A 45 year old M w/ h/o HTN, HLD, T2DM, and newly-diagnosed ESRD is admitted for dialysis initiation 2/2 volume overload that is refractory to medical therapy. IR places a tunneled PICC in the L arm and he is successfully dialyzed.
You get a text from nursing at 7AM on Sunday stating his US IV is blown and the PICC isn't flushing. They're requesting that you place an USIV. Where will you place the IV?
L arm
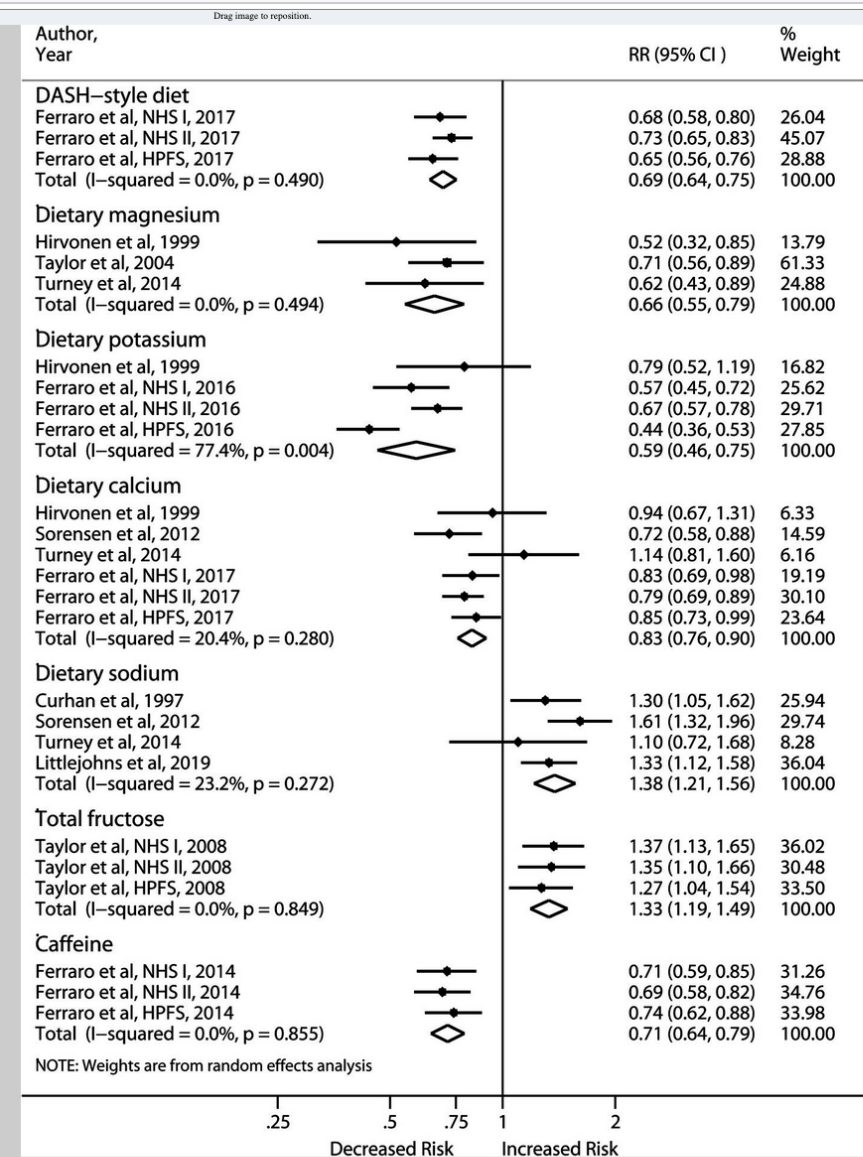
-PICCs placed before or after initiation of HD are independently a/w a 15 to 20% lower likelihood of transition to any working fistula or graft1
-Place a nursing communication for limb alert, bracelet
What is the most common cause of death in the first year post-transplant?
A. Cardiovascular disease
B. Cancer
C. Infection
D. Graft failure
CVD
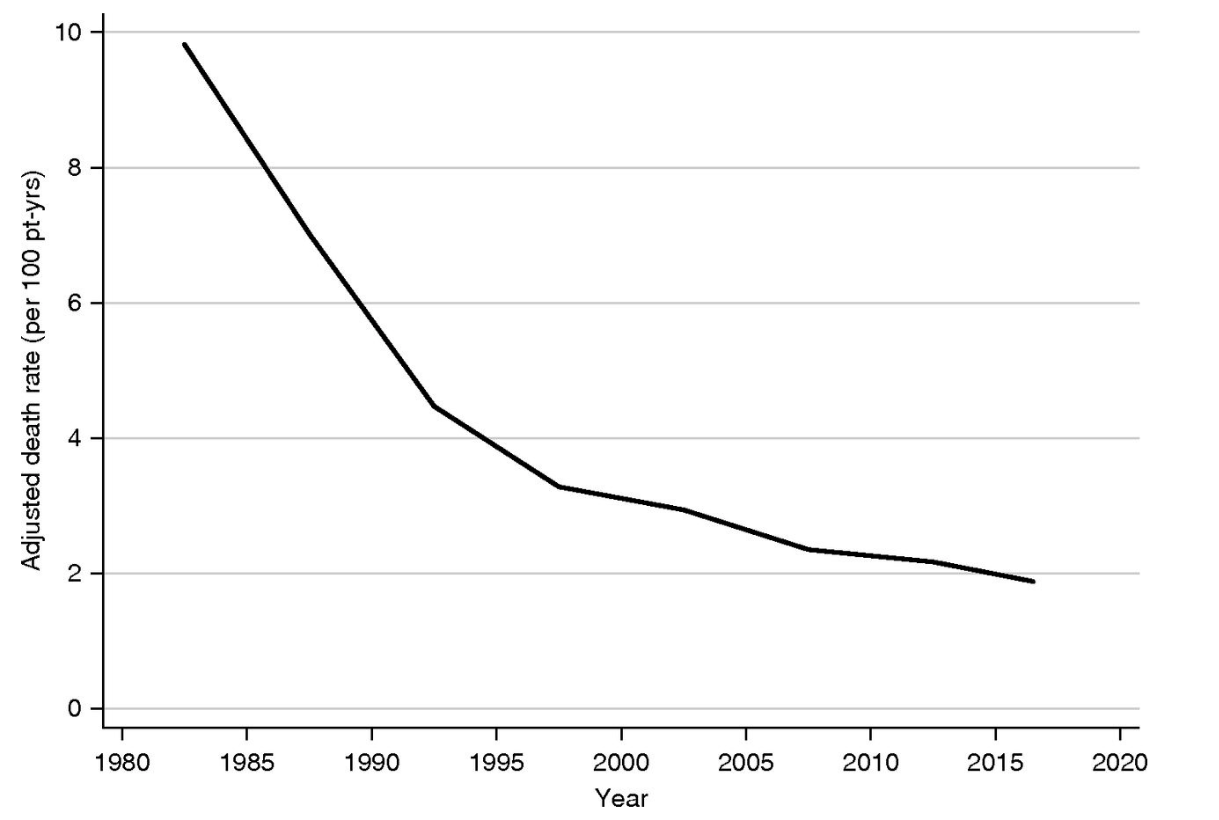
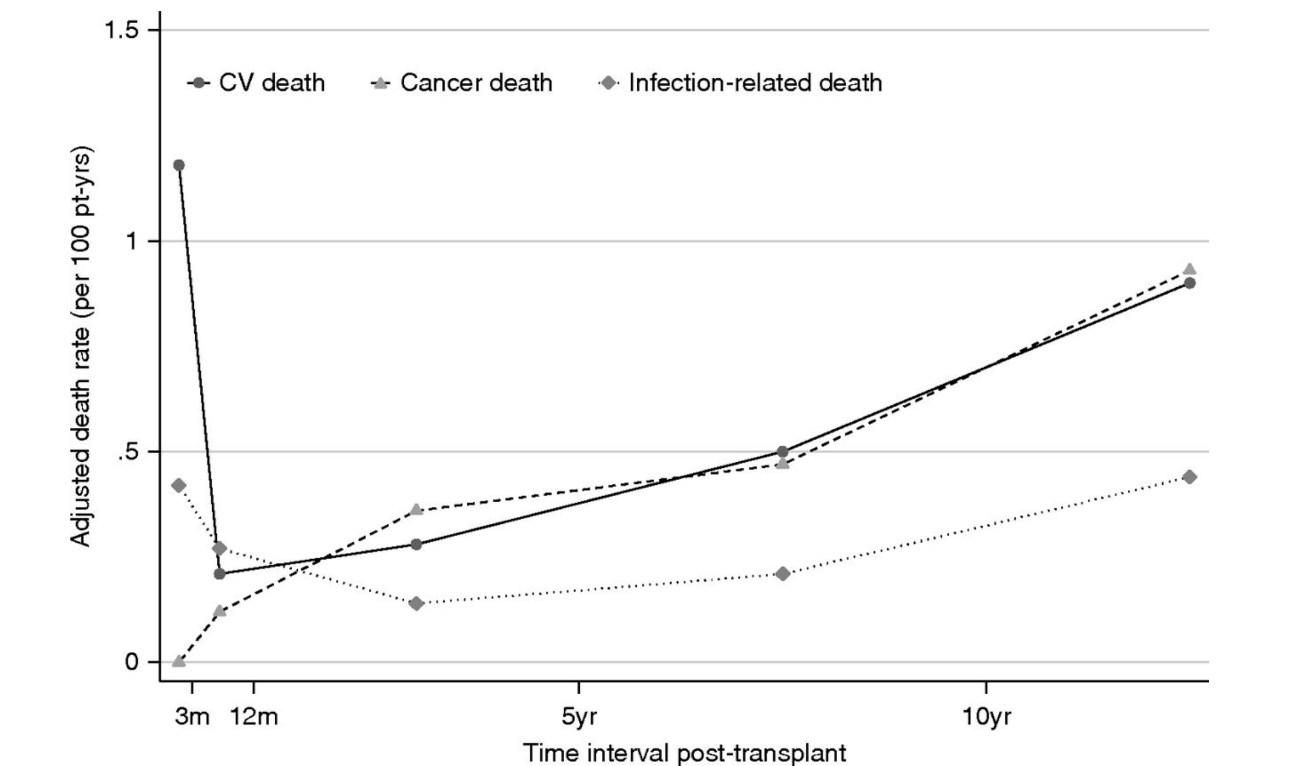
(Ying et al., 2020)
-Kidney transplantation = CVD risk factor
-Calcineurin inhibitors induce HTN by activating the Na-Cl cotransporter in the DCT
-Consider Thiazide diuretics
-Dyslipidemia is a common side effect of calcineurin inhibitors and steroids
-Treatment w/ statin improves CV outcomes, but statins have drug-drug interactions w/ calcineurin inhibitors and can increase toxicity of both drugs1
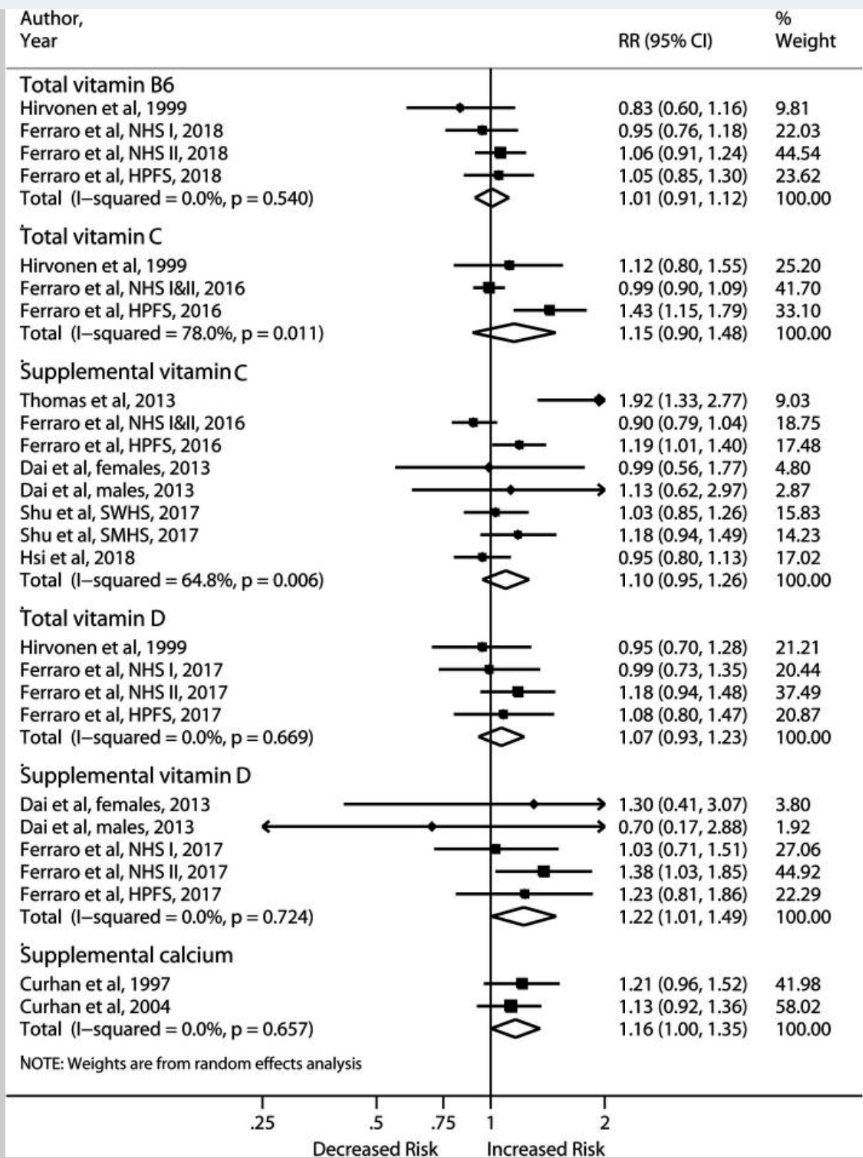
A 39 y/o M w/ h/o IVDU, HIV and Hep C who is experiencing homelessness presents w/ 1 week of painful, erythematous skin wounds, found to have SSTI w/ strep bacteremia.
