Name 3 things an elephant and a bacteria have in common.
Check the Unit Wall poster of Characteristics of Life for Answer.
Cells
What is the first main point of cell theory?
All Living Things are made of one or more cells.
Homeostasis is an organism's way of maintaining a stable _________ _______________.
Internal Environment
During the process of _______________, the macromolecules in our food are broken down into their monomers.
Digestion!
What is a characteristic of life that is on another list but not on ours?
movement, adaption, evolution,...
What do organs make up? Name one example (100 pts each).
Organs make up organ systems like the Digestive System, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System,...
BRICKS! Cells are the basic building block of organisms, like bricks are the building blocks of buildings. This is the second part of Cell Theory.
What does "-Stasis" mean as a suffix?
"-Stasis" = Staying in Place
Food can be used for __________ or __________. (100 pts each)
Energy or Growth
What is an example of a living thing that does not have all of the characteristics of life?
Someone who is infertile, someone in a coma, viruses could be argued...
What is another name for macromolecule?
Polymer!
Where do new cells come from?
Other Cells! This is the 3rd point of Cell Theory. All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division and the passing of genetic material from parent to offspring.
Name 3 examples of internal conditions maintained through negative feedback. (100 pts for each)
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, Blood Glucose, Body Temperature, Blood pH, water retention,...
Metabolism is the process of getting energy from the __________ obtained during digestion.
Monomers!
Name two types of single-celled organisms. (200 pts each)
Bacteria, Archaebacteria, some protists like Amoeba, some fungi
Polymers and monomers are examples of ______________.
Molecules!
What is the scientific name for cell division used to make new body cells?
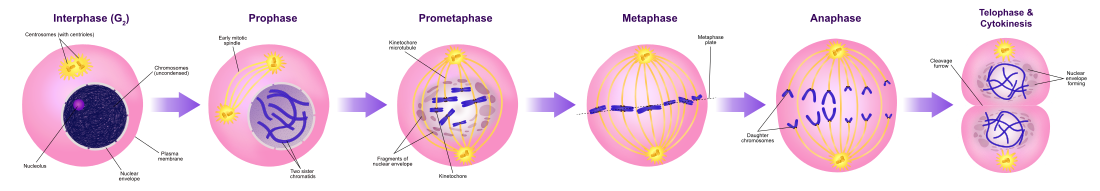
*This question is not covered on the test.
Mitosis!
What kind of feedback does this graph represent AND what is one thing controlled by that type of feedback?

Positive Feedback
(Breast Milk production, platelets clotting, uterine contractions...)
__________________ is used for growth because it is the process of putting monomers back together to make new macromolecules.
Biosynthesis
How many domains of life are there?
3
Name 1 type of macromolecule and the monomers that make them up.
* This question is not covered on the test. (It will be on the next test :))
Carbs - Sugars
Proteins - Amino Acids
Lipids - Fatty Acids & Glycerol
Nucleic Acids - Nucleotides
What is the name of the scientist that observed a piece of cork in a microscope, noticed box-like structures, and called them "cells"?
*This question is not covered on test.
Robert Hooke
Please explain why maintaining homeostasis is a Characteristic of Life.
Why would our bodies want to break down macromolecules in digestion just to build them back up again in biosynthesis?
The macromolecules we take in through out food might not be the right kind or in the right form that we need to build the structures of our bodies. So, we reduce the macromolecules to the monomers, reuse the monomers for new macromolecules, essentially recycling them for our own use.