Name the condition involving a broken bone that protrudes through the skin (be specific)
Open/compound fracture
Perform an effective FAST assessment on a partner.
Face: inspect for drooping
Arms: hold them up with eyes closed
Speech: must repeat a semi-complex sentence (you can't teach an old dog new tricks)
Time: time of symptom onset (or last seen well) + time to call 10-52
List out the compression:breath ratios for adult, child, infant, neonate. When do these change?
Adult: 30:2 (always)
Child: 15:2 (2-person)
Infant: 15:2 (2-person)
Neonate: 1:3 (always)
What is perhaps the most important question to ask in an acute mental health risk assessment?
Are you thinking of suicide?
How many geese can colton take on?
What is your first step when you suspect a patient has external bleeding?
Expose/inspect the wound
What is the adult and child dose of epinephrine in an EpiPen?
0.3mg / 0.15mg
What is the maximum amount of time a BLS provider should simultaneously check for a pulse and breathing?
10s normal
45s–1min hypothermia
What is anxiety versus anxiety disorder?
Anxiety = normal daily stressors, evolutionary basis
Anxiety disorder = abnormal or debilitating response to stressors
What's the best campus response team in Canada?
SERT!! ;) shhh
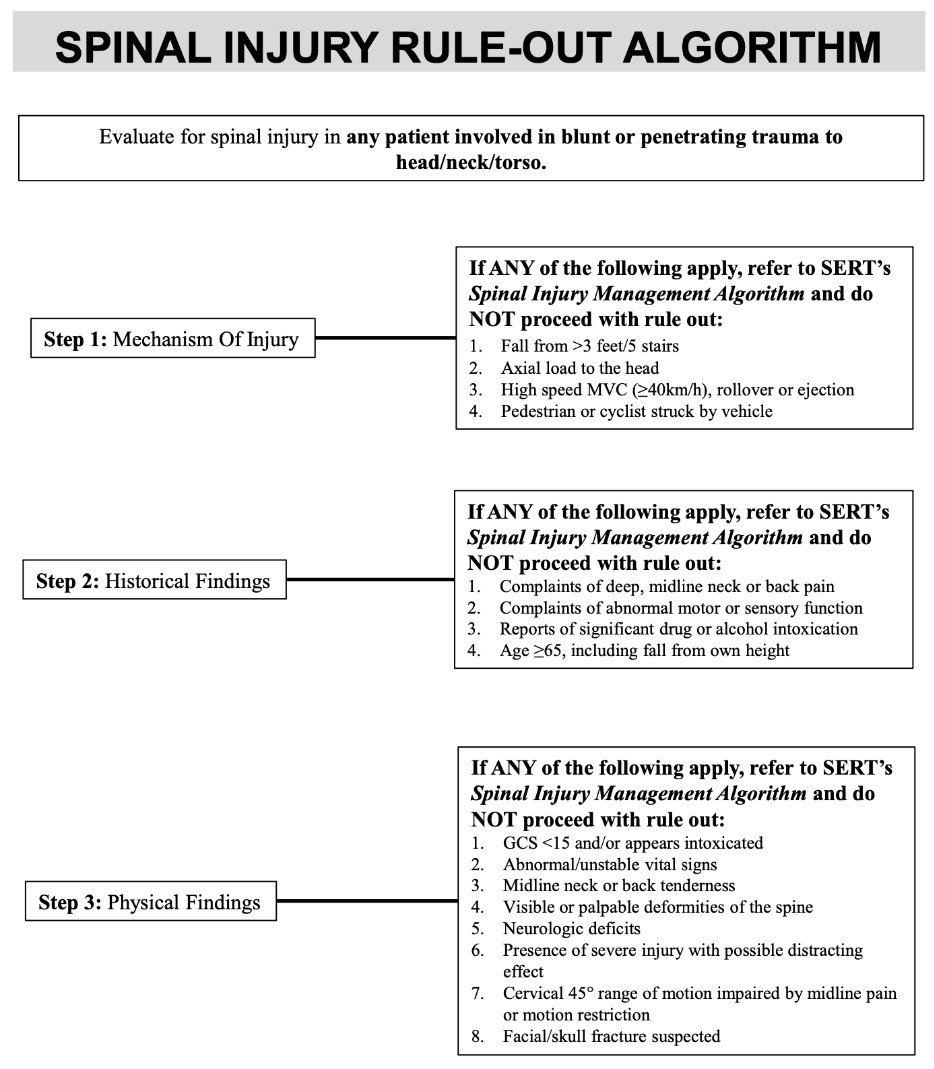
List out the spinal rule out
Name and describe 6 types of shock with examples:
Hypovolemic Shock: Absolute or relative blood loss from haemorrhage or massive vasodilation.
Cardiogenic Shock: Heart's inability to pump blood effectively due to damage or dysfunction (heart attack or cardiac arrest).
Septic Shock: Triggered by a severe infection leading to vasodilation and hypotension.
Neurogenic Shock: Caused by spinal cord injury or nervous system damage leading to widespread vasodilation.
Anaphylactic Shock: Severe allergic reaction causing vasodilation, airway constriction, or other systemic responses.
Obstructive Shock: Physical obstruction to blood flow such as with a pulmonary embolism or cardiac tamponade preventing effective blood circulation.
List 3 differences between the scope of BLS versus CPR-C.
What level comes after BLS and list 1 difference between that level and BLS.
1) Pulse check
2) BVM use
3) 2-person/high-performance CPR
ACLS comes after BLS and involves ECG rhythm interpretation, cardiac pharmacology, and manual defibrillation.
