
Name ONE of the causes of the French Revolution.
1. Unpaid debt of the US following the American Revolution
2. Volcanic eruption leading to harsh weather/ poor crops
3. Inflation and unfair taxation
4. Lavish lifestyles of the rich & famous while the 3rd Estate struggled

a sudden overthrow of the government
coup d’état
The countries defeated by Napoleon and forced to join his struggle against Britain became...

allied states
belief that people should be free from government restraint
liberalism
This word means "unable to be taken away."
unalienable
The French Revolution entered an increasingly radical phase after

the execution of King Louis XVI.
the political club that was most influential in passing the decree to condemn Louis XVI
 the Mountain
the Mountain
unique cultural identity of a people
 nationalism
nationalism
belief in tradition and social stability
conservatism
This word means "rule by a small group."
This movement influenced both the bourgeoisie and the nobles before the French Revolution.
the Enlightenment

a person qualified to vote in an election
elector
Napoleon’s new government after 1799
the consulate

led British and Prussian armies’ defeat of Napoleon

Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
Justice is to law codes as __ is to citizenship.
nationalism
The economic crisis that triggered the French Revolution was caused in part by

inflation and widespread unemployment.
policies of the Committee of Public Safety to defend France from domestic threats

Reign of Terror
Kingdoms ruled by Napoleon’s relatives would be referred to as this...
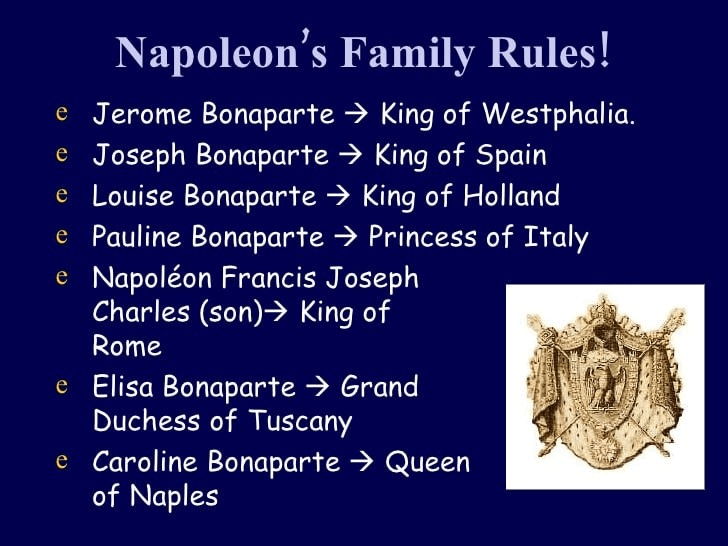 "dependent states"
"dependent states"
a conservative Austrian statesman and diplomat who was at the center of European affairs for three decades as the Austrian Empire's foreign minister, he was the most influential leader at Congress of Vienna
Klemens Wenzel Nepomuk Lothar, Prince of Metternich-Winneburg zu Beilstein (aka: Klemens von Metternich)
During Napoleon's 1798 campaign in Egypt, a corps of 167 technical experts (savants) accompanied the French expeditionary army to Egypt. They spotted THIS slab written in three ways: hieroglyphics, which were used mainly by priests; Demotic, a somewhat simpler script used for everyday purposes; and ancient Greek-- & rightly suggesting that the 3 inscriptions were of the same text.
the Rosetta Stone
(la Pierre de Rosette)

Also known as the Old Regime, this was the political and social system of the Kingdom of France before the Revolution of 1789.

Ancien Régime

executive under the Constitution of 1795
Directory
Napoleon’s unified system of law
Napoleonic/ Civil Code
The Russians defeated Napoleon’s Grand Army by

Scorched Earth:
retreating hundreds of miles and burning their own villages and countryside.
After Napoleon’s defeat, European rulers met at the Congress of Vienna in September 1814 to arrange a final peace settlement. Claiming to be guided by the principle of __, Metternich supported returning power to the lawful __ who had ruled before Napoleon.
legitimacy; monarchs