy fixed in organic matter at each level in an ecosystem. Standing crop is the biomass of an organism at a particular moment.
Define the term carrying capacity of an environment.
Carrying capacity is the total population able to be supported by a particular environment.
Determine why being an r-strategist would be an advantage to a pioneer species but not to a plant in a climax community.
Being an r-strategist would be an advantage for a pioneer species since they need to disperse rapidly and have a large number of offspring to survive in the harsh environment. This is not advantageous for a plant in a climax community because this community is stable and each species has its own niche and limiting factors are causing those species to remain at their carrying capacity.
Explain why the different strands of replicating DNA are called lagging or leading in a replication bubble.
The leading strand is the strand being replicated from the DNA template from the middle of the replication bubble to the fork, whereas the lagging strand is the strand being replicated from the fork to the middle of the replication bubble.
Explain the types of cell division involved in gametogenesis.
Both mitosis and meiosis are involved in gametogenesis. Mitosis produces the primary cell from the germ cell, and meiosis occurs to produce the gametes.
A student claimed that a point mutation could be described as a frameshift mutation. Consider their claim using examples.
A point mutation is a change to one nucleotide (substitution) and this does not cause a shift in the reading frame, so therefore it is not a frameshift mutation. A point mutation can be silent (no amino acid change), missense (amino acid change) or nonsense (stop codon).
Define the term continuous variation
Continuous variation refers to a variety of phenotypes as a result of more than one gene contributing to a characteristic.
Distinguish between genetically modified organisms and transgenic organisms.
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are any organisms that have had their DNA modified in any way, whereas transgenic organisms are GMOs that have genes from another organism introduced into their DNA.
If natural selection acts on individuals, describe how this results in changes to the allelic frequencies of a population.
Natural selection is the process whereby organisms that have physical characteristics suited to the environment are more likely to survive. If an organism is more likely to survive, it has a higher viability because it will be more likely to reproduce. This then affects the allelic frequencies of the next generation and therefore changes the allelic frequencies of a population.
Differentiate between clinal variation, geographical isolates and zones of hybridisation.
Clinal variations are the gradual changes or differences in inherited characteristics of adjoining populations of a species spread across a range of environments, whereas geographic isolates are populations separated by an external barrier that prevent gene flow between the populations. Zones of hybridisation are areas in which two divergent subspecies may interbreed.
An organism has been found that has eukaryotic cells, is multicellular and heterotrophic. Determine which domain and kingdom you would place it in. Consider what further information you would require to be sure of your answer.
Domain – Eukarya; Kingdom – Fungi or Animalia. To determine which of these two kingdoms is correct, more information on the organism’s locomotion and/or nervous system would be needed.
Distinguish between a biome and an ecozone.
A biome is an area with a specific set of climatic conditions that control the distribution of organisms and the adaptations they display. An ecozone is a large area where organisms have been evolving in relative isolation over a long period of time.
Identify which of the pyramids in Figure 5 would best show the relative numbers of individuals in a food chain containing a tree, caterpillars and insectivorous birds.
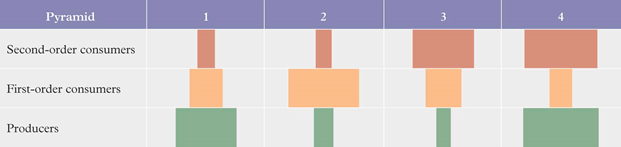
Pyramid 2
Describe how limiting factors determine the carrying capacity of an environment.
Limiting factors are any factors that limit the growth of a population. If a population’s growth is limited then it has reached its carrying capacity.
Biomes are partially determined by altitude. True/false? Justify your decision.
Biomes are partially determined by altitude. More specifically, biomes are determined primarily by temperature and precipitation and altitude is going to have effects on both temperature and precipitation.
As altitude increases, temperature decreases. This is going to change the structure and composition of our biome.
Describe the role of the following enzymes in DNA replication.
a DNA helicase
b DNA polymerase
c DNA ligase
a DNA helicase
DNA helicase breaks down the hydrogen bonds to separate the two strands of DNA.
b DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase synthesises the new strands of DNA from the DNA template.
c DNA ligase
DNA ligase joins the DNA strands together on the lagging strand.
Compare the process of spermatogenesis and oogenesis (with reference to haploid and diploid cells).
