The weighted average mass of an atom compared to 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12. As it is a relative scale, values are dimensionless (do not have units).
The relative atomic mass (Ar)
The number of protons in the nucleus of at atom or the nuclear charge.
The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
The atomic number (Z)
The mass number or nucleon number (A)
When outer electrons are blocked from the attraction of the nucleus by inner electrons.
Electron Shielding
A bond formed by non-directional (the force of attraction occurs in all directions) electrostatic attraction between oppositely-charged ions by elements with an electronegativity difference of approximately 1.8 units and greater.
Ionic Bond
Electrostatic attraction is the force of attraction between opposite charges, for example, between a negatively-charged ion and a positively-charged ion. Electrostatic forces of attraction also exist between positive nuclei and bonding electrons and positive ions and delocalised electrons.
Pressure =100 kPa and Temperature = 0°C/273 K
verus
Pressure =100 kPa and Temperature = 25°C/298 K
Standard Temperature and Pressure, STP (gases)
verus
° (thermochemistry)
The minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must have for a chemical reaction to occur.
activation energy (Ea)
A state where the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction (the concentrations of reactants and products are constant, not necessarily equal!).
Dynamic Equilibrium
(Static equilibrium = balanced forces like on a balanced seesaw)
A substance can act as both an acid and a base.
amphoteric
A species that oxidises another species.
A species that reduces another species.
Oxidising Agent (gets reduced)
Reducing Agent (gets oxidised)
A series of closely-related compounds in organic chemistry with same general formula and functional group (each successive member of the alkane series differs from the previous one by a CH2 group; the general formula is CnH2n+2)
Homologous Series
The mass in grams of one mole of a substance. The unit for this is grams per mole (g mol-1).
The molar mass (M)
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons in the nucleus but a different number of neutrons.
Isotopes
The strength of this attraction depends on two factors:
- The distance between the nucleus and the electrons (the atomic radius).
- The number of shielding electrons within the atom.
(sometimes calculated at total electrons minus shielding electrons)
Effective Nuclear Charge
A bond formed by electrostatic attraction between positively charged nuclei and shared pairs of bonding electrons.
Covalent Bond
The heat content of a system (a state function ie, the value is independent of the path taken to reach that specific value)
Enthalpy
The highest energy state on a reaction coordinate; it indicates a point at which new bonds are being formed at the same time as old bonds are being broken.
transition state
A measure of the relative amounts of reactants and products for a reaction that is not yet at equilibrium.
reaction quotient, Q (or Qc)
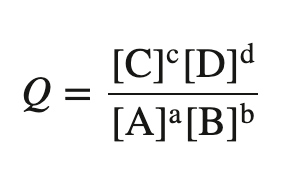
A proton/H+ donor
versus
A proton/H+ acceptor
Brønsted–Lowry acid
versus
Brønsted–Lowry base
A number which, together with its sign, indicates the gain or loss of electron control of an atom during a reaction.
The numerical part of that value (can be a Roman numeral).
Oxidation State, for example the oxidation state of copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4, is +2
Oxidation Number
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms (different structural formulae).
Structural Isomers
The lowest whole number ratio of atoms (or ions) in a compound.
versus
The actual number of atoms in a compound.
empirical formula
versus
molecular formula
X (g) → X+ (g) + e–
(The energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions.)
First Ionisation Energy
The number of bonds between a pair of atoms.
Bond Order
The enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from the elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
The enthalpy change of formation (ΔHf), or standard enthalpy change of formation (ΔH°f )
The change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit of time. The unit for this is usually mol dm–3 s–1 (or M/s).
rate of reaction
'When a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change, the system will respond to minimise the effect of the change.'
Le Châtelier’s principle
A species that is able to act as both a proton/H+ donor AND a proton/H+ acceptor depending on what it is reacting with.
(ie it can act as BOTH a Brønsted–Lowry acid and a Brønsted–Lowry base)
An amphiprotic species
An ion that appears unchanged on both sides of the complete ionic equation.
Spectator Ion
Single atoms or groups of atoms that give organic compounds their characteristic properties.
Functional Group
The attraction of an atom for a bonding pair of electrons. It is measured on the Pauling scale, a relative scale that assigns fluorine a value of 4.0 and francium a value of 0.7.
Electronegativity
Different forms of the same element in the same physical state.
Allotropes
The energy required to break a chemical bond.
Bond Enthalpy, H or Bond Dissociation Energy, E
A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway that has a lower activation energy (they don't lower the Ea); they are not used up in the chemical reaction.
catalyst
This pair differs by a proton (H+)
A conjugate acid-base pair
Consists of an electrode, usually a metal, in a solution of its own ions. For example, a piece of solid zinc metal in a solution of aqueous zinc (Zn2+) ions.