Vitals: BP 178/110, T 98.8F, HR 75, O2 98% on RA. Labs: s/f Cr 4.97 (3.1 two weeks ago at HUP), Ca 8.0, Alb 2.4, WBC 16.5, Hgb 7.7, Plt 411.
Medications: Methadone 300mg daily (confirmed with Parkside Recovery), stopped taking Biktarvy 1 month ago
UDS is positive for Amphetamines, Fentanyl, and Cocaine.

Identify three social conerns from this patient's history
-Undomiciled (housing instability)
-Access to medication (transportation)
-Built environment
-Stigma/self-fulfilling prophecy
-Economic instability
-HIV, Hep C status?
Epidemiology: Which type of kidney stone is more common in women?
Stone Breakdown: Struvite
Women - 10.6%
Men - 3.0%
Calcium oxalate
Women - 47.1%
Men - 57.3%
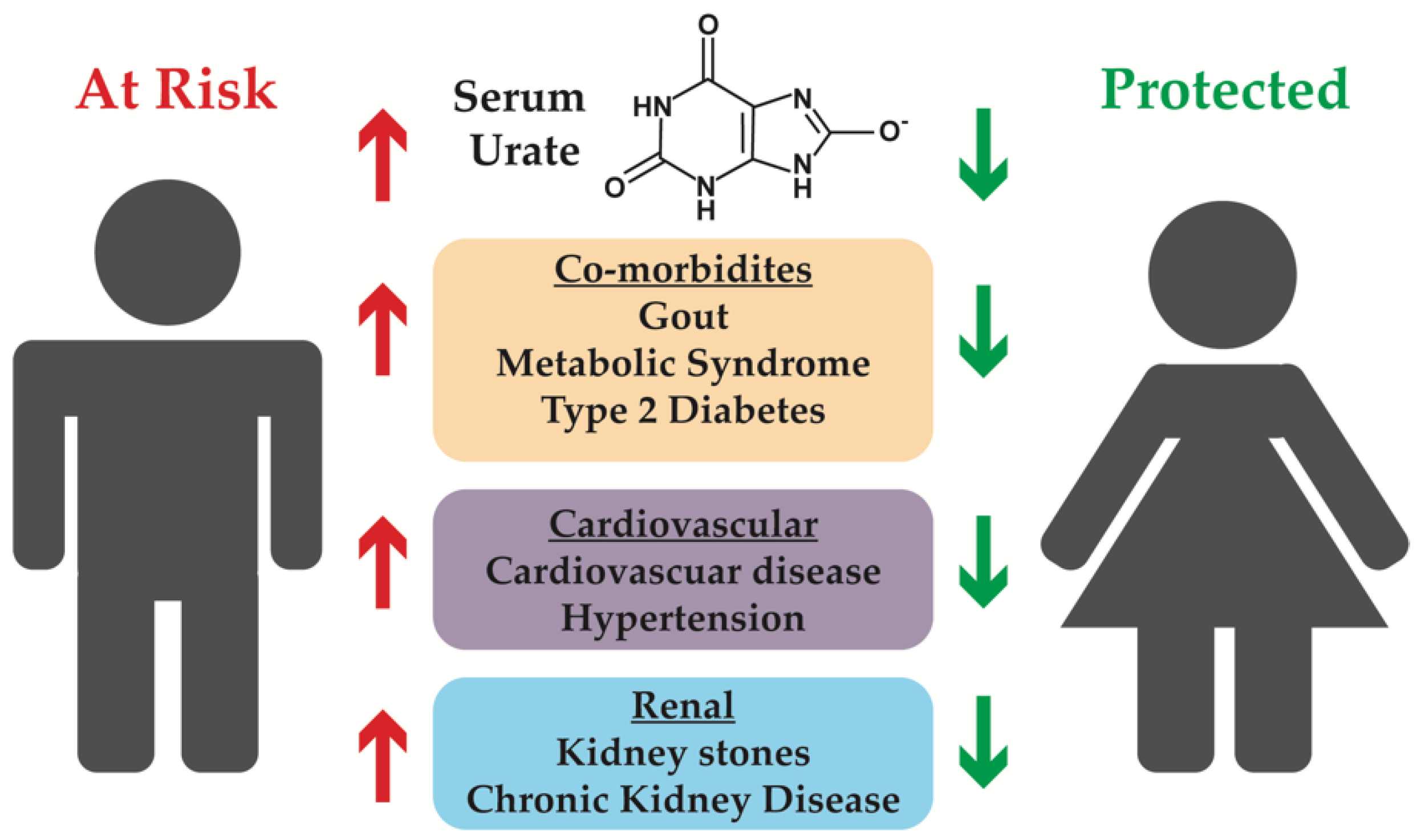
Source: https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&sca_esv=581793872&
-Men excrete more calcium and oxalate into their urine (p < 0.0001)
-Higher concentrations of uric acid
-Estrogen up-regulates uric acid transporters
-Men have lower pH than women (males, 6.03 vs females, 6.20, p = 0.0001)
A 57-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for hypertension and slowly progressive chronic kidney disease. He reports he feels well and has no symptoms. Medications are amlodipine, calcitriol, clonidine, lasix, metolazone, metformin, semaglutide, and tadalafil.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 132/75 mm Hg; other vital signs are normal. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show Cr of *** with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of *** mL/min/1.73 m2.
