The hard material that forms the main substance of the trunk or branches of a tree, used for timber

Wood

Horseshoe Arch
When were the High Middle Ages?
12th and 13th Centuries
A person involved in trade
Merchant or Shopkeeper
Anonymous writings that celebrated the heroic actions of knights
Epic Poems
A small rectangular block typically made of fired or sun-dried clay, used in building

Brick
A tall, upright structure, typically cylindrical, used as a support for a building

Pillar or Column
A sovereign head of state, especially a king or queen
Monarch
A worker in a skilled trade, especially one that involves making things by hand
Artisan
A crisis that divided the Catholic Church, which included up to 3 competing popes at the same time
Western Schism
A hard, solid mineral of which rock is made, especially as a building material

Stone
A curved structure spanning an opening and typically supporting the weight of a bridge, roof, or wall above it
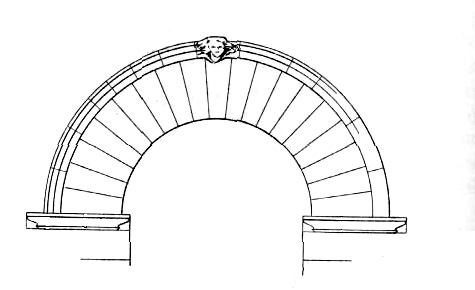
Arch
A high-level educational institute where students study for degrees and academic research is done
University
An agricultural labourer bound by the feudal system who was tied to working on their lord's estate
Serf
A Greek philosopher who was a student of Plato and is known for logic and reason

Aristotle
A thin rectangular slab of baked clay or other material, used in overlapping rows for covering roofs

Tile
A roof in the form of an arch or a series of arches, typical of churches
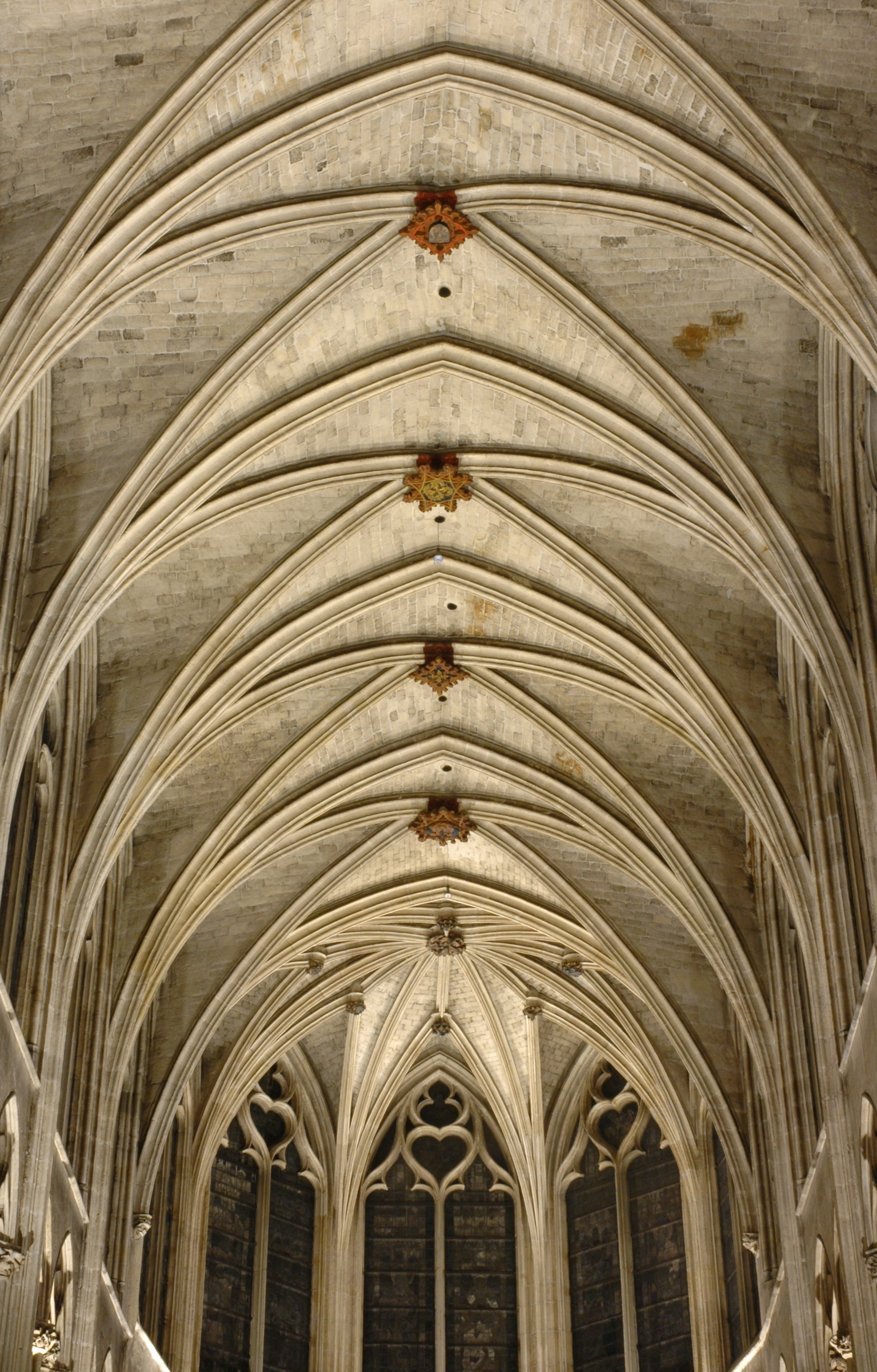