Half-cell
A compound that has only carbon-carbon single bonds.
A compound that has carbon-carbon double or carbon-carbon triple bond(s).
Saturated compound
versus
Unsaturated compound
F (g) + e− → F− (g)
(The energy released when one mole of electrons is added to one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1− ions.)
Electron Affinity
A bond formed by the non-directional (the force of attraction occurs in all directions between the positive ions and delocalised electrons within the lattice structure) electrostatic attraction between the lattice of positive ions and the 'sea' of delocalised electrons.
Metallic Bond
The enthalpy change when one mole of bonds are broken in the gaseous state averaged for the same bond in similar compounds.
average bond enthalpy (or average bond dissociation energy)
Substances that neutralize an acid and substances that neutralize an acid AND are soluble.
Bases and Alkalis
The difference in the electrode potentials of the half-cells in a voltaic cell, measured in volts (V).
Cell potential (E°cell), also known as the electromotive force (EMF)
A chemical reaction that involves the replacement of an atom or group of atoms with another atom or group.
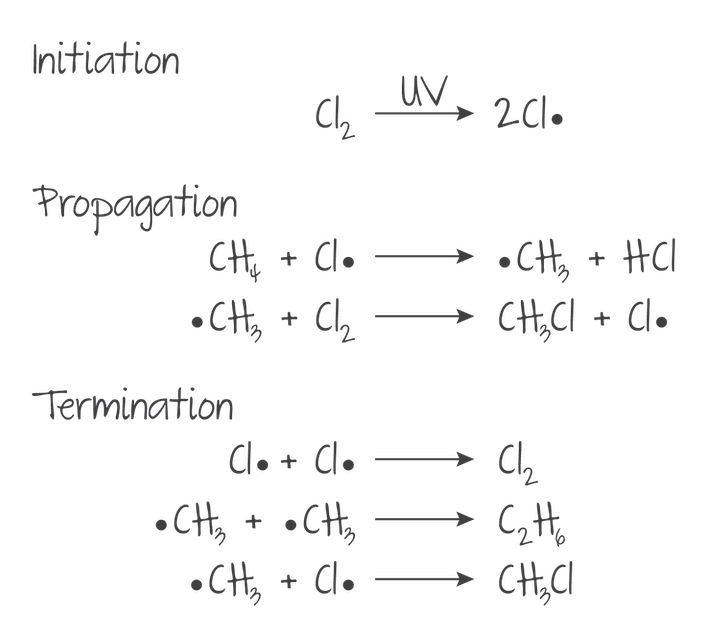
Substitution Reaction
(alkanes undergo substitution via Free Radical Substitution Mechanism)
−log[H+(aq)]
pH
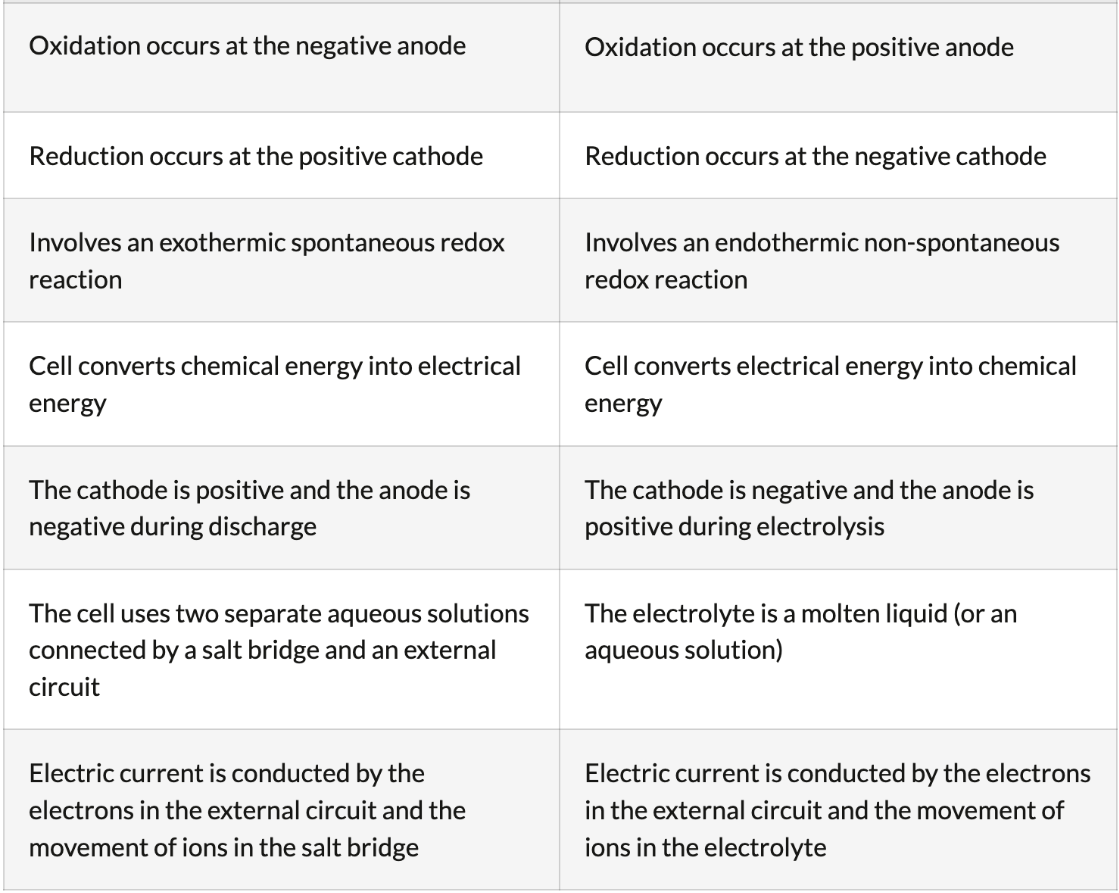
Voltaic Cell Electrolytic Cell
An organic chemical reaction where two smaller molecules, one of which has a double bond, combine to form a larger molecule.
