Fill in the blanks.
___________ shoes should be always worn when working in the laboratory.
Closed toe
TRUE or FALSE
Always add acid to water, not the other way around.
TRUE
This refers to the level of biocontainment precautions required in isolating biological agents in an enclosed facility.
Biosafety Levels (BSL)
What does MSDS stands for?
Material Safety Data Sheet
What do you call the GHS document shown below?

The Purple Book
It is used to protect oneself when working with hazardous materials.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
How should you dispose of hazardous chemical waste?
(a) Place it in the regular trash bin.
(b) Store it indefinitely for future use.
(c) Pour it down the sink with plenty of water.
(d) Follow proper disposal guidelines and regulations.
(d) Follow proper disposal guidelines and regulations.
How many biological safety levels are there currently?
4
This section of the SDS requires information which includes appearance, odor, odor threshold, pH, melting/freezing point, initial boiling point and boiling point range, flash point, evaporation rate, flammability, explosive limits, vapor pressure, vapor density, relative density, solubilities, partition coefficient, auto-ignition temperature, decomposition temperature and viscosity
Physical and chemical properties
What are the three hazard classifications according to GHS?
physical, environmental, health
These are primarily used to protect the eye and face area against chemical splashes, dusts, and vapors.
Laboratory goggles and face shields
What does the “corrosive” symbol on a chemical container indicate?
(a) The chemical is explosive.
(b) The chemical is highly toxic.
(c) The chemical can cause electric shocks.
(d) The chemical can cause severe burns or damage to materials.
(d) The chemical can cause severe burns or damage to materials.
This level is suitable for work involving biological agents that can cause moderate potential hazard to humans and the environment.
Biosafety Level 2
Identify which section should the information below be included.
In case of skin contact, wash off with soap and plenty of water.
Section 4: First-aid measures
What does GHS stands for?
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals
Explain why the following rule is important in maintaining safety in the research laboratory.
You should never work alone in the laboratory.
There is always risk when working with hazardous materials. These risks are heightened when one is working alone in the laboratory because help is not readily available in case of emergency.
What should you do in case of accidental exposure (spills or splashes)?
Inform the laboratory supervisor and evacuate the area.
This level is suitable for any work with dangerous and exotic agents that pose a high individual risk of aerosol-transmitted infection, which can cause severe to fatal disease in humans.
Biosafety Level 4
Identify which section should the information below be included.
Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions. -Carbon oxides, Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Section 10: Stability and Reactivity
Which element of a GHS label is represented by #2?
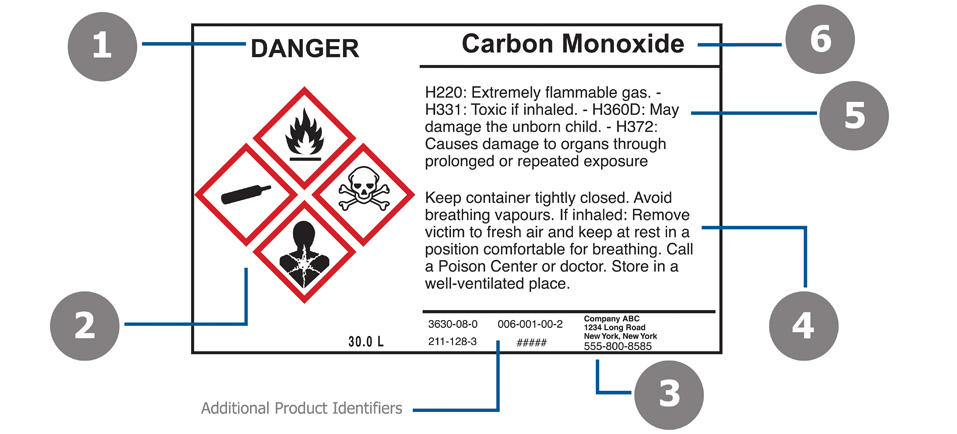
Hazard Pictograms
Enumerate the three different types of gloves which may be used in the laboratory depending on what will be handled.
nitrile, butyl and neoprene gloves
disposable latex and vinyl gloves
temperature-resistant gloves
Describe the procedure for smelling a chemical.
Point vessel away from face while gently fanning vapors toward nose
Which of the following definitions best describes disinfection?
a. The use of antimicrobial agents on inanimate objects to destroy all non-spore-forming organisms that could pose a hazard to humans or compromise the integrity of an experiment.
b. Processing clean items to kill all living agents.
c. Application of a liquid antimicrobial chemical to living tissue to prevent infection.
d. Heat treatment of a liquid for the destruction of non-sporeforming organisms.
The use of antimicrobial agents on inanimate objects to destroy all non-spore-forming organisms that could pose a hazard to humans or compromise the integrity of an experiment.
List 8 sections of the safety data sheet.
Chemical Product and Supplier’s Identification
Hazard Identification
Composition or Ingredient information
First-aid measures
Fire-fighting measures
Accidental release measures
Handling and storage
Exposure controls and personal protection
Physical and chemical properties
Stability and reactivity
Toxicological information
Ecological information
Disposal considerations
Transport information
Regulatory information
Other information
What does this hazard pictogram mean?

Biohazardous infectious materials