What is an enzyme?
The loss of electrons. ex: NADH to NAD+
What is oxidation?
NAD+
What is the most important product of fermentation in animal and yeast cells?
The three- dimensional conformation assumed by a polypeptide chain
What is tertiary structue?
The gaining of electrons. ex: FAD+ to FADH2
What is reduction?
The active transport of chemicals
What is chemiosmosis?
The metabolic pathways that breaks large molecules into smaller molecules, releasing energy
What are catabolic pathways?
The catabolic pathway takes place outside of the mitochondria. Hint: glucose is an input
What is glycolysis?
The most electronegative atom in the ETC.
What is oxygen?
The allosteric regulation of enzyme activity in which the inhibitor binds to the enzyme not at the active site
What is noncompetitive inhibiton?
Glucose, ATP, and NAD+
What are the inputs of glycolysis?
The stepwise harvest of energy that pumps H+ ions from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
What is the electron transport chain (ETC)?
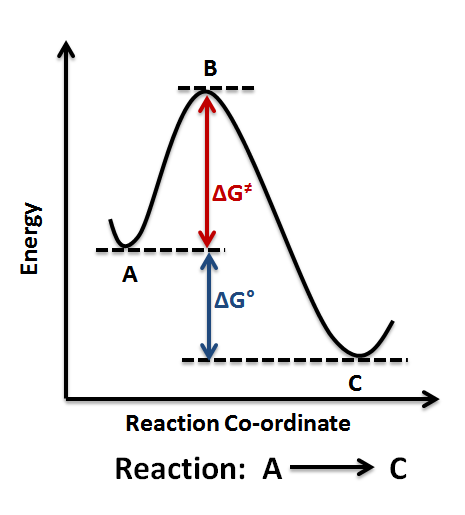
The change in free energy of the reaction.
What is delta G0?
acetyl-CoA, NAD+, FAD
What are the inputs of the citric acid cycle?
Transmembrane protein that synthesis ATP
What is ATP synthase?