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both begin with a diploid germ cell, which then undergoes mitosis to produce a diploid primary cell. These cells under meiosis produce haploid secondary cells. Spermatogenesis results in four haloid sperm, whereas oogenesis results in one haploid ovum that undergoes fertilisation to form a diploid fertilised egg cell.
Describe the action of the SRY gene.
The SRY gene is responsible for the production of transcription factors that control the expression of specific DNA regions that cause the foetus to develop male gonads.
Codominance is the genetic inheritance of two or more traits of a characteristic, each of which is expressed in the phenotype.
Briefly describe the key steps in the polymerase chain reaction process.
Denaturation: two strands of DNA separate by heating to 90–95℃
Annealing: mixture cooled to 52℃ so that primers bind to the single-stranded DNA.
Elongation: mixture is heated to 75℃ so that Taq polymerase produces new strands of DNA so that it is now double stranded.
Explain why the presence of key adaptations are important before adaptive radiation can occur.
Key adaptations are novel phenotypic traits that allow the organism to evolve to exploit a new niche or resource and although the variation may have been present for some time, it is not until an environmental pressure acts upon the populations that these variations will be selected.
Describe, giving examples, four mechanisms that prevent interbreeding between different populations.
Four of the following mechanisms should have been chosen: ecogeographical isolation, seasonal isolation, behavioural isolation, mechanical isolation, gametic isolation, developmental isolation, hybrid unviability, hybrid sterility and selective hybrid elimination.
Ecogeographical isolation occurs when two populations are initially separated by some extrinsic barrier and, in time, become so specialised for different environmental conditions that neither can survive in the habitat of the other. An example is the Australian white-naped honeyeater and the white-throated honeyeater. In the overlap zone of these species, the white-naped honeyeater occupies the high country and the white-throated honeyeater occupies the lowlands.
Seasonal isolation is when two closely related species are sympatric but breed in different seasons of the year, so interbreeding between them will be effectively eliminated. For example, pines in California, the Pinus radiata and Pinus muricata, do not form hybrids because they shed their pollen at different times of the year.
Behavioural isolation is the visual, auditory or olfactory signals (or a combination of them) that reproductively isolate a species. For example, the black-throated finch dances with a piece of grass in its bill, and the long-tailed finch does not.
Mechanical isolation occurs if structural differences between two closely related species make it physically impossible for mating between males of one species and females of the other. For example, each species of cotton bush has distinctively shaped pollen sacs with corresponding stigmal slits making pollination between the species impossible even though the species are sympatric.
Define the term ‘species’ in terms of reproductive isolation. Explain difficulties with this definition.
A species is a group of similar organisms whose members can interbreed with each other in their natural environment to produce viable and fertile offspring. Difficulties with this definition include:
• some species reproduce asexually, so their ability to reproduce in natural conditions cannot be tested
• fossils cannot be classified on the basis of their ability to reproduce
• embryos can occur without fertilisation
• ring species are able to interbreed with neighbouring species
• some organisms are infertile.
Explain the difference between Simpson’s Index and Simpson’s Diversity Index.
Simpson’s Index (D) measures the probability that two individuals randomly selected from a sample will belong to the same species. The larger the value of D, the lower the diversity of the ecosystem. Simpson’s Diversity Index (SDI) represents the probability that two individuals selected from a sample will belong to different species. The higher the value of SDI, the greater the diversity.
Several large geckoes are found in Australian rainforests; for example, the banded gecko, the chameleon gecko and the leaf-tailed gecko. They feed on insects and other small animals, which they encounter as they forage through the forest. These lizards blend into the general pattern of bark and leaves around them and are extremely difficult to observe when they are motionless. All geckoes are insectivorous, but will eat smaller lizards and sometimes frogs. They are nocturnal in habit. Discuss abiotic requirements of these geckoes.
Geckoes require a suitable water supply, sunlight to control their body temperature, oxygen for energy production, warmer temperature range and rocks and soil for sunbaking and habitat formation.
A knowledge of population growth curves can help in controlling pests as well as in the conservation of endangered species. Discuss the most effective time to control a rat outbreak in a racing stables complex. Justify your answer.
The most effective time to control a rat outbreak would be as the population has begun to increase. This will avoid the population reaching its carrying capacity and becoming out of control.
Describe the features of pollen and spores that make them good indicators of past ecosystems.