Addition reactions
(Alkenes undergo addition reactions due to the presence of an electron rich carbon-carbon double bond which attracts electrophiles, positively or slightly positive species)
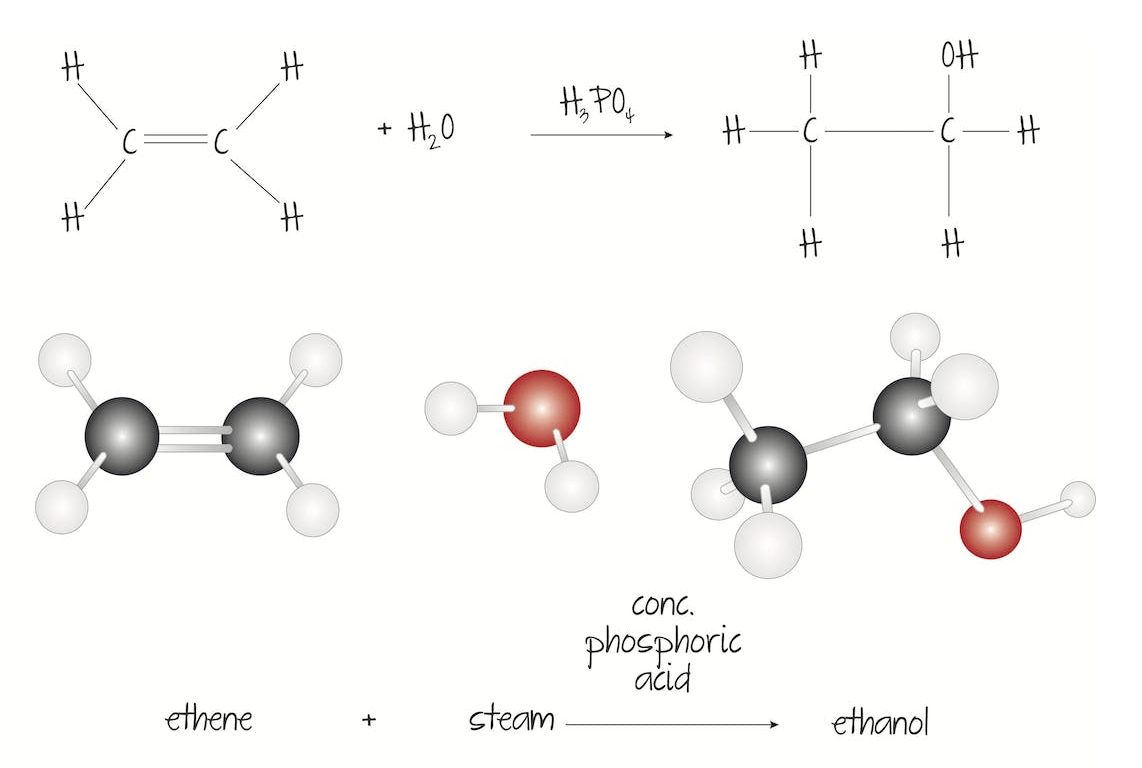
Acids (or bases with OH-) where the concentration of H+ ions, [H+], is equal to the initial concentration of the acid (ie the acid dissociates or ionizes 100%).
Strong acids or bases
An electron-rich species with a lone pair of electrons that is attracted to regions of positive charge.
versus
An electron deficient species (they have either a positive charge or a partial positive charge).
nucleophile
versus
electrophile