What is critical temperature?
The temperature beyond which a gas cannot be compressed.
State Raoult's Law and formula
Raoult’s law states that a solvent’s partial vapor pressure in a solution (or mixture) is equal or identical to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution. Psolution = ΧsolventP0solvent
Which deviation does minimum and maximum azeotrope pair with? positive or negative deviation
Positive deviation correlates with minimum azeotropes. Negative deviation correlates
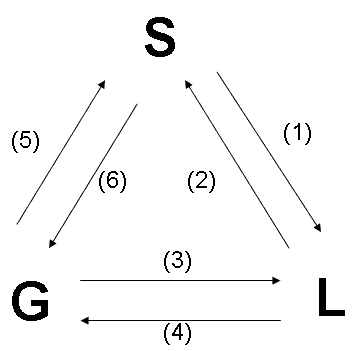
States Henry's Law and formula
Partition coefficient is dependent on:
Polarity of solute
Its molecular weight
Relationship to the polarity of solvents
Why is the boiling point of some liquids lower at a higher altitude?
This is because at higher altitudes pressure decreases. There is not a lot of atmospheric pressure stopping the vapor from escaping.
Describe an ideal solution.
An ideal solution is a mixture in which the molecules of different species are distinguishable, however, unlike the ideal gas, the molecules in ideal solution exert forces on one another. When those forces are the same for all molecules independent of species then a solution is said to be ideal.
Which liquid has the greater composition at the azeotrope?

X
What does the amount of a gas which dissolves in a liquid depend on? (3)
The nature of a gas and the liquid
The temperature
the partial pressure of the gas over the liquid
What is partition coefficient?
It is the ratio of the concentration of a solute in the organic phase to its concentration in the water phase.
Fill in the blanks on the phase change
1) Melting
2) Freezing
3) Condensation
4) Vaporization
5) Deposition
6) Sublimation
Name the three types of liquid solution in liquid.
Complete Miscible liquid
Half miscible liquid
Immiscible liquid
What is an Azeotrope?
it is a mixture of two or more liquid whose proportion that cannot be separated by simple distillation.
What are limitations of Henry’s Law?
This law is only applicable when the molecules of the system are in a state of equilibrium. Henry’s law does not hold true when gases are placed under extremely high pressure.
Calculate the partition coefficient of caffeine in water/methylene chloride from the following data: 10.3 g/100 mL for methylene chloride and 2.04 g/100 mL for water.
K = (10.3g/100mL) / (2.04g/100mL)
K = 5.049019608
K = 5.05
What does 'boiling point' mean? What is 'normal boiling pressure'?
The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
The normal boiling point is the temperature at which its vapor pressure is 760 torr.
Calculate the expected vapor pressure at 25° C for a solution prepared by dissolving 97.4g of common table sugar (sucrose C12H22O11. MW=342) in 453 mL of water. At 25° C the density of water is approximately 1.00g/mL and the vapor pressure is 23.76mm of Hg.
We will use Raoult's law in the form
PSOLN=XH20P° H2O
We need to determine the mol fraction of water
97.4g (1mol/342g)=0.285
435mL(1.00g/1mL)(1mol/18g)=25.2mol H2O
XH2O= 25.2mol/(25.2mol+0.285mol)
XH2O= 0.989
PSOLN=.989 (23.76mm)=23.5mm of Hg
What is fractional distillation?
Why does the solubility of gases in liquids depends upon pressure?
Since the gases are highly compressible, their solubility in liquids is highly influenced by pressure changes.
Calculate the partition coefficient if the concentration of solute in the stationary phase is 9 M and 5 M in the mobile phase.
Solution: We have, Cs = 9 Cm = 5
Using the formula we get, Kd = Cs/Cm = 9/5 = 1.8
Fill in the blanks on the phase diagram.
a) Solid phase
b) Liquid phase
c) Gas phase
d) Sublimation
e) Triple Point
f) Evaporation
Calculate the vapor pressure of a mixture containing 252 g of n-pentane (Mw = 72) and 1400 g of n-eptane (Mw = 100) at 20° C. The vapor pressure of n-pentane and n-eptane are 420 mm Hg and 36 mm Hg respectively.
Calculation of molar fractions (x)
moles n-pentane = 252/72 = 3.5
moles n-eptano = 1400/100 = 14
Totals = 3.5 + 14 = 17.5 moles
xn-pentane = 3.5/17.5 = 0.2
xn-eptane = 14/17.5 = 0.8
Thus
Pn-pentane = 0.2 x 420 = 84 mm Hg
Pn-eptane = 0.8 x 36 = 28.8 mm Hg
and the vapor pressure of mixture is
Pmixture = 84 + 28.8 = 112.8 mm
Fill in the blank (TO BE PASSED OUT)
ON HAND
Calculate the concentration of a helium gas dissolved in water, if the partial pressure of the gas is 4 atm and the value of henry’s law constant, k = 15 L atm/mol.
Given data:
Concentration of a dissolved gas, C = ?
Partial pressure of the gas, P = 4 atm
Henry’s law constant, k = 15 L atm/mol
Using the equation of henry’s law,
C = k P
C = 15 × 4
C = 60 mol/L
An aqueous solution has an iodine concentration of 2.00 x 10-3M. Calculate the percentage of iodine remaining in the aqueous phase after the extraction of 0.100L of this aqueous solution with 0.050 L of CCl4 at 25° C
The number of Moles of I2 present is:
(2.00 x 10-3 mol L-1)(0.100L) = 2.00 x 10-4 mol
Suppose that y mol remains in the aqueous phase and (2.00 x 10 -4 - y)mol passes into the CCl4 phase. Then,
[I2]CCl4/[I2]aq= K = 85
=[(2.00 x 10-4 - y)/0.050]/[y/0.100]
= 2(2.00 x 10-4 - y)/y
Note that the volumes of the two solvents used are unchanged because they are immiscible. Solving for y gives
y=4.6 x 10-6 mol
The fraction remaining in the aqueous phase is (4.6 x 10-6)/(2.0 x 10-4) = 0.023, or 2.3%. Additional extractions could be carried out to remove more I2 from the aqueous phase.
