- THIS IS A BONUS QUESTION -
Where did Mr. Scoggins go to school?
Tarleton State University
Conduct Impulses; structural unit of the nervous system
Neurons
Cordlike bundles of Axons
Nerves
Not gated, always open
Leakage Channels
ECF > Na+ ICF > K+
The difference in ionic composition of ICF and ECF
Most abundant and versatile; support, guide the migration of young neurons, etc; “the Parents of neurons”
Astrocytes
Extreme longevity
Amitotic
High metabolic rate: requires a continuous supply of Oxygen and glucose
Characteristics of Neurons
Impulses towards the CNS
Sensory (afferent) nerves
Proteins change shape to open and close
Gated Channels
More permeable to K+, more diffuses out than sodium diffuses back in (3 Na+ out 2 K+ pump back in)
Differences in membrane permeability
Touch and monitor neurons, migrate toward injured neurons, get rid of or destroy pathogens through phagocytosis
Microglial cells
By oligodendrocytes, each cell can wrap multiple axons, including white and gray matter
Myelination of CNS
Carry impulses away from the CNS
Motor (efferent) nerves
Ligand-gated, open with the binding of specific chemical (neurotransmitters)
Chemically gated channels
Short-lived, localized changes in potential receptors (seen in sensory receptors and postsynaptic potentials)
Graded potential
Ciliated, line the cavities of CNS, permeable barrier, regulate ionic and chemical composition of CSF
Ependymal Cells
Protection and electrical insulator of an axon increases the rate of impulse transmission (faster depolarization)
Myelin Sheaths
Mixed Nerves
Electrical, open and close in response to changes in membrane potential
Voltage-gated channels
Long-distance neural communication (only in muscle cells and neurons)
Action Potential
Form insulating myelin sheaths in thicker nerve fibers
Oligodendrocytes
By Schwann cells, one cell forms one segment of the myelin sheath, each separated by Nodes of Ranvier
Myelination of PNS
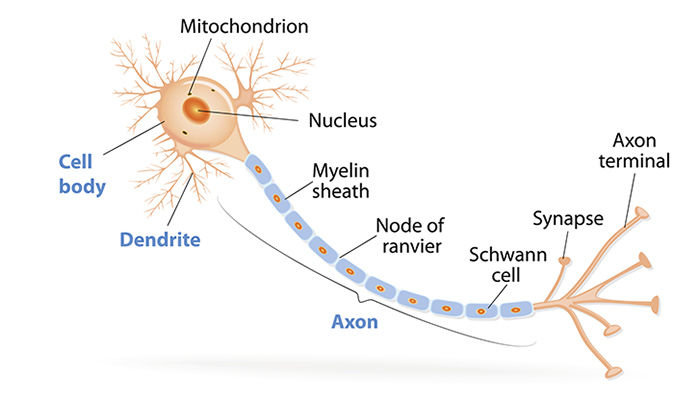
DRAW AN AXON
Open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors
Mechanically gated channels
Na+ influx in one area causes local Na channels to open, thus depolarizing one area to the nest, it is self-propagating
Propagation of an Impulse