Pollen and spores are resistant to decay and are produced in large quantities. They can accumulate on any undisturbed surface. Pollen grains of each species have their own unique size and shape. Therefore, scientists can determine the exact species that existed in that area at that particular time.
Describe how a segment of a DNA molecule replicates.
DNA replication begins with the separation of the DNA strands by DNA helicase, which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases. DNA polymerase attaches to a primer at the 3′ end of the template strands (initiation) and begins adding nucleotides (elongation) until the replication fork is stopped or blocked. This occurs when a special protein binds to the termination sequence site in the DNA (termination).
Describe three major differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Spermatogenesis is the formation of sperm that begins at puberty and continues into old age. Following spermatogenesis, there are four haploid spermatids that take approximately six weeks to mature into sperm. These sperm have a head containing the haploid nucleus and enzymes to dissolve the protection coating the ovum and a tail to provide propulsion. Oogenesis is the formation of an ovum that occurs in the ovaries of the female from early embryonic development. Females have a finite number of follicles, and from puberty they mature on average once per month. When meiosis continues after puberty, a secondary oocyte forms with a polar body and meiosis does not fully complete until fertilisation.
Describe the events during meiosis that result in the non-disjunction of chromosomes.
During anaphase I, homologs separate, and sometimes this process doesn’t occur properly (non-disjunction) and the homologs end up on the same side of the cell. Non-disjunction can also occur during anaphase II when the sister chromatids do not separate properly. This results in the gametes having two copies of a particular chromosome while other gametes do not have that chromosome.
In snapdragons, tallness (T) is dominant to dwarf-ness (t) and red flower colour (R1) shows intermediate dominance to white flowers (R2). The hybrid condition results in tall plants with pink flowers. A dwarf red snapdragon is crossed with a plant pure-breeding for tallness and white flowers. Determine the expected proportions of genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring.
ttR1R1 × TTR2R2 will result in all offspring with genotype: TtR1R2 with phenotype: tall with pink flowers.
Describe different applications of PCR.
PCR is a significant tool used in the detection of infectious diseases and mutations in genes.
Differentiate between stabilising, disruptive and progressive selection.
Stabilising selection maintains constancy of the species over generations when the environment is stable. If the environment changes suddenly, selective pressures change, and this results in the emergence of new phenotypes – this is known as progressive selection. Once the new mean is established, it is then maintained by stabilising selection. The last type of natural selection is disruptive selection, which increases the frequencies of the extreme types in a population and eliminates the intermediate types.
Distinguish between divergent and convergent evolution.
Divergent evolution occurs when a population is separated due to geographical barrier, a new niche or competition for a particular resource. This results in the separation of the population with different variations that have been selected for. The groups of organisms become different and no longer breed together. Divergent evolution results in speciation from a recent common ancestor. Evidence of divergent evolution is homologous structures. This differs from convergent evolution, which is the direct result of similar environmental pressures between two distantly related organisms. These organisms develop structures that are similar in appearance and function, with key differences in internal structure, making them analogous structures.
Define the terms ‘homologous’ and ‘analogous’ as used by biologists to describe structures. Identify an example of each type of structure.
Homologous structures are structures with different functions but a similar structure and development, suggesting that they share a recent common ancestor. An example of a homologous structure is the forelimb of terrestrial vertebrates.
Analogous structures are structures with a similar function but no structural relationships, which therefore do not share a recent common ancestor. An example of an analogous structure is the wings of birds and insects.
Distinguish between species richness and species diversity.
Species richness is a measure of the numbers of species present and the evenness of species in relation to one another. Species diversity is a measure of the number of species, compared to the number of individuals found in a sample.
Consider the way energy and matter move through an ecosystem. Determine how they differ.
Energy enters an ecosystem by the producers and is not recycled. Energy is transferred through an ecosystem, with most of it being used by the organisms at each trophic level or lost as heat, and some of it transferred to the next trophic level. Unlike energy, matter is recycled in an ecosystem. Matter moves through an ecosystem via the feeding relationships. Decomposers release inorganic matter back into the ecosystem when they break down dead organisms.
Define J-Shaped population curve.
the graphical representation of the change in population density of an organisms as it increases rapidly and then stops suddenly, due to environmental or other factors.
Describe the possible consequences, in relation to the soil, associated with removal of vegetation.
