Correctly identify the 5 colors location for lead placement in the 5 lead ECG
White (UR) Green (LR) Black (UL) Red (LL) Brown (Midline)
Sinus tachycardia and decreased cardiac output is related to which ventricular factor?
Decreased fill time
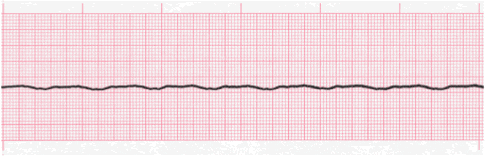 What should you do when you see this on the monitor of a unresponsive pulseless patient?
What should you do when you see this on the monitor of a unresponsive pulseless patient?
Start chest compressions.
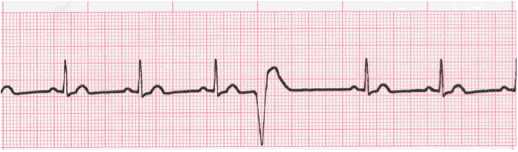 Interpret the rhythm.
Interpret the rhythm.
NS with PVC's
Before inserting an IV, what should the nurse consider for the patient.
Planned therapy for the IV.
A patient in sinus bradycardia is hypotensive and dizzy. What condition are these symptoms associated with
Decreased cardiac output.
When monitoring a densely hairy male patient, what intervention by the nurse with improve conduction?
Clipping or shaving the dense hair where the leads will be placed.
What heart block is identidfied in the rythym below.
Second-Degree type I (Wenckebach)
What is the normal distance of the PR interval in NSR?
0.12-0.20 seconds
Before removing an NG tube, what action should be taken by the nurse.
Complete abdominal assessment.
What should the nurse do after noticing a patient on 5 lead telemetry in first degree heart block.
Monitor closely for a more serious block or possible progression.
Trace the conduction system on a healthy heart beat starting at the SA node
SA node -> AV node -> Bundle of HIS -> L and R Bundle Branches -> Purkinje Fibers
Describe the rhythm above:
Atrial rate is faster than the ventricular rate
Normal p waves
Gradually lengthening PR Intervals
Dropped QRS complexes
QRS <0.12 seconds
During a type I second degree AV block, what occurs in the PR interval?
Drop in the QRS due to progressive lengthening of the PR interval
Best time to remove the tourniquet after inserting the PIV?
Immediately after advancing the catheter.
Which complex characteristics during PVC's make them dangerous (2)
Multiformed with increased frequency
What is the treatment of choice for a patient admitted for an MI with increasing PVC's?
Defibrillation/Cardioversion
Identify the interpretation of the strip.
Atrial flutter
What can b causes of a Third-Degree Heart block?
Congenital heart disease, Digoxin Toxicity, Heart valve damage, worsening heart block
Which important step should be taken before removing an NG tube to prevent aspiration?
Flush a small bolus of air in the tube.
A nurse caring for an MI patient notes and increased HR of 200 beats with decreased cardiac output and SOB. What ifs the priority action.
Apply oxygen to the patient.
 Which phenomenon is this
Which phenomenon is this
R on T
Identify the hallmark of a rhythm strip on a patient with Atrial fib or flutter
Sawtooth baseline
If someone has ischemia of the heart, how with the T wave be interpreted?
T wave inverted after the QRS complex
What are some symptoms of speed shock
Facial flushing and chest tightness