Patients should be referred to Renal Replacement Therapy education once they fall below which GFR cutoff?
A. GFR 60-89 (G2)
B. GFR 45-59 (G3a)
C. GFR 30-44 (G3b)
D. GFR 15-29 (G4)
Bonus: What should be done with this patient's Metformin?
D. GFR 15-29 (G4)
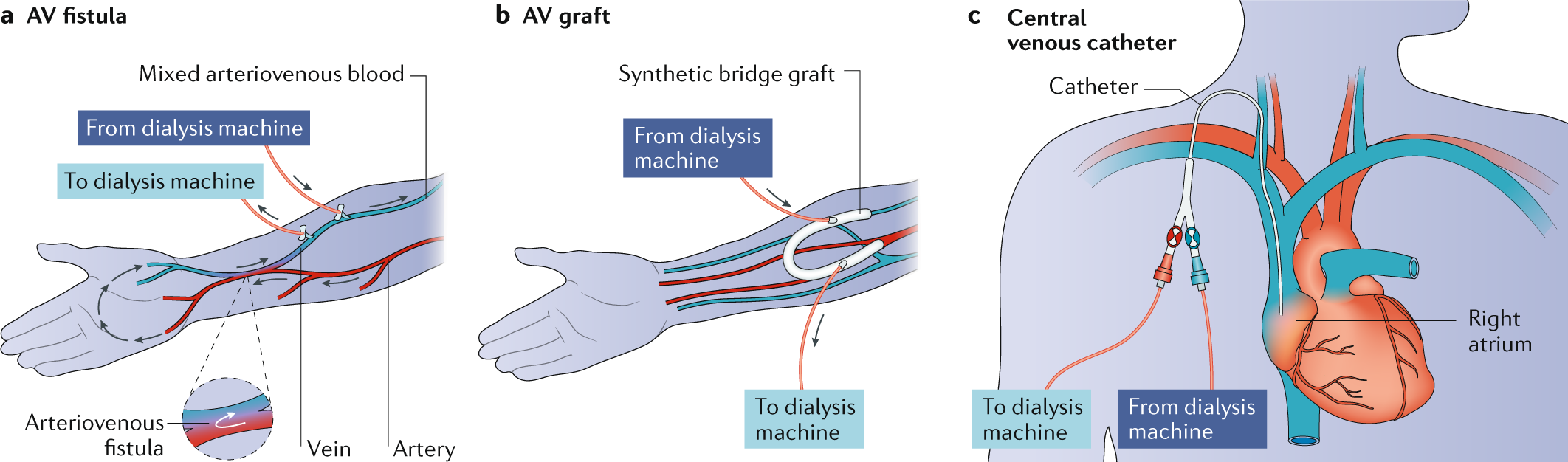
-maturation 2-4 months vs. 2 weeks
-risks of stenosis
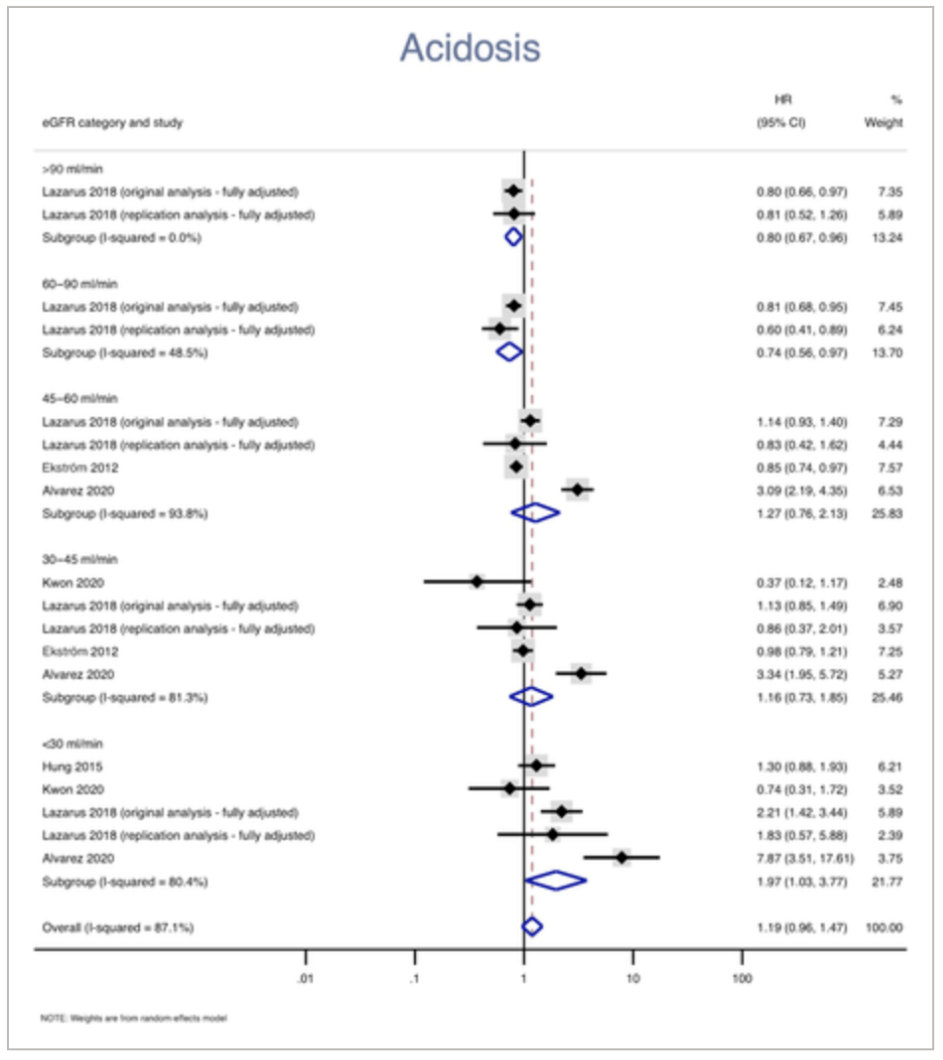
Metformin
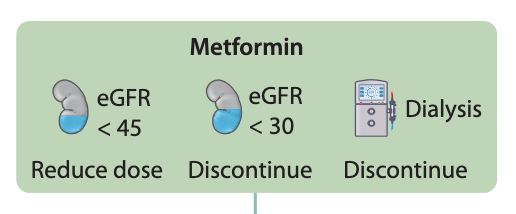
-Safety and effectiveness of metformin in patients with reduced renal function: A systematic review (2021)19
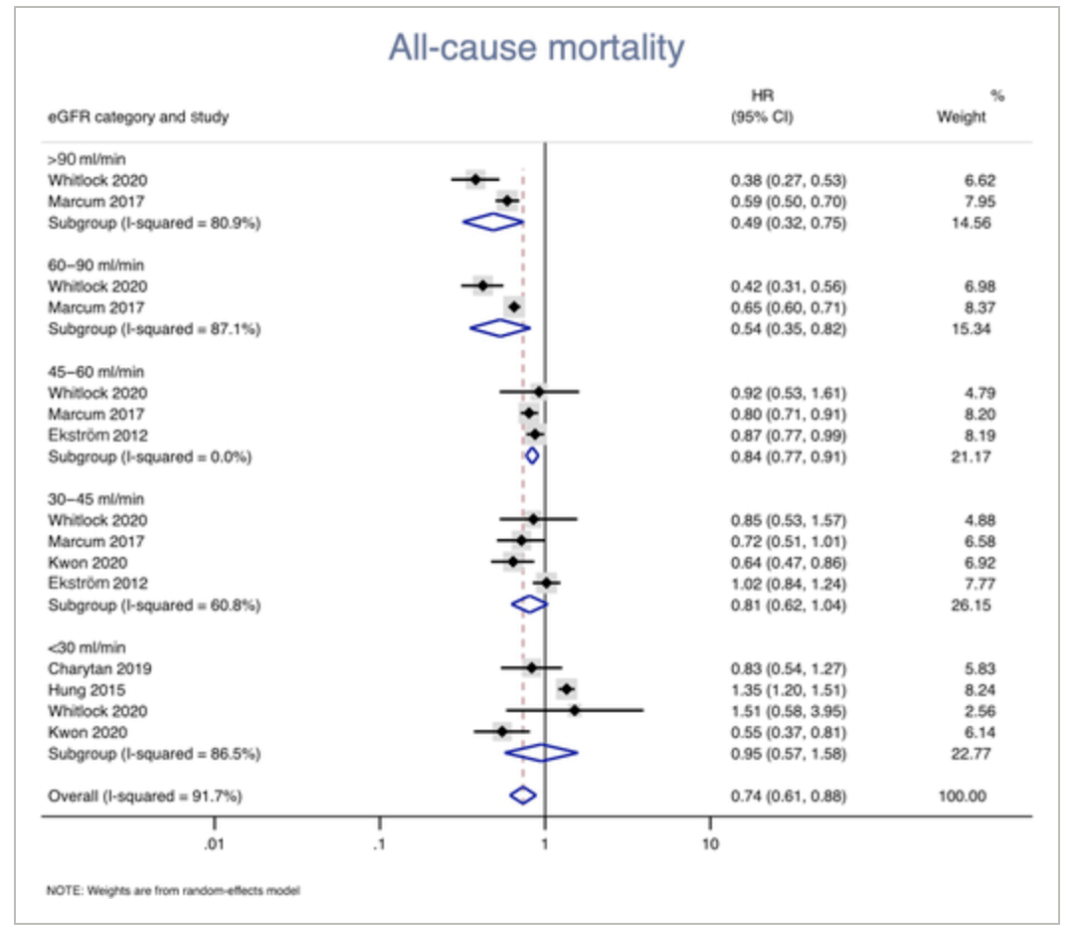
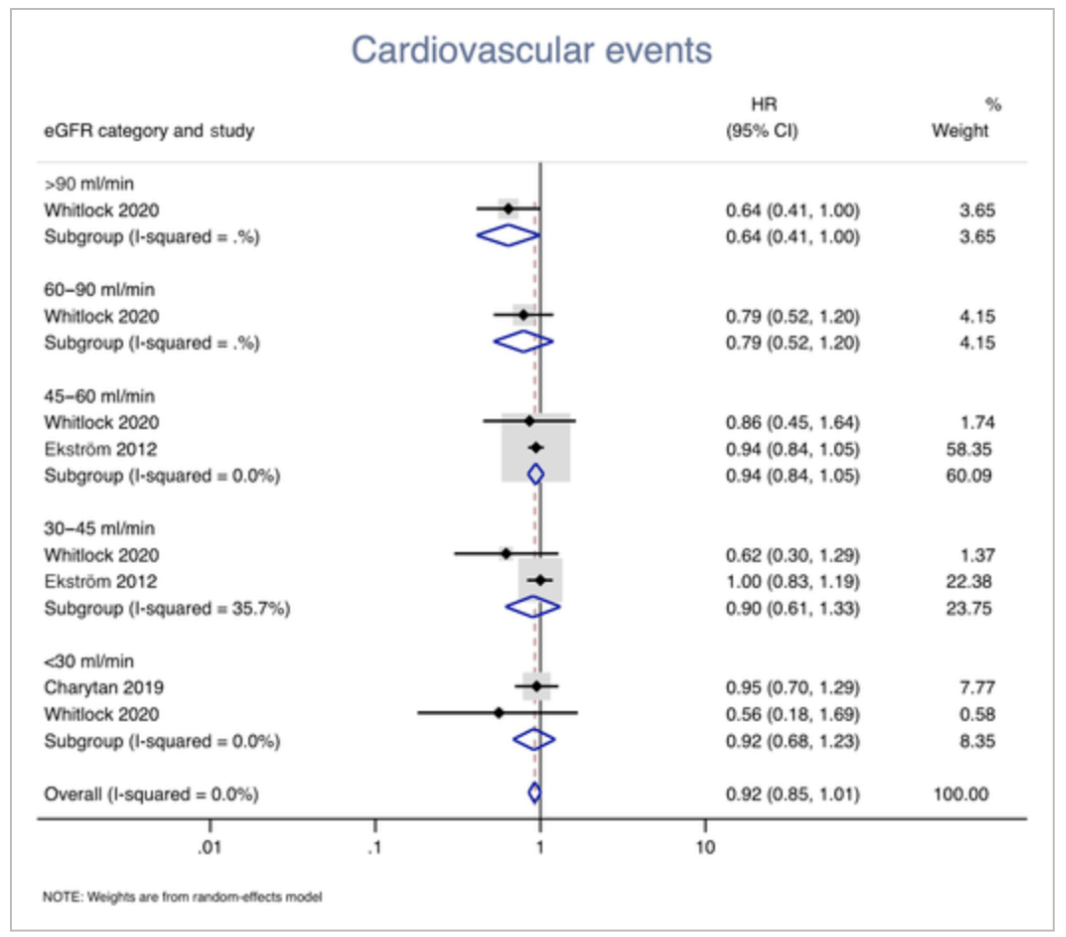
Other considerations
-IV contrast
-Discontinued starting the day of the procedures and up to 48 hours post-procedures if the eGFR is <6018
-Outpatient implications
Immunosuppressive medications increases the risk for several forms of malignancy. Which malignancy is the most common in renal transplant patients?
A. Non-Hodgkins lymphoma
B. Non-melanomatous skin cancer
C. Renal Cell Carcinoma
D. Cholangiocarcinoma
B. Non-melanomatous skin cancer
-Meta-analysis of 36,000 patients
Incidence
The pooled incidence of NMSC in renal transplant recipients was 12.6%
-55% cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
-Risk of cSCC development is 65-250 times greater than in non-transplant patients9
-Thorough skin check
A 39 y/o M w/ h/o IVDU, HIV and Hep C who is experiencing homelessness presents w/ 1 week of painful, erythematous skin wounds, found to have SSTI w/ strep bacteremia.
Vitals: BP 178/110, T 98.8F, HR 75, O2 98% on RA. Labs: s/f Cr 4.97 (3.1 two weeks ago at HUP), Ca 8.0, Alb 2.4, WBC 16.5, Hgb 7.7, Plt 411.
PE:
Skin: Scattered areas of necrosis at injection sites. No LE edema
UDS is positive for Amphetamines, Fentanyl, and Cocaine.
What labs/imaging would you like to work up his renal disease?
UA: 2+ protein, 2+ glucose, trace blood. Nitrite, LE ngd.