When vegetation is removed, there is an immediate catastrophic effect on the biodiversity of the area. There is loss of food and loss of nesting sites for insects, birds and arboreal mammals. Those species that cannot relocate, perish.
Determine how Okazaki fragments are formed.
Okazaki fragments are formed on the lagging strand of replicating DNA by the DNA polymerase producing short sections of DNA from each primer.
Describe the processes of crossing over and recombination.
Crossing over is the breaking and rejoining, with exchange of DNA, between non-sister adjacent chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I. Recombination is the result of crossing over to produce gametes with differences in their genetic material.
Investigate other environmental factors that may have altered your gene expression.
Student answers may vary. Examples include UV radiation, exposure to toxic substances, and lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise.
When red shorthorn cattle are mated with white shorthorns, all of the offspring are roan (a combination of red and white). When two red cattle are mated they produce only red offspring. When two white cattle are mated they produce only white offspring. When two roans are mated, half of the offspring are roan, a quarter are red and a quarter white. Explain this phenomenon.
This phenomenon is due to codominance where the alleles for red and white are equally dominant and both show in the phenotype, giving rise to roan shorthorn cattle.
Explain the term ‘DNA profiling’.
DNA profiling is a technique used to identify the characteristics of an individual’s DNA by extracting and identifying the base-pair pattern of their DNA.
Describe possible causes for adaptive radiation.
Adaptive radiation is a form of divergent evolution where groups with a common ancestor accumulate mutations over time, resulting in new species. For this to occur, the common ancestor must have a key adaptation that allows the organism to evolve to exploit a new niche or resource. Possible causes for adaptive radiation would be a mass extinction that opens up niches previously occupied and changes in environmental conditions that open up new niches or a mutation in an allele providing a new trait.
Explain the similarities and difference between a pre-mating and a post-mating isolating mechanism.
Pre-mating mechanisms are factors that cause a species to mate with members of the same species and prevent mating occurring between members of different species. Post-mating mechanisms are factors that occur after mating, such as preventing the production of viable hybrids or affecting the hybrid reproducing. They both are isolating mechanisms that keep populations reproductively separated.
Distinguish between convergent and divergent evolution.
Convergent evolution is the development of similarities between species from different ancestral forms as a result of similar ecological roles and selective pressures. Divergent evolution leads to descendants becoming different in form from their common ancestor due to different selective pressures.
A survey of a wallum heathland ecosystem (approximately 50 hectares in size) showed that there were 15 species of birds. A total of 100 birds were counted. Calculate the species richness of this wallum heathland ecosystem.
S=s/sqrtN
S=1.5
Describe the roles of reservoir and cycling pools using an example from one nutrient cycle.
Water cycle: Reservoir pools are a non-biological source of an element that has relatively little turnover. In the water cycle, glaciers, polar ice caps and artesian basins are important reservoirs for water storage. Cycling pools actively exchange their contents between the environment and organisms. In the water cycle, transpiration, evaporation and precipitation are cycling pools.
Carbon cycle: Reservoir pools are a non-biological source of an element that has relatively little turnover. In the carbon cycle, carbon is stored in deep sea sediments below the Earth’s surface that act as reservoir pools. Cycling pools actively exchange their contents between the environment and organisms. In the carbon cycle, respiration and photosynthesis are cycling pools.
Distinguish between r-strategist and K-strategist
R- rapid reproduction, produces many offspring, no parental care
K-Slow reproduction, few offspring, parental care
Explain how the application of fertilisers to farmland can result in the death of organisms in nearby freshwater ecosystems.
Fertilisers can be washed by rain into waterways, increasing the concentration of nutrient ions in the water. This can cause a rapid population growth in water-based producers. This leads to oxygen deficiency during the night when those producers are not photosynthesising. This, in turn, leads to an increase in decomposer bacteria, which further decreases the oxygen levels of the water. Without oxygen, freshwater organisms cannot survive.
Analysis of a sample of DNA extracted from a tissue showed that 38% of the bases were adenine. Determine what percentage of the bases in the DNA would be guanine. Show how you arrived at your answer.
If there is 38% adenine, there is 38% thymine. This means that 24% of bases are guanine and cytosine – so therefore, 12% would be guanine.
