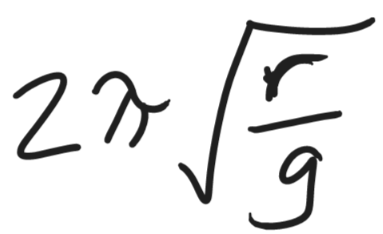The velocity component that is zero at the highest point in a basketball's arc.
Y velocity
The velocity of a free-falling object 4 seconds after its velocity was 10m/s.
-30m/s
"Opposite"/"hypoteneuse"
Sine
The direction of the resultant...
Eastward
The direction of acceleration for an object traveling in a circle at a constant speed.
toward the center
This velocity vector has the same initial, final, and average values.
X velocity
Distance fallen by a dropped ball after 6 seconds.
180m
"opposite"/"adjacent"
Tangent
In a typical river problem, one of the three vectors is not the actual velocity of anything, and this is how that vector is described.
Speed in still [water] and heading
or
[water] speed and heading
When a string is causing a ball to travel in vertical circles, this is the tension in the string at the top, in terms of the m (ball's mass), v (ball's speed), and r (radius of the circles)
mv2/r -mg or m(v2/r -g)
Of v, vx, and vy, this is the only vector whose direction is always tangent to the object's path.
v
Height reached by a vertically thrown ball with a hang time of 8s.
80m
If theta is the angle between the horizontal and vector V, this vector has a magnitude of v*cos(theta).
Vx
It's the third vector in a typical 3-vector river problem where the two provided vectors are 1) an object's velocity, and 2) its heading + its speed in still water.
Velocity of the current (or the surroundings through or across which the object is traveling)
7m/s
The sine of twice the launch angle for a symmetric flight, if the initial speed is 10m/s and the range is 10m.
1
The point in free-fall when acceleration is zero.
Never
Tan^-1("Vy"/"Vx")
Direction of the other component vector...
Westward
When a string is causing a ball to travel in vertical circles, this is the tension in the string at the bottom, in terms of the m (ball's mass), v (ball's speed), and r (radius of the circles)
mv2/r + mg or m(v2/r + g)
The initial speed of an object that is launched horizontally from a 1.25m high table, and which hits the floor 1m away from the table.
2m/s
The time aloft for a ball thrown directly upward at 10m/s from a height of 40m and landing at ground level (0m).
4s
If g=10, this is the cosine of the launch angle of a projectile that travels 240m horizontally during an 6 second symmetric flight.
0.8
The magnitudes of two forces that can, when oriented in the proper directions, be added together to produce any resultant force from 10N to 40N, inclusive.
15N and 25N
The maximum amount of time it would take for a car to drive through a loop-the-loop of radius r at a constant speed, without losing contact with the road -- in terms of g and r.