This neurotransmitter is responsible for the overstimulation of neurons in the brain and can cause brain damage.
What is glutamate.
This part of the brain, which only makes up 1% of the brain's mass, regulates autonomic functions such as appetite, hunger, sleep and body temperature.
What is the hypothalamus?
The opening of ligand-gated ion channels is regulated by this.
What is neurotransmitters?
Starting with dendrites, these are the 5 major parts of a typical CNS neuron in order.
Dendrite, cell body, axon hillock, myelinated axon, axon terminal.
Communication BETWEEN neurons is this type of process.
What is chemical?
Damage to this part of the brain can cause issues with impulse control, inappropriate behavior, and issues with memory and planning.
What is the frontal lobe?
This structure in the brain plays a major role in development of memories and its volume is decreased in various in psychiatric disorders such as PTSD, AD, and MDD.
What is the hippocampus?
Serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, belong to a group of neurotransmitters called this.
What are monoamines?
An area of the neuron with many voltage gated Na+ channels from which action potentials originate.
What is the axon hillock?
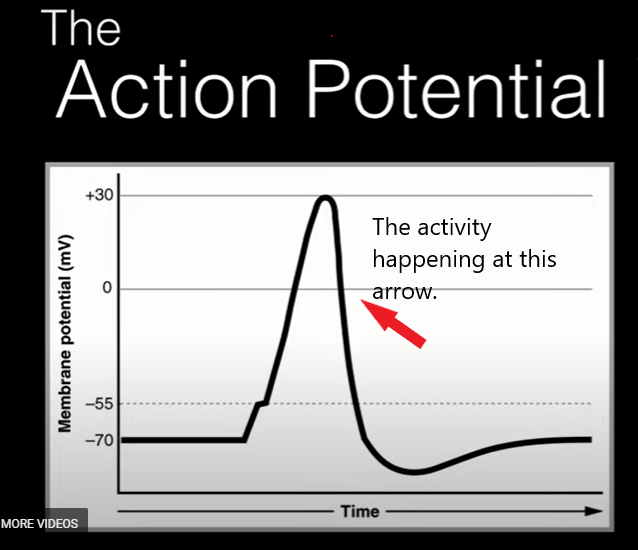
What is K+ efflux causing repolarization?
A disorder that affects the left frontal lobe and speech.
What is Broca's aphasia?
Antagonism of dopamine in the nigrostriatal pathway can lead to this troubling side-effect.
What are extrapyramidal symptoms?
True or false: The prefrontal cortex has an abundance of dopamine reuptake pumps.
What is false.
You would find VMAT2 inhibitors in this area of a neuron.
What are vesicles in the axon terminal?
When postsynaptic receptors are bound by a ligand and allow negative ions in, the cell becomes depolarized. This is considered an ______ potential.
What is an excitatory potential. (Positive ions are inhibitory because they make the cell depolarized).
This part of the brain plays a central role in the experience of anger and anxiety.
What is the amygdala?
This pathway is believed to be involved in the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
What is the mesolimbic pathway?
This neurotransmitter is the major inhibitory transmitter in the brain. Some might call it the "brakes" of the car.
What is GABA?
This structure of the neuron has been dubbed the telephone wire of the brain and can transmit a signal quickly without degradation to other neurons or end organs.
What is the axon?
This type of agonist binds to the receptor and causes it to open more frequently than resting state, but less frequently than full effect.
What is a partial agonist?
The pathologic basis of autism and schizophrenia may be explained by disordered ______.
What is synaptic pruning?
(too much in schizophrenia, not enough in autism)
The sympathetic division of the nervous system originates in this part of the brain.
What is the posterolateral zone of the hypothalamus?
Dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are this type of monoamine.
What is a catecholamine?
Ion channels on the surface of cell membranes in this region of the neuron (sometimes referred to as the "ear" of the neuron open in response to ligand binding?
What are the dendrites?
The opening of voltage-sensitive ion channels is regulated by this.
What is the charge across the membranes?