A1c: 5.7%
FENa c/w intrinsic renal disease
CK: 271 (22-198)
Renal US: refused
CD4: 142
Urine microalbumin: 15mg/g (wnl)
UPCR 21 mg/mg = 21,000mg/g (>0.2mg/g)
= 21g/day
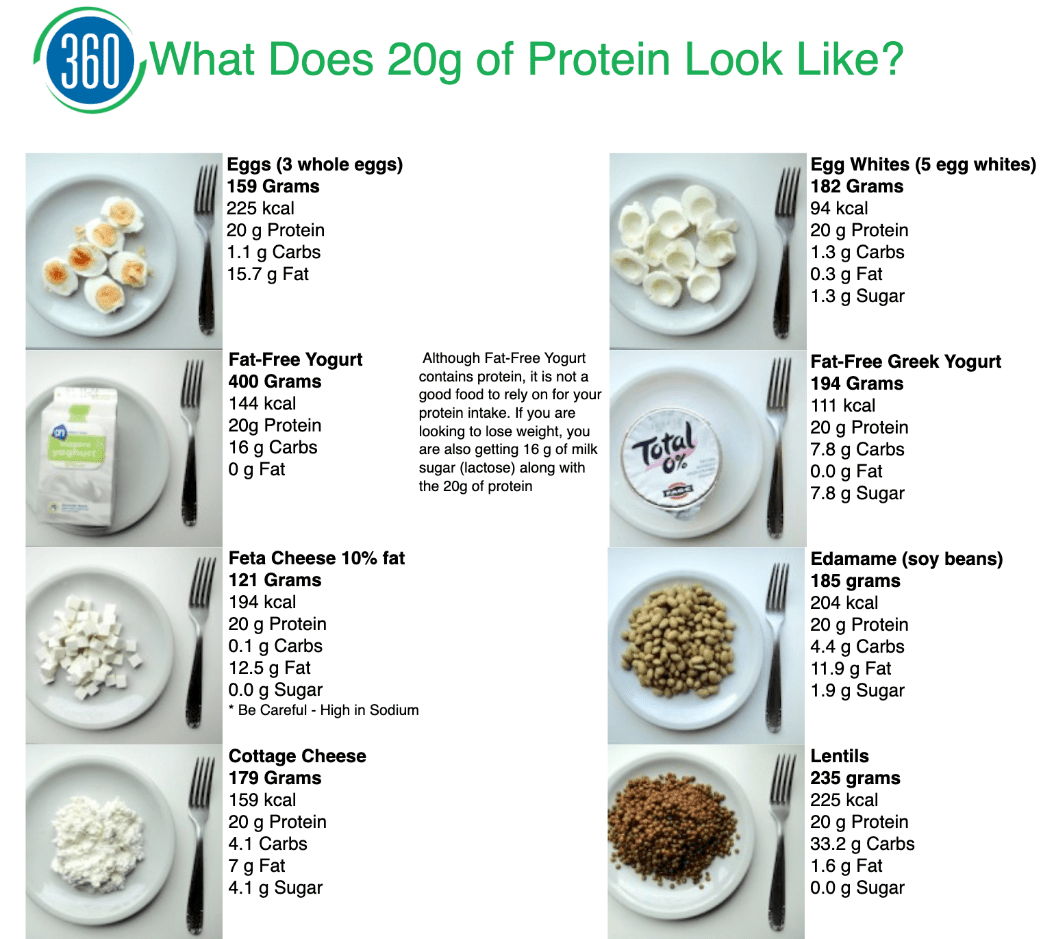
Source: https://sa1s3.patientpop.com/assets/docs/70318.pdf
A 36-year-old woman w/ h/o HTN presents to the ED with severe and colicky left flank pain that radiates to the groin. She reports increased urinary frequency and urgency.
PE: Afebrile, BP 148/73, HR 87, O2 98% on RA.
Abd: LLQ abdominal tenderness radiates to L CVA
Labs: WBC 8.7, Hgb 13.4, Plt 321. Cr 1.1 (BL 1.0)
CTAP reveals a 6mm stone in the left ureter.

What is the best next step?
A. Observation (Discharge)
B. Lithotripsy
C. Cystoscopy
D. Tamsulosin
D. Tamsulosin (for up to four weeks)
Size Guide
<=5mm - observation
6-10mm - tamsulosin 0.4mg daily for up to one month
> 10mm - referral to urology, possible intervention (lithotripsy)
Stone remains after four weeks of tamsulosin? ->Urologic eval
Confidence index
-Grade 2B recommendation
-Weak
-"this is our suggestion, but you may want to think about it"

A 45-year-old man is evaluated during an annual routine health maintenance visit. History is notable for NIDDM diagnosed 3 months ago. FHx s/f ESRD in his father at 64 2/2 T2DM. He reports no symptoms and takes no medications. Vitals: T 98.6F, BP 133/74, HR 70, RR 12. BMI is 30. PE s/f 1+ LE edema. Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 1.0 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Measure urine albumin excretion
B. Order kidney ultrasonography
C. Perform dipstick urinalysis
D. Start an angiotensin receptor blocker
A. Measure urine albumin excretion
-urine albumin/creatinine ratio
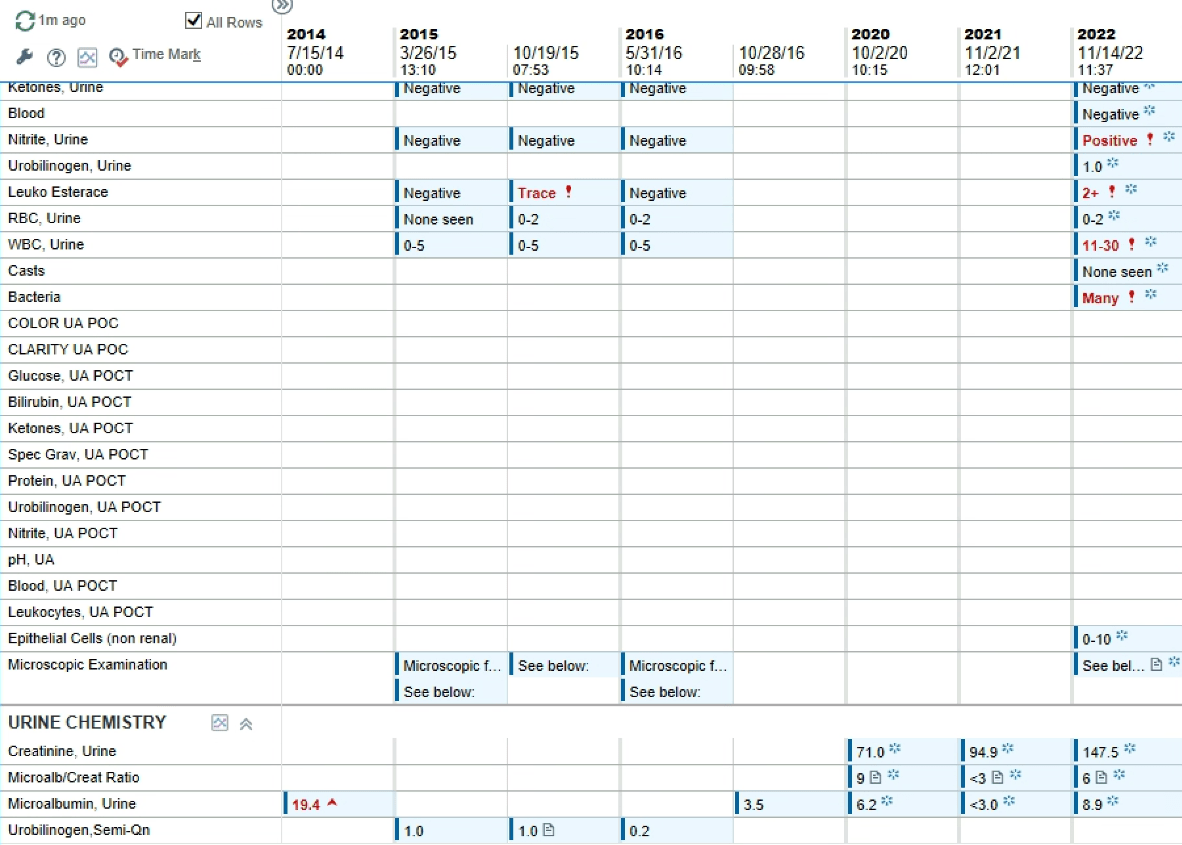
Screening:
-DMT1: 5 years after diagnosis
-DMT2: at time of diagnosis w/ yearly checks
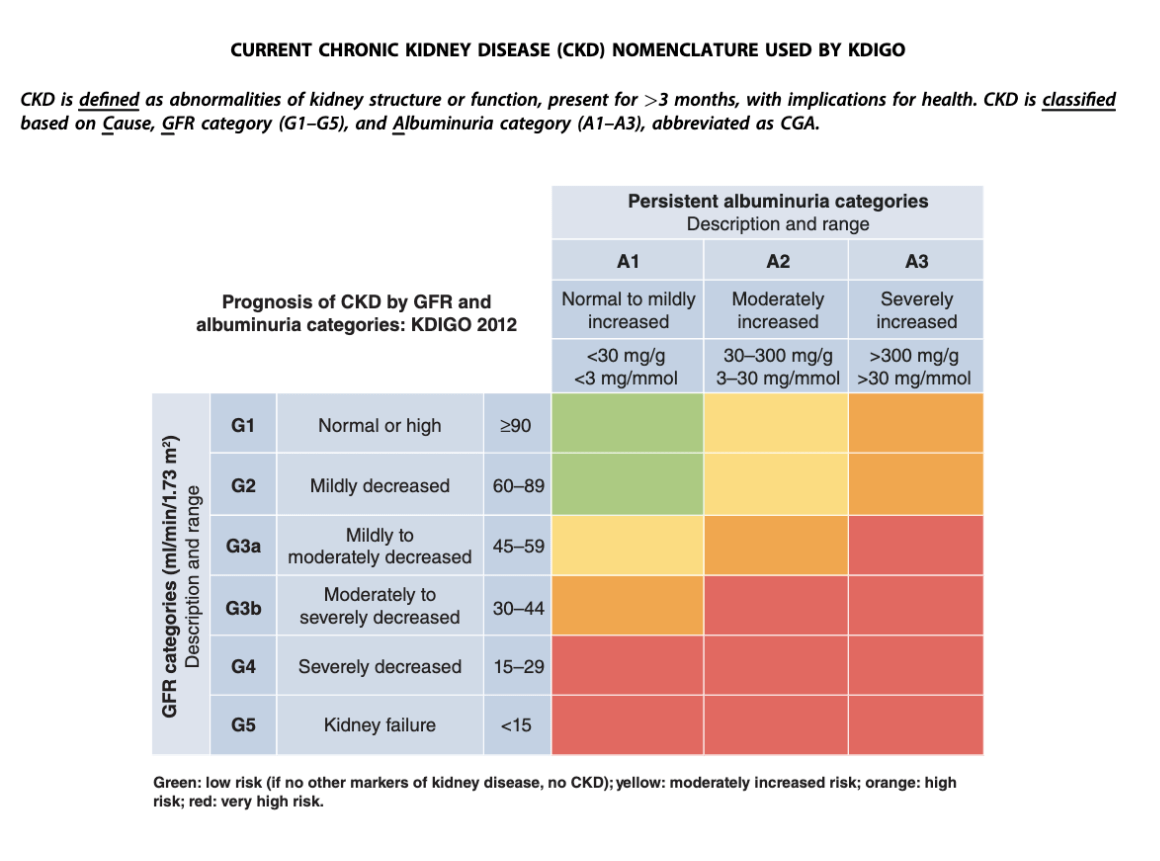
-The American Diabetes Association recommends yearly checks for albuminuria in T2 diabetics.
