
Anterior STEMI
Lifestyle modification to reduce risk for atrial fibrillation
Weight loss
Drug treatment of HF-related cardiogenic shock
Dobutamine or milrinone
Symptomatic Disease
Indication to treat someone Hypertensive in the hospital with IV medications
Hypertensive Emergency (End Organ Damage)

Acute Pericarditis
Treatment for idiopathic Pericarditis
NSAIDS plus Colchicine
QRS measurement that best predicts benefit from cardiac resynchronization therapy
QRS >150 msec
Severe aortic stenosis mean gradient
>40 mm Hg
According to ACP, patients who are low risk for PE/DVT should be evaluated with this criteria prior to ordering a D-Dimer
The PE rule out criteria (PERC)

Third Degree AV Block
Primary CV side effect of bevacizumab
Hypertension
Therapy for patients with end-stage heart failure who are not candidates for heart transplantation
Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD)
Valve abnormality associated with aortic coarctation
Bicuspid aortic valve
Indication for oxygen in patients with chest pain or acute MI
A: SpO2 is <90%.
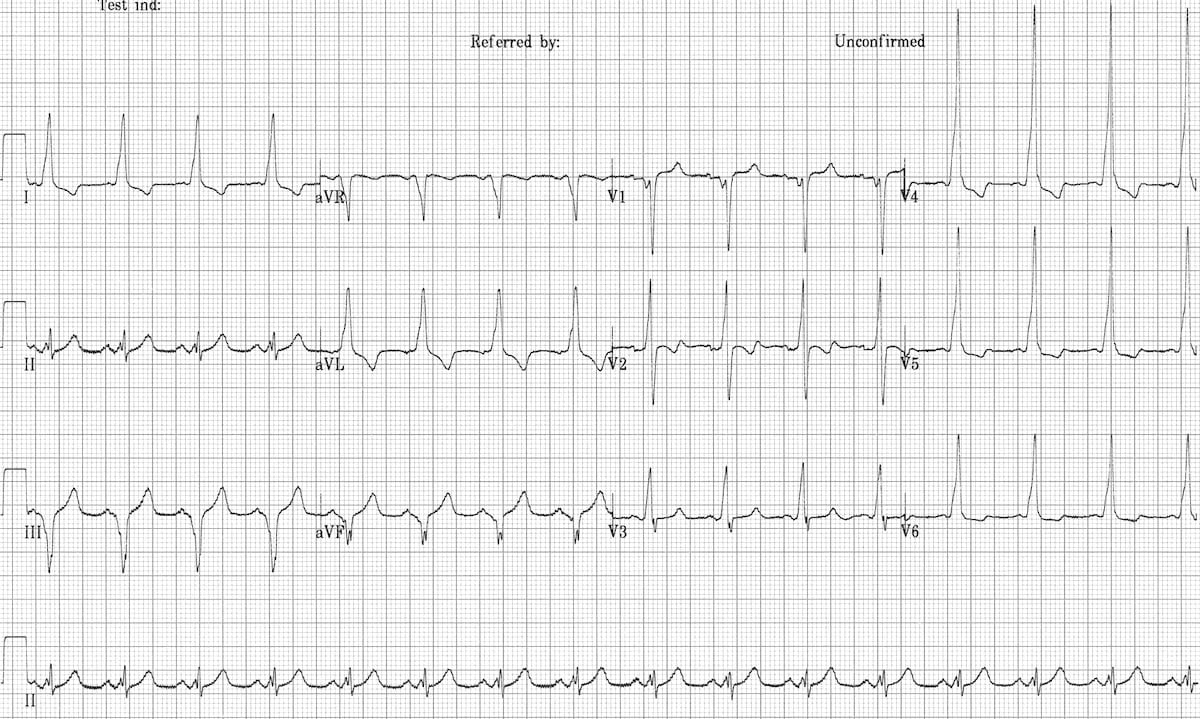
WPW
A treatment option for patients with high thrombotic risk and atrial fibrillation who are not candidates for long term anticoagulation
Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (Watchmen Device, Surgical Closure)
First-line drugs for symptomatic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Nonvasodilating β-blockers (not carvedilol, labetalol)
Early surgery for IE should be considered for patients with which conditions (name 3)
heart failure
annular or aortic abscess
heart block
recurrent emboli on appropriate antibiotic therapy
infections resistant to antibiotic therapy
fungal endocarditis
persistent infection (>5-7 days)
For most patients not at increased ischemic/thrombotic risk with Atrial Fibrillation who undergo PCI when can Aspirin be discontinued
At hospital discharge

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Indication for revascularization of unilateral renal artery stenosis
Failure of optimal medical therapy to control the blood pressure, Intolerance to optimal medical therapy, Recurrent flash pulmonary edema and/or refractory heart failure
Echocardiogram Characteristics of Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
biatrial enlargement and severe diastolic dysfunction in the setting of normal ventricular size, wall thickness, and systolic function.
Most common valvular disorder associated with tetralogy of Fallot repair
Pulmonary valve regurgitation
Name an indication to order an echocardiogram in a patient with syncope
history of cardiac disease, examination suggestive of structural heart disease or congestive heart failure, abnormal ECG, or abnormal cardiac biomarkers.