9 month old with nasal discharge and congestion past 3 days presenting to the ED with fever of 101.5, barking cough, increased respiratory efforts.
PE significant for mild subcostal retractions and inspiratory stridor at rest
What is croup?
4 year old with congestion, rhinorrhea, dry cough for past 3 days and diarrhea x2 days
PE: erythematous posterior oropharynx, clear nasal discharge.
Vitals stable
Diagnosis?
What is: viral/ common cold
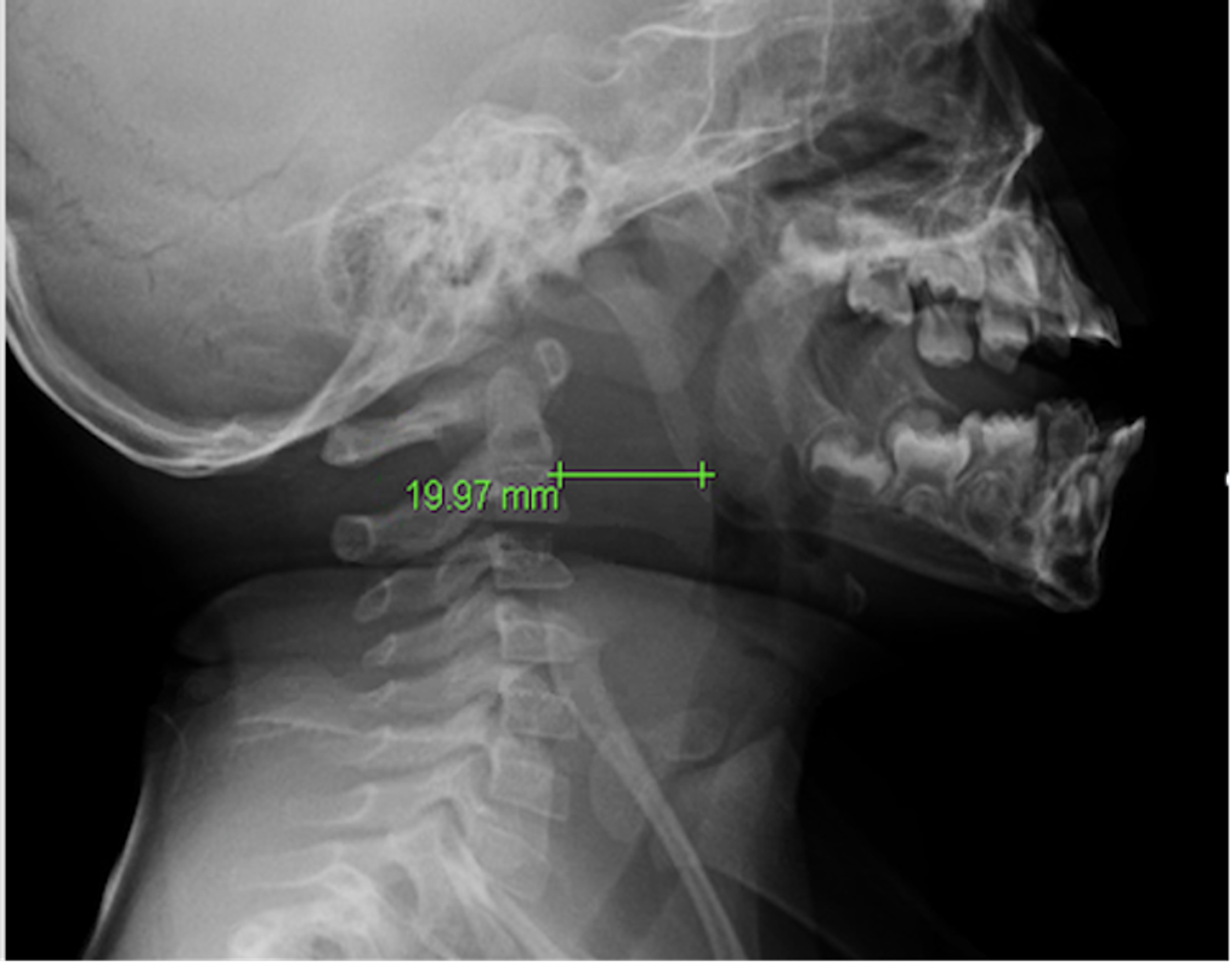
Diagnositic imaging of croup
What is clinical, no imagining necessary?
Treatment for pharyngitis with CENTOR score >4
What is Amoxicillin or Penicillin
Bacterial isolates of bacterial tracheitis
What is S Aureus, S pneumonia, GAS, Moraxella
Clinical features of epiglottis
What is: respiratory distress, anxiety, tripod or sniffing position, stridor, drooling, change in voice, toxic appearance
PE red swollen epiglottitis
CENTOR SCORING
What is:
Cough (absent) +1
Exudates +1
Nodes +1
Temp >38 C +1
OR age <14 +1 OR age >44 -1
diagnostic imagining for retropharyngeal abscess
What is lateral neck radiograph an/or CT with contrast of neck.
Treatment for bacterial tracheitis
Microbiology for retropharyngeal abscess
12 year old with rapid onset fever of 104.5, appears anxious, difficulty swallowing for 3 days, neck pain, decreased oral intake.
Physical exam noticeable for saliva pooling, enlarged anterior cervical LN
What is retropharyngeal abscess
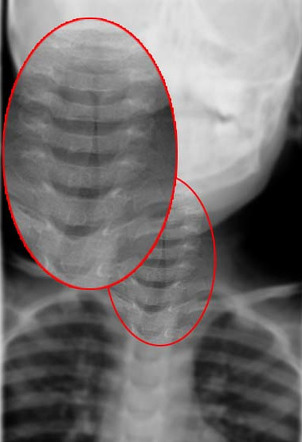
What is bacterial tracheitis or croup
Treatment for patient with suspected suspected retropharyngeal infection and signs of severe airway obstruction
What is: secure airway followed by surgical incision and drainage
what is anterior boundary is middle layer of deep cervical fascia
posterior boundary is deep layer of deep cervical fascia
Child with respiratory distress with acute onset of fever, inspiratory stridor, pain with swallowing and hoarseness of voice
Diagnosis for epiglottitis
What is clinical
If no other diagnosis established & unable to visualize the epiglottis direct visualization with fiberoptic nasopharyngoscopy or indirect laryngoscopy preferred OR soft tissue lateral neck radiograph
thumb print sign on xray
epiglottitis
Treatment for mild croup
What is single dose of oral dexamentahsome (0.15mg-0.6mg/kg)
Infectious etiology of epiglottis besides Hib
What is:
S. Aeurus ( MRSA), S. Pneumo, Strep pyO, Nisseria, Pausterlla
Unilateral mucupurelent nasal dischage past week with mouth breathing in 2 year old
Definitive diagnosis of bacterial tracheitis
soft tissue lateral neck radiograph in patient with epiglottitis findings
thickened epiglottis or aryepiglottic folds
Treatment for moderate to severe croup
What is racemic epinephrine
What is supportive care: oxygen or humidified ai, antipyretics and encourage fluid intake