Discuss the factors that result in genetic diversity in gametes and thus the genotypes and phenotypes of an individual
Factors that determine genetic diversity in gametes include: (i) independent assortment, where the hereditary factors assort independently during gamete production, giving different traits an equal opportunity to occur together; (ii) crossing over, which produces recombinant chromosomes; (iii) and lastly, spontaneous mutations.
Explain the difference between an inherited and an acquired mutation.
An inherited mutation is one that is passed from parent to child, is present throughout a person’s life, and is found in virtually all cells. An acquired mutation may occur at some point during a person’s life in their somatic cells and is therefore not passed onto offspring.
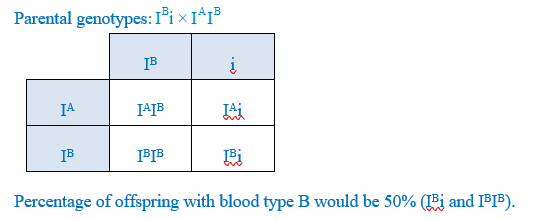
If a man with blood type B, one of whose parents had blood type O, marries a woman with blood type AB, determine the theoretical percentage of their children with blood type B.
A biologist working in the Daintree rainforest found a new species of orchid. Discuss techniques that could be employed to help classify this plant and place it in a phylogenetic tree.
The biologist should take a sample of the suspected new species of orchid. DNA could be extracted from the sample and amplified using PCR. DNA–hybridisation technique could be used to compare the DNA sequence against other known species of orchid to analyse degree of relatedness. Gel electrophoresis could be used with a particular DNA sequence and again compared to other known species of orchid to analyse any differences in fragment length. From the information gathered from these different techniques, the species could be placed in a phylogenetic tree.
Many zoos are attempting breeding programs to increase the numbers of endangered species. The aim of this venture is to release animals back into the wild once adequate numbers have been bred. Apply your knowledge of gene frequencies to analyse the inherent danger of such programs.
Student answers may vary. Endangered species will have a small gene pool. Zoos are taking a small sample of the species gene pool (founding population) and breeding from them. This means that the descendants of the breeding population will have a limited gene pool. When these individuals are released back into the wild (immigration), they may have an advantage over the original population and there will be a decline in the original population, or the opposite may occur and they will be disadvantaged in the environment. It is difficult to determine the outcome and therefore there is inherent danger with such programs.
Two trends in macroevolution are stasis and character change. Define these two terms and give examples of each.
Stasis is a block of little or no evolutionary change in a species. Coelacanths are a fish species that has experienced stasis for over 80 million years as seen by the modern coelacanth, which is similar to the fossilised forms from
80 million years ago.
Character changes are the changes in phenotype over time, rapidly or gradually. Trilobites have experienced character changes over a long period of time. Some trilobite species gradually increased in the number of body segments, while others rapidly gained and lost body segments over the same time period.
Explain the assumptions that underpin cladistics.
There are three basic assumptions that underpin cladistics:
• Any group of organisms are related by descent from a common ancestor.
• New organisms arise when existing populations divide into two groups.
• Changes in characteristics occur in lineages over time.
Identify three reasons why old growth forest ecosystems should be managed.
Old growth forest ecosystems are a storage of carbon due to the density and volume of wood. It is important to maintain such forests to ensure the continued uptake and storage of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
These forests are ecosystems with high biodiversity.
A number of animal species rely on these forests for the range of nesting hollows, variety of microclimates and greater structural complexity.
Explain the meaning of an ‘engineer’ when related to keystone species.
Particular keystone species can be described as ‘engineers’. This refers to species that ensure the continuance of a particular ecosystem through their behaviour.
Classify the following ecosystem:
Species A: 30m 40% coverage
Species B:28m 60% coverage
Species C: 12m 20% coverage

tall open forest
Urbanisation has created changes in climate that affect whole settlements and also microclimates within specific parts of them. Consider how this might occur and what environmental effects it might have.
Urbanisation can create changes in the climate. This could be due to increased air pollution, which can be trapped in an urbanised area and which increases the temperature. Concrete city surfaces absorb more heat during the day and rows of tall buildings can create wind tunnels that spread the heat further. Effects of this climate change are numerous, but one example is that plants bud and bloom earlier, and that some birds are attracted to this warmer area.
Explain what is meant by the ‘antiparallel strands of DNA’.