Vault
Extreme shortage of food
Famine
An assembly of townspeople headed by a mayor who manage city life
City Hall or Council
An Italian philosopher who was inspired by Aristotle and wanted to reconcile reason with religious faith

Saint Thomas Aquinas
A soft mixture of sand and cement for spreading on structures to form a smooth hard surface when dried

Plaster
A rounded vault forming the roof of a building or structure, typically with a circular base
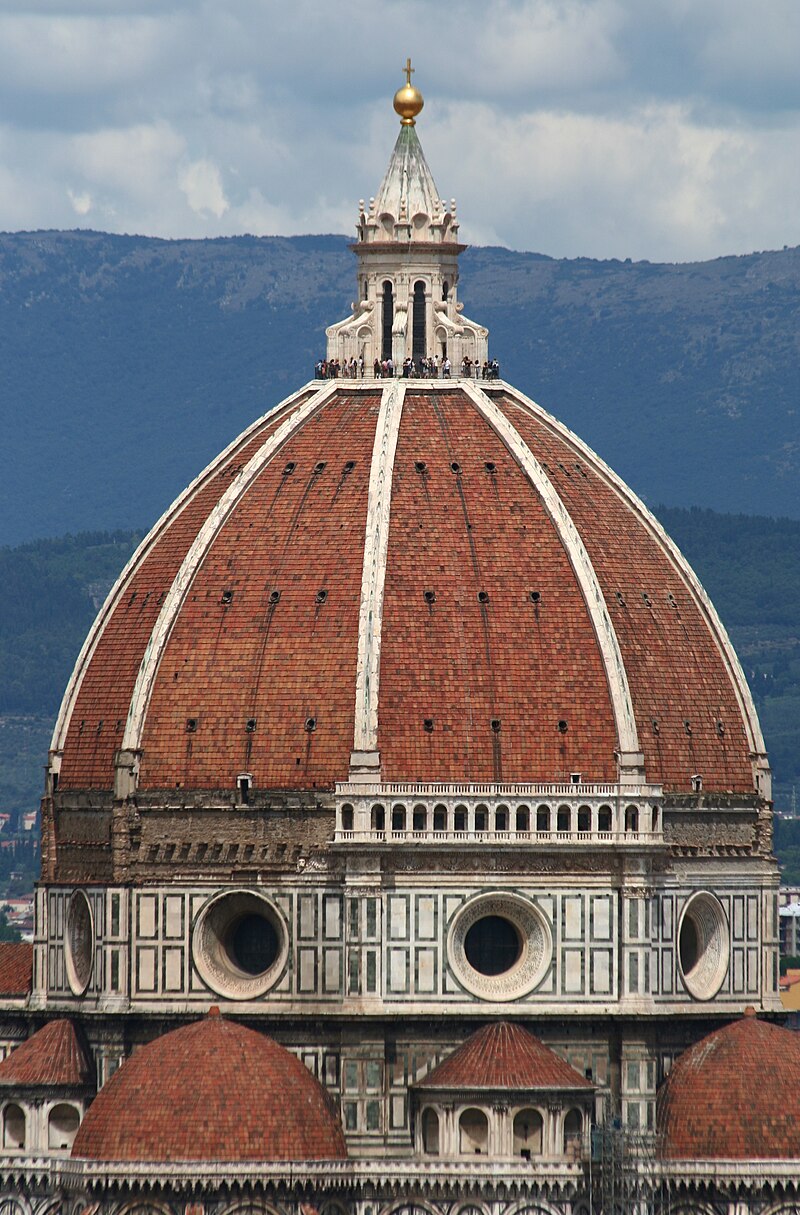

Dome
Orders of payment that could be converted into money in a different place at a later date
Bills of Exchange
A legal document that established self-government for a city, specifying its rights and privileges
Charter or Fuero
Hundred Years' War