-Urine albumin to creatinine ratio of 30 to 300 mg per gram and 2 of 3 random samples obtained over 6 months makes the diagnosis.
-ACEi/ARB indicated if microalbuminuria present.
-In the absence of microalbuminuria, existing evidence does not demonstrate clear clinical benefit of RAS inhibition for CKD
-Microalbuminuria in a patient with diabetes is an indicator of cardiovascular risk.
-No need to measure urine protein excretion in patients who are taking ACEs or ARBs
Guidelines
-National Kidney Foundation and the American Diabetes Association: support screening for kidney disease in all patients with diabetes1
-American College of Physicians: insufficient evidence to support or discourage screening for CKD in persons with CKD risk factors such as diabetes
At which GFR should patients be referred to a kidney transplant center?
A. GFR 60-89 (G2)
B. GFR 45-59 (G3a)
C. GFR 30-44 (G3b)
D. GFR 15-29 (G4)
D. GFR 15-29 (G4)
-Tonelli et. al, 2011
-904,000 patients
-Mortality HR at 3 months after transplantation: 0.9–5.03
-Mortality HR at 1 year after transplantation: 0.19–0.49
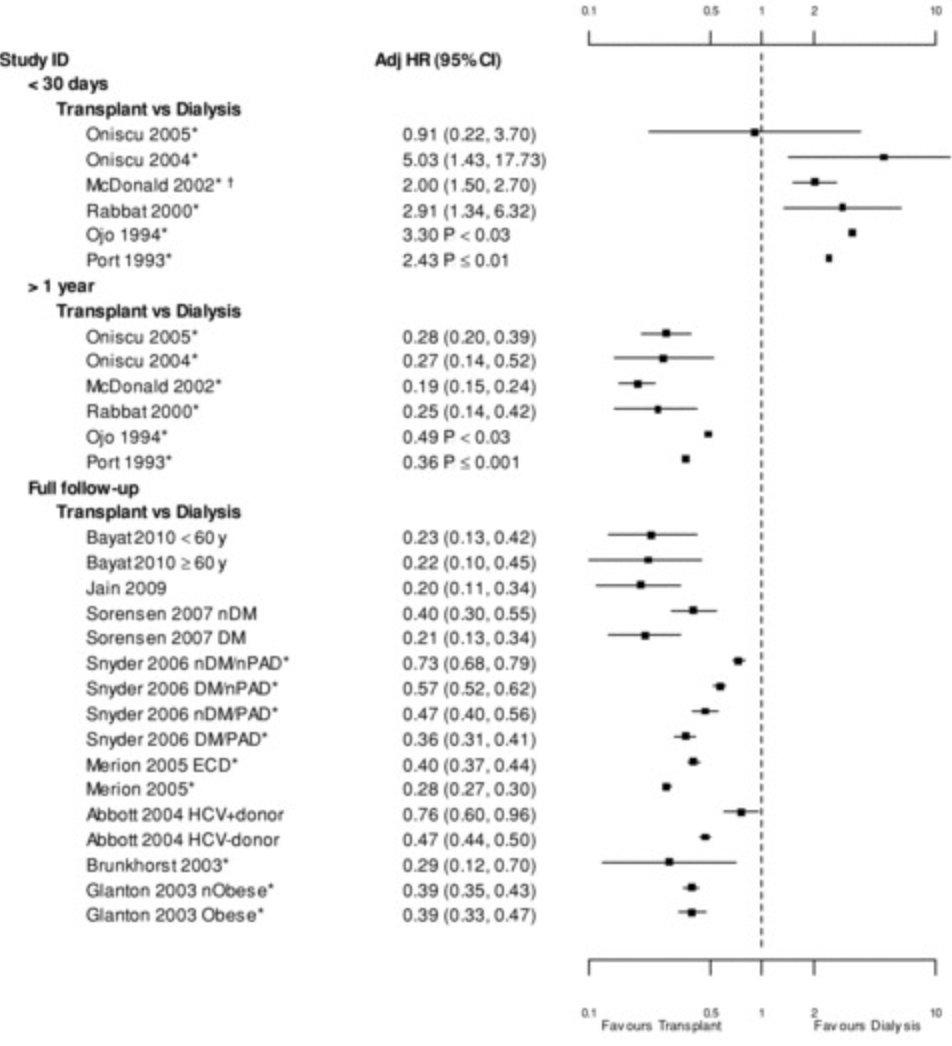
What about QoL?

A 39 y/o M w/ h/o IVDU, HIV and Hep C who is experiencing homelessness presents w/ 1 week of painful, erythematous skin wounds, found to have SSTI w/ strep bacteremia.
Vitals: BP 178/110, T 98.8F, HR 75, O2 98% on RA. Labs: s/f Cr 4.97 (3.1 two weeks ago at HUP), Ca 8.0, Alb 2.4, WBC 16.5, Hgb 7.7, Plt 411.
PE:
Skin: Scattered areas of necrosis at injection sites. No LE edema
UDS is positive for Amphetamines, Fentanyl, and Cocaine.
UA: 2+ protein, 2+ glucose, trace blood. Nitrite, LE ngd.
A1c: 5.7%
FENa c/w intrinsic renal disease
CK: 271 (22-198)
Renal US: refused
TTE: refused
CD4: 142
Urine microalbumin: 15mg/g (wnl)
UPCR 21 mg/mg = 21,000mg/g (>0.2mg/g)
What's on your differential diagnosis?