Antiparallel refers to the two strands of DNA running in opposite directions. One strand starts with the 3¢ end, while the other strand faces in the opposite direction at the 5¢ end.
An individual was found to exhibit trisomy of an autosomal chromosome. Propose how and when this condition arose.
A trisomy for an autosome can occur during anaphase I if the homologous chromosomes do not separate, or
anaphase II if the sister chromatids do not separate.
In multicellular organisms there are several post-transcriptional controls on gene activity. Identify these and describe the source of the controls.
Post-transcriptional modification includes several mechanisms. Introns are removed from the mRNA; however, if not done correctly, the resulting mRNA can be broken down by enzymes. Another mechanism is small non-coding RNAs binding to the mRNA, preventing translation. Lastly, the mRNA must leave the nucleus through the nuclear pores. This is an active process where receptors in the lining allow further control.
Define Barr Body
Barr body refers to the inactivated X chromosome in the cells of female mammals.
Describe the aims of the Human Genome Project.
The Human Genome Project aimed to map and analyse the nucleotide sequences of each of the 100 000 human genes. The project also aimed to examine the social, ethical and legal implication of the research.
Infer why some organisms survived more or less unchanged for millions of years, while others were evolving or becoming extinct.
Some organisms remained relatively unchanged for millions of years because they have a particular niche that has remained constant over time. Some organisms are continually evolving as the environment changes. This is because within the population certain traits have a selective advantage. Some organisms become extinct because the environmental conditions change and they may not have adapted well to survive and reproduce.
Critique, with examples, the circumstances under which divergent speciation could occur.
All types of speciation (allopatric, parapatric and sympatric) result in divergent speciation.
Allopatric species occurs when an initiating factor in divergent speciation is geographical separation. For example, the eastern and western grey kangaroos arose due to evolving in isolation in the eastern and western parts of Australia. Each group gradually expanded their range and stopped interbreeding.
Parapatric speciation occurs when mating in a population is not random and individuals at one end of the range are unlikely to mate with individuals at the other end. There is reduced gene flow but not total isolation. An example is seen in Australian oaks. Neighbouring populations of Australian oaks became distinct while sharing a common border where limited hybridisation occurs. This leads to three distinct species diverged from one common ancestral species.
Sympatric speciation occurs when a population of a species becomes reproductively isolated while in the same habitat. This occurs most commonly through polyploidy in plant species or parthenogenesis in animals. For example, durum wheat has four sets of chromosomes and bread wheat has six sets of chromosomes. These species are likely to have diverged from a common ancestor due to sympatric speciation.
Both hypothetical phylogenetic trees below show that the human is more closely related to the chimpanzee than it is to the gorilla and orangutan. Tree a is based on overall similarities resulting from plesiomorphic characteristics. Tree b is based on apomorphic characteristics. Deduce which of these trees is a cladogram. Give reasons for your answer.
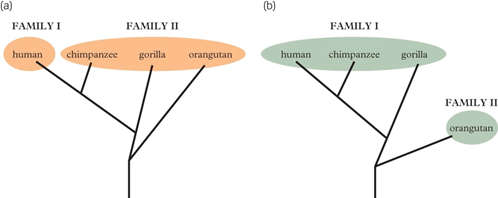
Both trees are cladograms. A cladogram is a branching diagram showing the evolutionary relationship between a number of species.
A soil has been identified as a clay loam. It has a composition of 40% silt, 30% clay and 30% sand. Determine where within the clay/loam dimensions of the grid you place this soil.
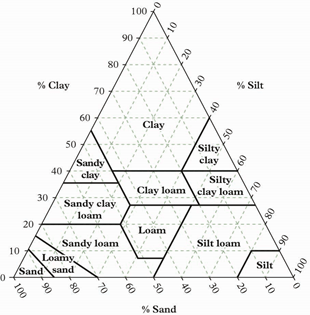
A soil with a composition of 40% silt, 30% clay and 30% sand would be in the middle in the clay loam classification.
Herbivores have generally been considered to have a negative impact on their plant prey. However, a controlled study of a natural community provides evidence to the contrary. The crustacean herbivore Daphnia pulex was fed on planktonic algae, and it was shown that the Daphnia had a stimulatory effect on the algal populations that approximately balanced its impact on algal mortality. Predict, with justification, mechanisms for the Daphnia-induced stimulation of algal growth.
Student answers may vary. One possible prediction could be that Daphnia and the algae have a mutualistic relationship in which the Daphnia obtains a source of energy from the algae, and the algae receives nutrients from the Daphnia excretion for energy transformation reactions.
The data below was collected as a result of concerns over the numbers of kangaroos in particular areas and the possibility of overgrazing. On the basis of this data, which area is in most need of culling? Justify your answer from calculations of the data.
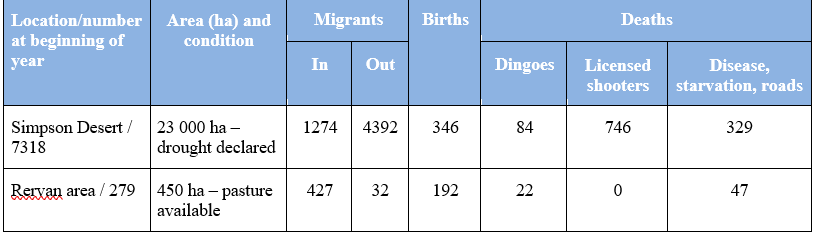
Due to a positive population rate in the Rervan area, the population in this area is in need of culling. The Simpson Desert population is decreasing rapidly per year.
Distinguish between a primary and a secondary air pollutant.
A primary pollutant is a substance that has a direct adverse effect on the environment (for example, smoke), whereas a secondary pollutant is formed as a result of the interaction between wastes and the environment (for example, smog).
Bacterial cells were supplied with nutrients that contained radioactively labelled nitrogen. After division, the DNA strands of the daughter cells were found to contain labelled nitrogen. These daughter cells were then fed on normal food and, when they in turn divided, it was found that only half of the ‘granddaughter’ cells they produced contained DNA with radioactive nitrogen atoms. Justify an explanation for this finding.
This is due to semiconservative replication in which the replicated DNA contains one strand of the original DNA (containing radioactive nitrogen) and one new strand. Therefore, after each division there would be half as much radioactive nitrogen.
Two allelic versions of different genes were found to always be inherited together. Propose a conclusion about their relative positions on the chromosome.
These alleles must be very close to one another on the chromosome so that crossing over is unlikely to occur between the alleles.
Distinguish between a somatic and germ line mutation and state how these types of mutations differ in their effect on the next generation.
A somatic mutation is when the mutation occurs in a somatic cell (body cell). When this happens, it doesn’t affect the entire organism, just the one cell and the cells it gives rise to during replication. A germ line mutation is when the mutation occurs in a gamete (egg or sperm) and if this cell is fertilised, then the entire organism is affected.
The diagram below represents a family pedigree showing the inheritance of phenylketonuria (PKU), a fatal disease where urine is black and which is controlled by a single pair of alleles, A and a. Use this pedigree to determine whether the allele for PKU is dominant or recessive.
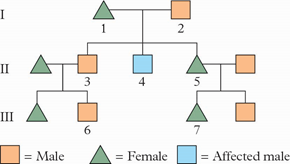
The allele for PKU is recessive due to individuals 1 and 2 not being affected but having an affected son 4.
The figure below represents the DNA fingerprint of a girl (A), her parents, her sister and a number of other individuals, two of whom are brothers and are unrelated to the first family. Any band present in the DNA fingerprint of a child must also be present in at least one of the parents. Identify the parents of girl A.
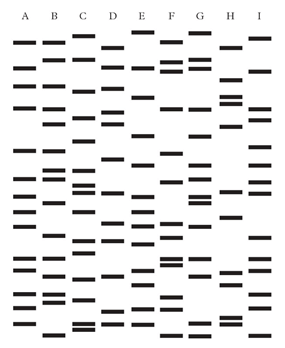
The parents are bands B and E.
Explain the conditions under which the ‘founder effect’ could occur in a population. Describe the possible long-term consequences of this.
The founder effect can occur in a population if a small subgroup of the original (parent) population colonises a new area. This subgroup will have a limited number of different alleles compared to the original population, and hence a small gene pool. The long-term consequences are the vulnerability to possible changing environmental conditions in the future; for example, the introduction of a disease may affect almost all individuals of this colonising population.
Explain how a genetic bottleneck could occur.
A genetic bottleneck may occur due to natural disasters such as bushfires and floods or because of habitat destruction by humans, where the population is reduced dramatically.