Atom
The smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction.
Electron Cloud
Electrons orbiting the nucleus
How to find the number of electrons in an element-
Atomic number
Atoms are to small to be seen- atomic models describe their structure.
Valence electrons during bonding are...
lost, gained, or shared between elements.
Why do atoms bond together?
To become more stable.
the electrons in the outermost energy
Atoms with 4 or more valence electrons will likely...
gain electrons to fill the shell.
Atoms with 3 or less valence electrons will likely...
lose electrons
Atoms with full valence electrons will likely...
not bond or react with other elements.
How do atoms combine with other atoms through chemical bonds?
Strong attractive forces that exist between the atoms.
Democritus
Believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible.
Covalent bonds
share valence electrons
Ionic bonds
transfer valence electrons
Metallic bond
pool valence electrons
John Dalton
All matter is made of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed.
"Billiard Ball Model"
Cation
lose electrons
positive charge
Anion
Negative charge
Electrons move in a circular orbit (electron shells) around the nucleus at a fixed distance.
J.J. Thomson
"Plum Pudding Model"
Electrons are embedded in a sphere of positive electrical charge.
Ion
an atom that is no longer electrically neutral because it has lost or gained valence electrons.
Rutherford
Erwin Shrodinger
Quantum Mechanical Model (today's model)
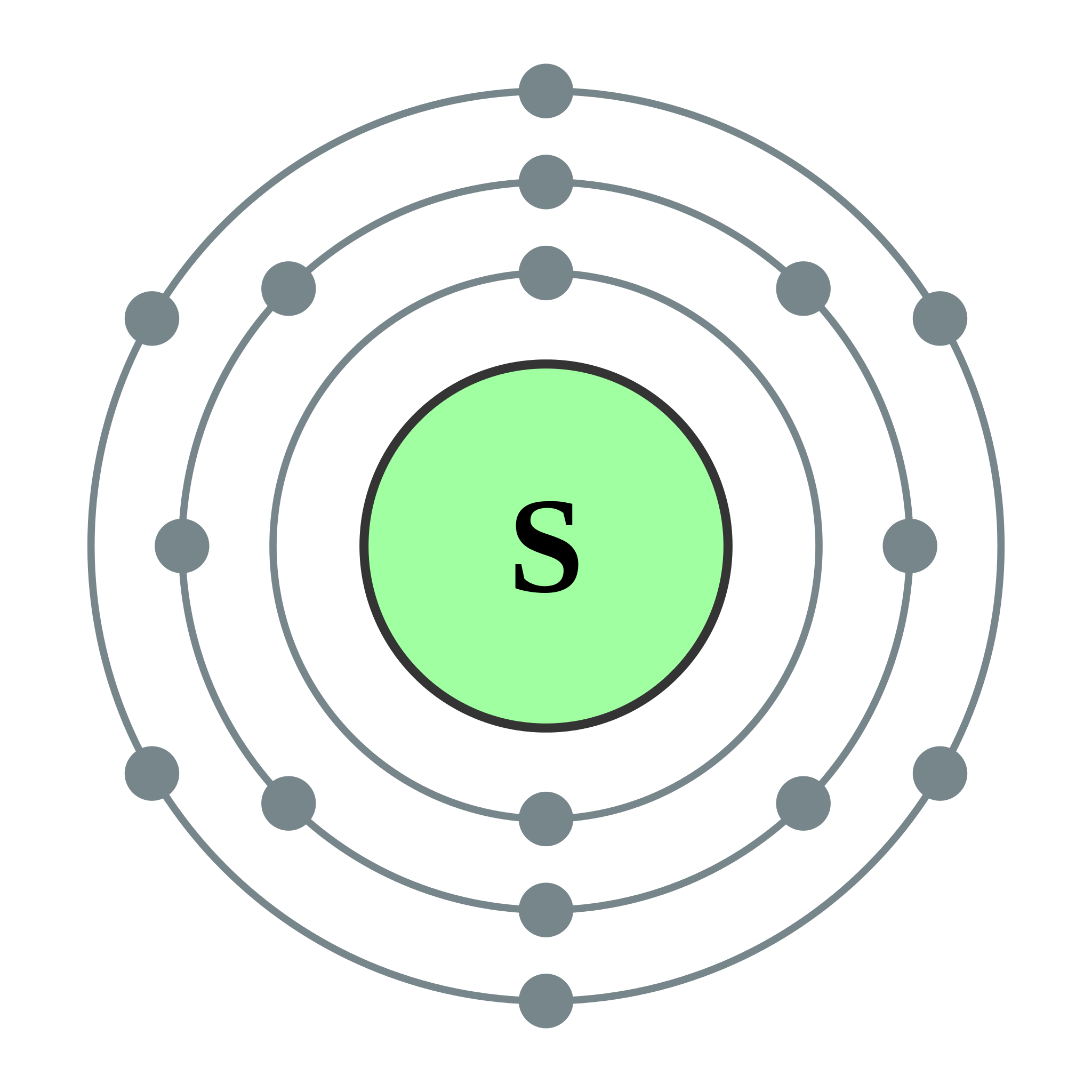
Write the electron configuration for Sulfur:
Bonus: Draw the electron shell diagram
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
Draw the Lewis Dot structure for Nitrogen
