Resolution is improved when ______.
A. OID increases
B. OID Decreases
C. SID Decreases
D. None of the above
B. OID Decreases
Which quality factor allows visualization of the image?
A. Brightness
B. Contrast
C. Density
B. Contrast
The x-ray beam that leaves the patient is made up of scatter and primary radiation. This beam is referred to as:
Exit (remnant) radiation
True or False: When using an AEC, the radiographer must set the kilovoltage.
A. True
The number of lead strips per inch in a grid is a measure of:
Grid frequency
Which of the following will influence the resolution in an image?
A. SID
B. OID
C. Focal Spot size
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
All of the following affect spatial resolution, EXCEPT:
A. mA
B. focal spot size
C. SID
D. OID
A. mA
If the x-ray tube is moved closer to the IR, the radiation intensity at the IR:
Increases
When using AEC for an exposure, if kVp is increased on a repeat exposure, the following will occur:
A. The exposure time increases
B. The exposure time decreases
C. None of the above is affected
B. The exposure time decreases
A grid should be used when part thickness exceeds:
10 cm
Which of the following groups of exposure factors would be MOST appropriate to control involuntary motion?
A. 400 mA, 0.03 sec
B. 200 mA, 0.06 sec
C. 600 mA, 0.02 sec
D. 100 mA, 0.12 sec
C. 600 mA, 0.02 seconds
The largest contributing factor to magnification in an image is:
OID
If the SID doubles and no other changes are made, the radiation intensity at the Image Receptor:
A. Doubles
B. Is cut in half
C. Quadruples
D. Is reduced by a factor of 4
D. Is reduced by a factor of 4
The tube current is the:
mA
Compton scattering occurs when an incident x-ray photon interacts with a _____ electron.
A. Loosely bound inner-shell
B. Tightly bound inner-shell
C. Loosely bound outer-shell
D. Tightly bound outer-shell
C. Loosely bound outer-shell
A lateral view of the cervical spine is requested. Which distance factor will give the least amount of recorded detail?
A. 36" SID
b. 40" SID
C. 48" SID
D. 72" SID
A. 36" SID
____________ is the loss of some of the energy from the x-ray beam as it passes through the tissue being imaged.
Attenuation
The 15% rule states that: an increase of 15% of the kVp will increase the IR exposure the same as:
Doubling the mAs
If the AEC center detector is used instead of the two outside cells for a PA chest exposure the radiograph will:
A. Be underexposed
B. Show motion
C. Have too much contrast
D. Be overexposed
D. Be overexposed
An object is placed at an angle to the image receptor. If the central ray is directed perpendicular to the image receptor through the center of the object, the image of the object will appear:
A. Spatially distorted
B. Foreshortened
C. Elongated
D. Blurred
B. Foreshortened
If the OID is decreased, unsharpness ______and recorded detail _______
Decreases, Increases
Factors that affect the Visibility of detail in an image include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Brightness
B. X-ray tube focal spot size
C. Image contrast
D. Use of radiographic grids
B. X-ray tube focal spot size
If I want to just increase IR exposure in my image by using the 15% rule, I would:
Increase kVp by 15%
The tissue interaction involving the photoelectric effect is associated with ________ .
A. Scattering of the primary photon
B. Exit radiation
C. Absorption of the primary photon
D. Transmission of the primary photon
C. Absorption of the primary photon
The total filtration in mm of Aluminum equivalent of a fixed radiographic unit operating above 70 kVp is required to be ______.
2.5 mm
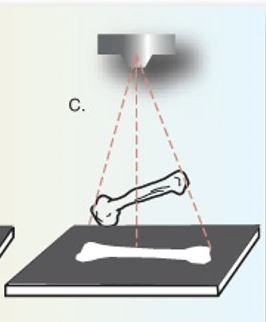
The following image is an example of what type of distortion?