Membranous nephropathy - undiagnosed Hep B, syphilis, cancer
FSGS - HIV/AIDS
Minimal change disease - recent, ongoing infection
IgA Nephropathy - intermittent hematuria
Diabetic nephropathy
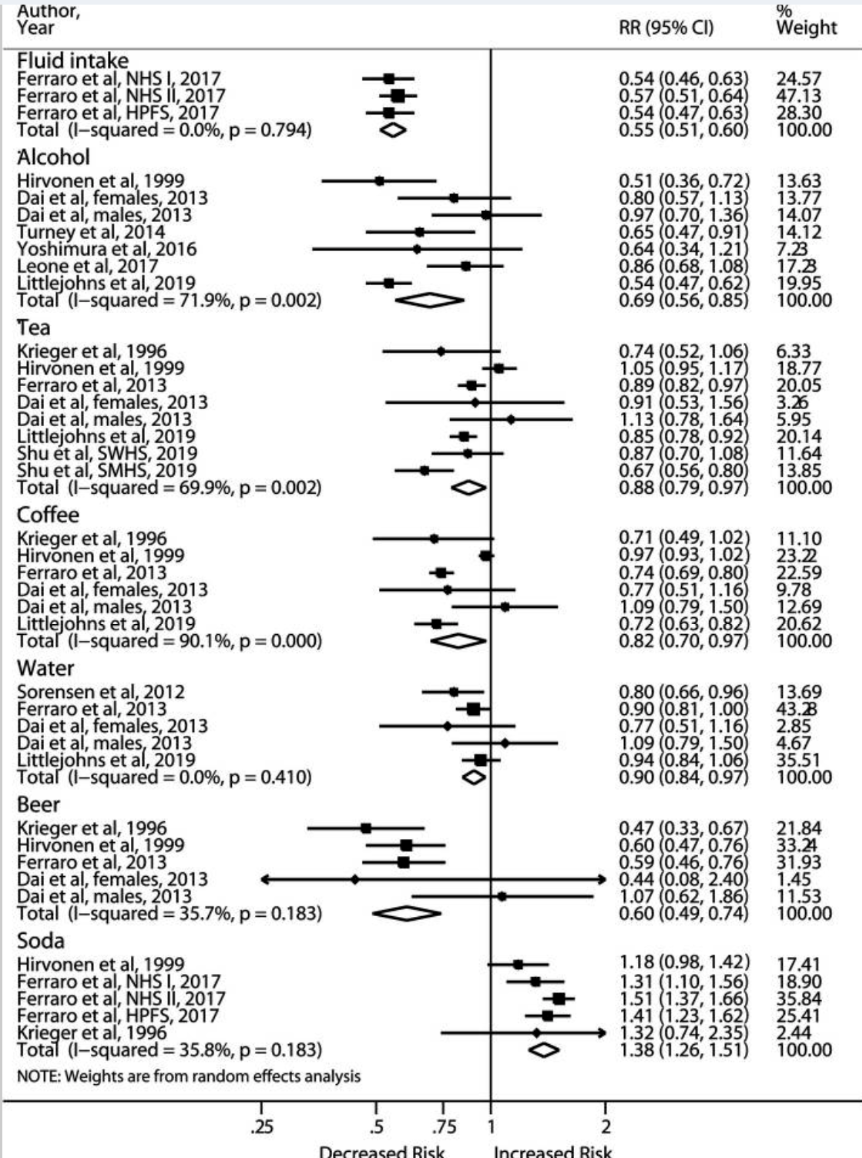
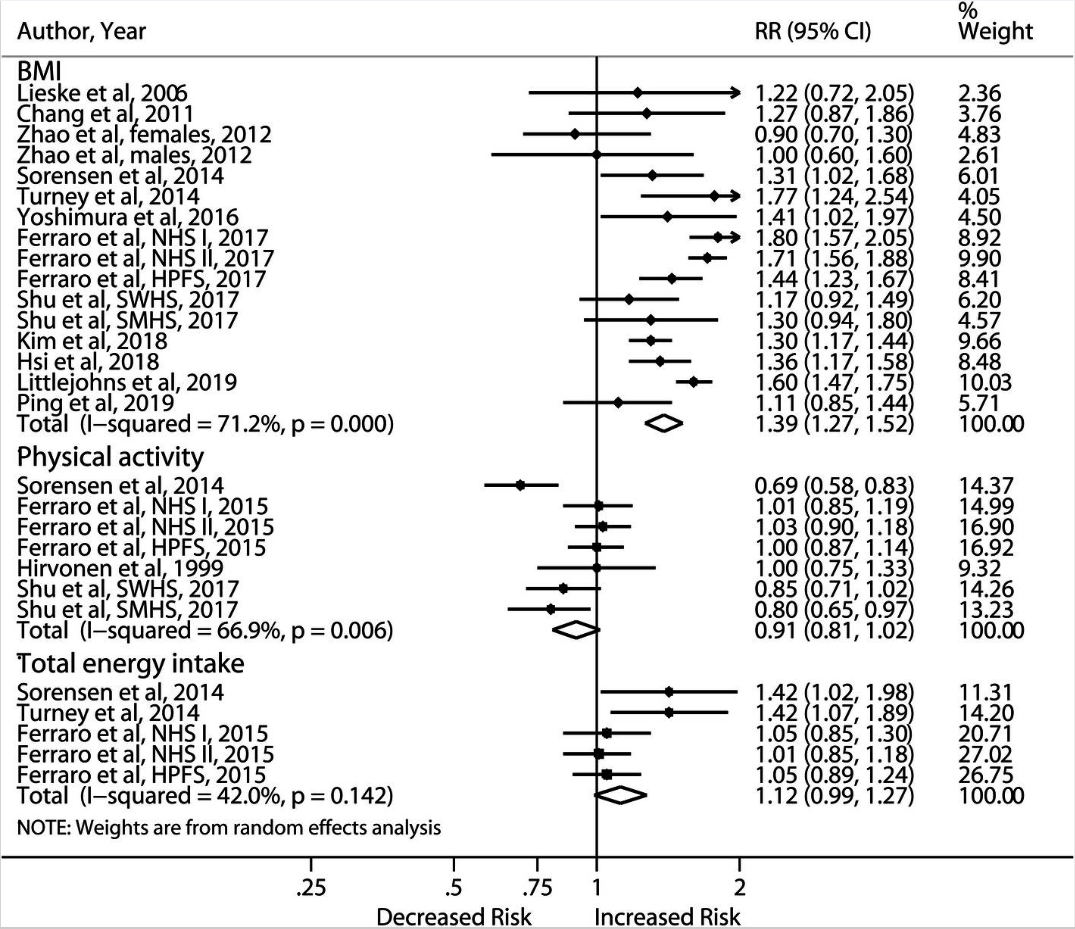
Regular consumption of which of the following beverages carries the highest risk for kidney stone formation?
A. Alcohol
B. Beer
C. Coffee
D. Soda
D. Soda
Comparison of high vs. low consumption14
1.1 million individuals

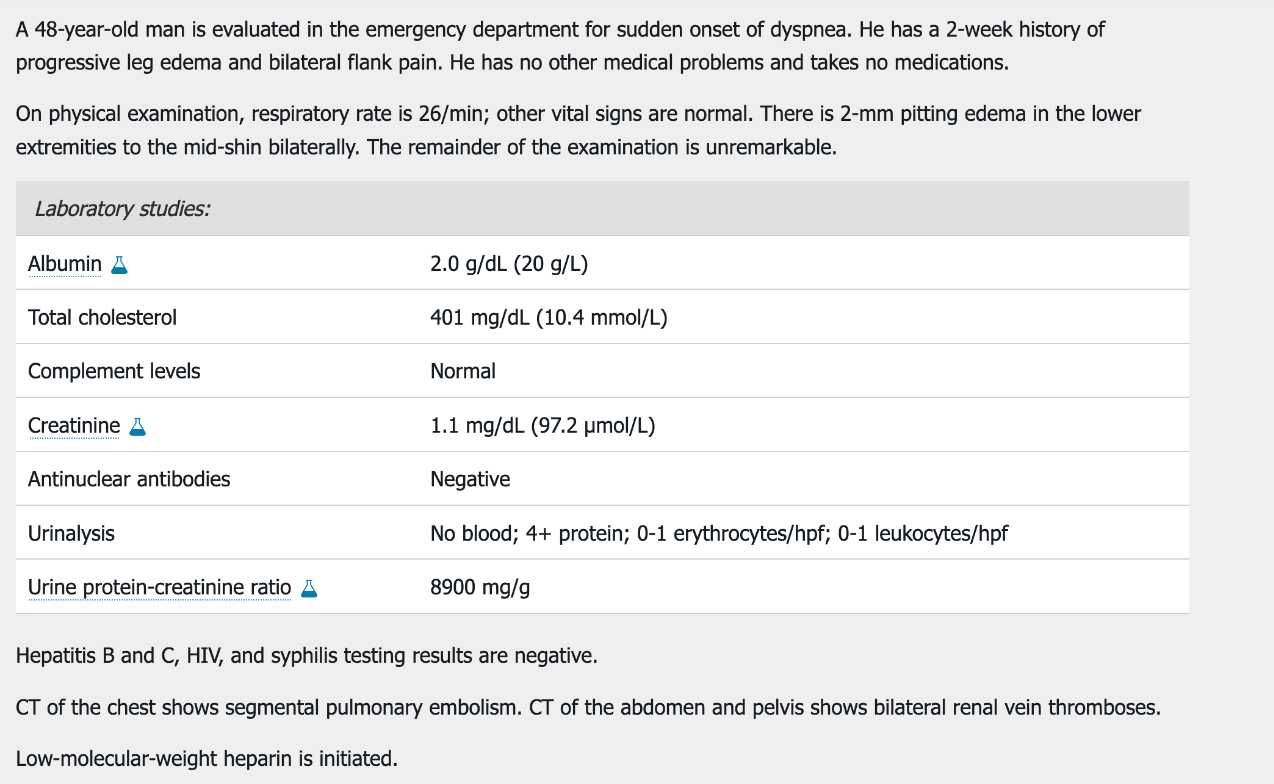 Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
A. ANCA antibodies
B. Anti-dsDNA antibodies
C. Anti-phospholipase A2 antibodies
D. Kidney biopsy following discontinuation of heparin
C. Anti-phospholipase A2 antibodies
"This patient with the nephrotic syndrome and venous thromboembolism most likely has membranous nephropathy. Patients with membranous nephropathy are particularly prone to thrombotic complications. These clots include lower extremity, pulmonary, and renal vein thromboses; they can occur in up to 25% of patients and are most likely to occur within the first 6 months of diagnosis. The risk for clotting increases when serum albumin is <2.8 g/dL (28 g/L) and increases proportionally with decreasing serum albumin levels."16
Which method of dialysis has a greater mortality benefit: Peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis?
