This is the name given to the charge -70mV where a neuron spends the majority of its time waiting for stimuli.
Resting Potential
This type of cell is known to help regulate the nutrition of neurons by facilitating transport from blood vessels to neurons
astrocytes
This region of the brain is responsible for coordinating movement and balance.
Cerebellum
ascending tract
Effector
This type of cell membrane gate responds to changes in electrical potential to open and allow select ions through.
Voltage-gated ion channel
What is the scientific sounding name for the process carried out by microglial cells
phagocytosis
This name is given to the piece of tissue to which the pituitary gland attaches
Infundibulum
This layer of the meninges is formed largely of fibrous connective tissue that protects the spinal cord
Dura Mater
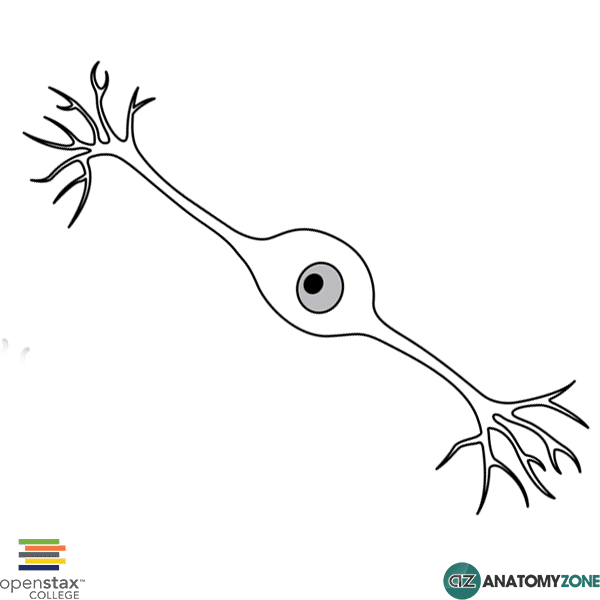 This type of neuron classified by shape.
This type of neuron classified by shape.
Bipolar
This is the voltage at which sodium voltage gates open
-55mV
Schwann Cells are responsible for producing myelin in what area of the body
Peripheral Nervous System
This region of the brain is responsible for both auditory and visual memory
Temporal Lobe
This region of the spinal cord is found between two layers of meninges and is filled with CSF
Subarachnoid space
At the synapse this type of molecule ends up passing impulses from one neuron to the next.
neurotransmitter
Action potentials are kicked off by a series of events at the synapse. The first event occurring at the post-synaptic neuron involves the movement of what molecule?
sodium ion
This molecule produced by several different neuroglial cells is responsible for speeding up signal transduction
myelin
The primary motor areas are found in the frontal lobe just anterior to this brain landmark
Central Sulcus
This structure contains many of the blood vessels that nourish the brain and spinal cord
pia mater
Multiple Sclerosis is a type of degenerative disease that destroys the myelin wrapped around neurons. What is one direct outcome of this.
slower signal transduction
Describe why the neuron has an all-or-none response.
This structure can be used to quickly differentiate between oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
Neurilemma
This piece of tissue divides the brain into hemispheres
corpus callosum
This region marks the point where spinal nerves branch off and lead to the arms
Cervical Enlargement