Elongation (Occurs when the object is parallel to the IR and the CR is angled to the long axis of the part
OR CR is perpendicular to the object and the object is not parallel to the IR)
True or False: As beam restriction increases, receptor exposure decreases
True
A positive beam limiting device is also known as:
Automatic collimator
True or False: The visual cues of exposure errors are obvious in digital radiography and are immediately displayed to the technologist in the image
False
You have a pregnant patient that needs a KUB for abdominal pain. Your typical KUB technique is 80 kVp at 50 mAs. What technique should you use to decrease your pregnant patient's dose while maintaining your normal KUB exposure?
92 kVp @ 25 mAs (15% rule)
You take an image using 80 kVp at 10 mAs and your EI # indicates that the image is overexposed. Using the 15% rule to decrease the exposure, what would your new technique be for your repeat image?
68 kVp @ 10 mAs
Which set of technical factors will result in the best spatial resolution?
mAS kVp SID OID FSS
A. 25 70 40” 4” 0.6mm
B. 12 80 72” 4” 0.6mm
C. 15 70 72” 8” 0.6mm
D. 20 80 40” 8” 1.2mm
B. We can solve this by comparing the SID, OID and FSS of each, or we can use the penumbra formula and finding the smallest number. P=FSS x OID/SOD
True or False: An x-ray image can be distorted by both magnification and minification.
False. X-rays are always slightly magnified
As the SID is increased, the recorded size of the object in the image will:
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain the same
B. Decrease
True or False: For accurate representation of air fluid levels, the patient must be as upright as possible and the CR should be angled to match the angle of the patient.
False. The CR must remain parallel to the floor to visualize air fluid levels
When an angle is used on the tube, SID should be adjusted by ______ inch(es) for every 5 degrees of CR angulation
1 inch
Which type of technique would produce the least radiation dose to the patient?
A. High kVp technique
B. Low kVp technique
A. High kVp
For a variable kVp chart, which factor is held constant?
mAs
If a satisfactory IR Exposure (acceptable EI/DI#) is obtained with 70 kVp and 20 mAs at 40inch SID, what mAs is required to maintain the same IR Exposure at 72 in. SID?
65 mAs (Exposure Maintenance Formula)
Which formula is used when calculating intensity with a change in distance?
Inverse square law
Write out the formula for the inverse square law.
old intensity/new intensity = new distance2/old distance2
The Anode Heel Effect results in less intensity at the _____ side of the tube
Anode
A compensating filter is used for:
A. Improvement of image quality
B. High kVp exposure to reduce scatter
C. An area of equal or consistent tissue thickness
D. Reduction of patient dose
A. Improvement of image quality
When an x-ray tube is not centered along the center-line of a focused grid, it is termed:
A. Off focus
B. Lateral decentering
C. Off angle
B. Lateral decentering
The radiolucent strips in a grid: _____________ . (select all that apply)
A. Absorb scattered x-rays
B. Allow transmitted photons to pass through
C. Absorb transmitted electrons
D. Have a low atomic number
B & D
Allow transmitted photons to pass through
Have a low atomic number
True or False: It is OK to use AEC Center cell for a lateral CXR exposure.
True
While performing an abdomen examination in the erect position using an AEC unit, You use 72 inches rather than 40 inches SID. The IR Exposure EI# / DI# of this radiograph will indicate that it was:
A. Underexposed
B. Overexposed
C. Acceptable
D. Mottled
C. Acceptable
If two anatomic parts received the same amount of radiation, which would display the greatest image receptor exposure?
A. The thinner anatomic part
B. The thicker anatomic part
A. The thinner anatomic part
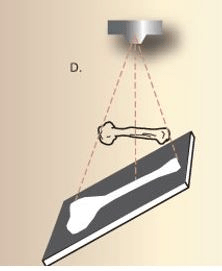
What type of distortion is shown here?
Foreshortening (occurs when IR and CR are perpendicular, but object is at an angle to the IR)
The range of acceptable source-image distances that can be used on a focused grid is called the:
A. Grid maximum distance
B. Grid ratio
C. Focal range
D. Grid frequency
C. Focal range