They’re the same.
-Peritonitis from peritoneal dialysis averages 1 episodes every 2-3years, most often w/ GP skin flora1
-Patients >75 years, female, non-Caucasian, uninsured, of lower socioeconomic or educational status, or have multiple comorbidities are most at risk for non-referral for CKD care2
Referral timing
Meta-analysis of 17,646 patients:
Nephrology referral 3+ months before RRT = early
Nephrology referral within 3 months of RRT = late
-Significant mortality reductions in early group (OR 0.51; P<0.0001) and remained significant at 5 years
(OR 0.45; P<0.0001)4
Costs
-Mean total costs per patient over five years:
-$87,711 for early referrals
-$110,056 for late referrals
-Differences in mortality and hospitalization data between the 2 groups not explained by
differences in prevalence of diabetes mellitus, previous CAD, BP control, serum phosphate, and serum albumin5
How much $$$ does HD cost Medicare per patient, per year?
A. $34,000
B. $56,000
C. $89,000
D. $112,000
C. $89,000
-Annual cost of kidney transplant? $35,00011
-Transplant insurance breakdown:
Medicare - 60%
Private - 32%
Medicaid - 6%
-Patients with ESRD are automatically eligible for Medicare, regardless of age
-Covers pretransplant workup, perioperative inpatient care, provider professional fees, and immunosuppression.
-Typically only covers 80% of costs
-Medicare eligibility ends at 3 years post-transplant, unless the recipient is aged ≥65 years or disabled
-Comprehensive Immunosuppressive Drug Coverage for Kidney Transplant Patients Act (December 2020)
-Extends Medicare immunosuppression coverage for the life of the transplant12
You get a call from the nurse on 10T:
"Hey I just went into his room and he looks really uncomfortable, is having some chest tightness and complaining of shortness of breath. He's also refusing to get vitals. Will you come take a look at him?"
What's on your differential? How does his (kidney) history affect your differential?
A 54 y/o woman w/ h/o pAF on eliquis, HTN, HLD, hypothyroidism, and OSA on CPAP is stepped down from the MICU after p/w severe urosepsis 2/2 obstructive kidney stone. On the morning of discharge she asks you what changes she can make in her diet to decrease the risk of future stones. Which of the following foods are high in oxalates?
A. Peanuts
B. Spinach
C. Dark chocolate
D. Sweet potatoes
Peanuts, nuts (especially almonds), legumes (navy beans), spinach, swiss chard, dark chocolate, sweet potatoes, tofu
Uric acid stones
-high-purine foods like red meat, organ meats, meat-based gravies, sardines, anchovies and shellfish15
A. Add a phosphate binder
B. Discontinue all medications except insulin
C. Intensify hypertension management
D. Refer for hospice care
C. Intensify hypertension management
-Shared decision-making
-Multidisciplinary approach
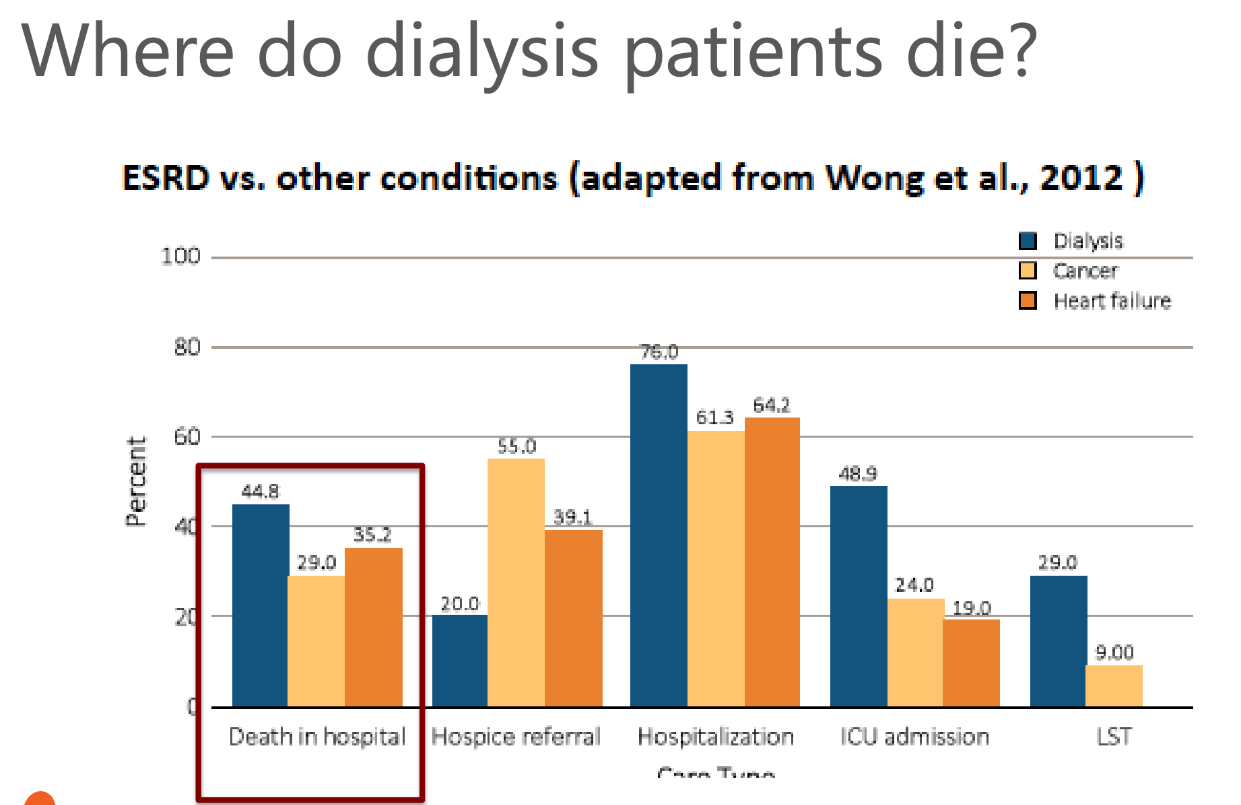
-Comfort focusedWhat percent of patients withdraw from RRT before death?
A. 5-15%
B. 16-25%
C. 26-35%
D. 36-45%
Bonus: What is the life expectancy after withdrawal of dialysis?
B. 16-25%
-For patients who withdraw from RRT, death usually occurs within 8-10 days.
-Patient and loved ones should be counseled on the likelihood of progressive encephalopathy
-Reported prevalence of patient MDM at time of withdrawl range from 37% to 80%6
Symptom prevalence
Confusion/agitation 70%
Pain 55%
Dyspnea 48%
Nausea 36%
Twitching/seizures 27%
Pruritis 24%
Peripheral edema 21%7
A 62 y/o FM w/ h/o T2DM, HTN, HLD, OSA, and ESRD s/p renal transplant two months ago presents w/ new onset productive cough and dyspnea x 1 week, found to have consolidative PNA on CXR. She is UA collected on admission is nitrite and LE NGD but shows 3+ proteinuria w/ no RBCs or WBCs.
Which of the following is the most common glomerular disease in renal transplant patients?
A. Membranous nephropathy
B. FSGS
C. IgA Nephropathy
D. HUS
B. FSGS
-Idiopathic FSGS
-Pathogenesis unknown, suspected circulating factor toxic to podocytes

FSGS
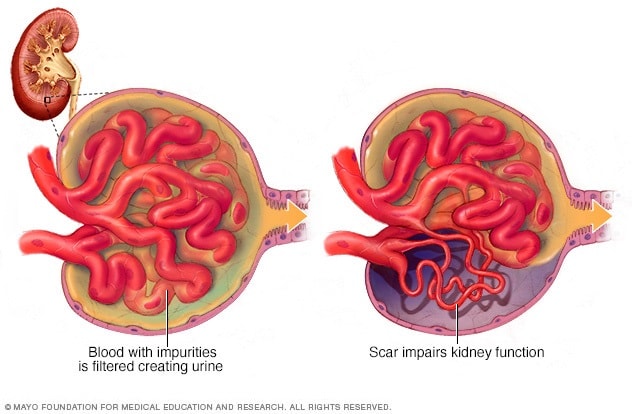
-HIV infection of tubular and glomerular epithelial cells
What percentage of kidney stones are calcium oxalate?
A. 50-60%
B. 60-70%
C. 70-80%
D. 80-90%
C. 70-80%
Breakdown
Calcium oxalate: 70-80%
Calcium phosphate: 15%
Uric acid: 8%
Struvite: 1% (more common in females)

 Sources:
Sources: