Anyone who, by virtue of assumed role or assigned responsibility, inspires and influences people to accomplish organizational goals
Army Leader
The flexibility of mind, a tendency to anticipate or adapt to uncertain or changing situations.
Mental Agility
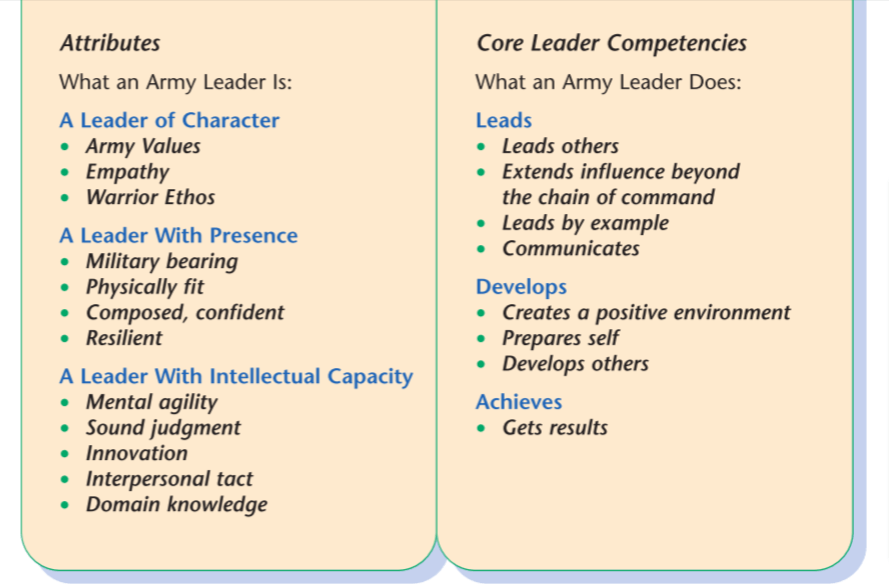
The Leadership Requirements Model
The extent to which you specifically define the duties and responsibilities of an individual or group. Examples include directing Soldiers on what to do, how to do it, and when to do it.
Task Behavior
A defining moment that unleashes abilities, forces crucial choices, and sharpens focus.
Crucible Experience
This informs everything you do and ask others to do. You demonstrate your commitment to this and to a leadership role in the Army by adopting and living the seven Army Values and the leader attributes.
Character
The ability to introduce something for the first time - producing ideas that are original and worthwhile.
Innovation
Focuses on leaders’ and followers’ self-interests. Involves an exchange in which followers work to receive benefits or to avoid penalty or punishment.
Transactional Leadership
The extent to which you engage in two-way or multidirectional communication with your subordinates. Includes listening, facilitating, praising, collaborating, counseling, consulting, and other socially and emotionally supportive actions.
Relationship Behavior
The ability to identify and seize opportunities. It allows leaders to act and then evaluate results instead of attempting to collect and analyze all the data before acting.
Adaptive Leadership
These leaders influence their subordinates one-on-one, but may still guide the organization through subordinate officers. They quickly see what works, what doesn’t work, and how to address problems.
Direct Leaders
Interacting effectively with others means being able to see things through their eyes. It requires accepting the character, reactions, and motives of others as being just as valid as yours.
Interpersonal Tact
Motivate soldiers to share a vision of success. These leaders reject self-interest for the greater good.
Transformational
Refers to the knowledge, experience, and skill a Soldier (or unit) brings to a particular assignment or activity. More specifically, it includes knowledge, or the demonstrated understanding of a specific task.
Ability
Two critical aspects that are the foundation of adaptive leadership.
Training & Education
Loyalty, Duty, Respect, Selfless Service, Honor, Integrity, & Personal Courage
The Seven Key Army Values
Army leaders are mindful of cultural factors in these three contexts:
Team Members, Countries, & Partners
Idealized influence, Inspirational Motivation, individualized Consideration, and Intellectual Stimulation.
The four main elements of transformational leadership.
The degree to which a Soldier or the unit shows confidence, commitment, and motivation to accomplish an assigned activity.
Willingness
Adaptive leaders exhibit this characteristic under pressure.
Poise
The mental resources or tendencies that shape a leader’s conceptual abilities and impact effectiveness are (name all four factors):
Mental Agility, Sound Judgement, Innovation, & Interpersonal Tact
The art and science of employing available means to win battles and engagements. The science includes capabilities, techniques, and procedures that can be codified.
Tactics
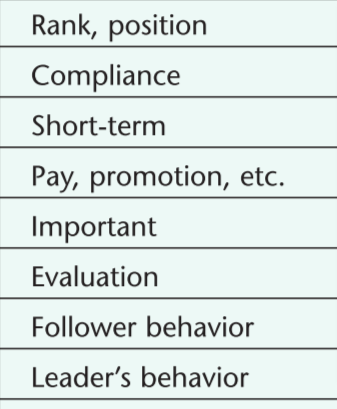
Characteristics of Transactional Leadership
Identify the four basic leadership styles based on task behavior and relationship behavior.
Directing, Coaching, Supporting, and/or Delegating.
Adaptive leaders focus on seven critical issues.
Knowledge of Self and Soldiers, Mission and Intent, Environment, Education/Experience, Leadership Style or Decision, Communicating/Motivating, and Results/Consequences