Define and differentiate empathy versus sympathy
Sympathy: knowing/understanding what someone is going through (requires recognition and critical thinking)
Empathy: feeling what someone is going through (requires experience and looking within)
Who are the 2 co-founders of SERT? What positions did they hold at Western? What year was SERT founded?
Robert Garland, Student
Dr. Tom Macfarlane, Director of Student Health Services
EST 1989
One attempt to perform a PERFECT primary trauma assessment.
DCAPP-BLS-TIC
Head, ears, eyes, nose, ABCs, facial bones
Neck, mid trachea, no JVD, c-spine, med alert
Chest, clavicles, sternum, ribs+bilateral expansion,
Back, wet check
Abdomen, consent expose, 4 quadrants, rebound
Pelvis, be careful, down, in
Femurs, be intentional, sager if needed,
Med alerts ankle, forearms, other
Does insulin OD cause hyper or hypoglycemia? Is this better or worse than a physiological response caused by fasting? Why?
During fasting hypoglycemia, the body has low blood sugar from not eating, but the liver is still able to raise blood sugar levels using glycogenolysis or gluconeogenesis.
During insulin OD, insulin will inhibit the liver's ability to break down glycogen or make new glucose through gluconeogenesis and BGL can become severely low.
What are the two ECG rhythms that require non-synchronized cardioversion (i.e., defibrillation)? Be specific
1) Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)
2) pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (pVT)
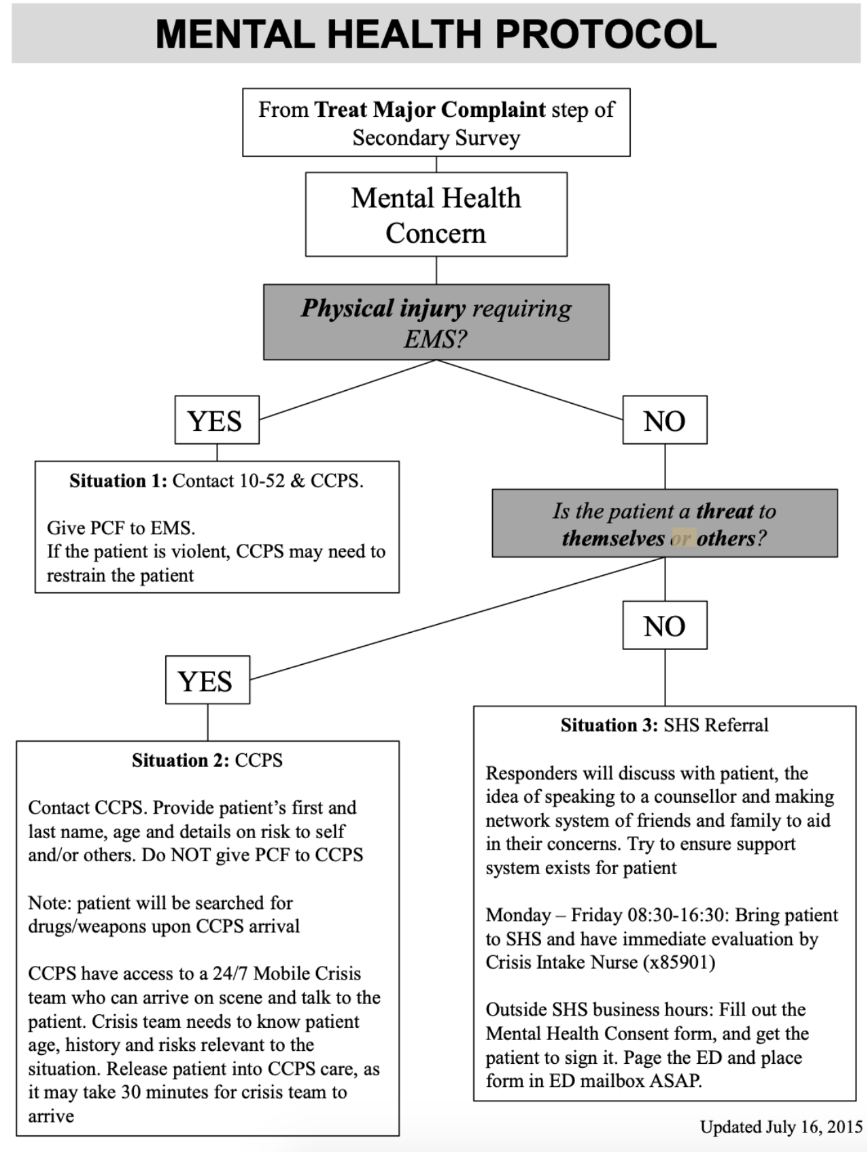
Draw or clearly describe the SERT MH flowchart protocol.
What year did Ryan make it onto SERT?
2019
V24h = (4(ml)/(%*kg))*(BSA%)*(Pt Weight Kg)
You are called to assess a 46 Kg male patient with partial thickness burns on their anterior L arm, whole anterior abdomen and chest, and posterior head.
Using the Parkland formula provided and any additional resources, what volume of ringer's lactate solution should be given to this patient in the next 8 hours?
BSA% = 4.5 + 18 + 4.5 = 27%
V24h= 4*27*46 = 4968 mL
V8h = 2.493L
Talk about the following with respect to A) epinephrine; B) salbutamol; C) ASA; D) nitroglycerine; and E) naloxone.
1) Indications
2) Contraindications
3) Drug class + mechanism + receptors involved
Epi = susp anaphyl, <1y/o, B1/B2 agonist, GPCR
Sal = asthma, AGMP, SABA-b2, GPCR
ASA = unstable ang/MI, 6 contr, COX1/2
Nitro = decomposes NO
Nal = mu opioid receptors
A diabetic patient with a severe peanut allergy is choking on a Reese's pieces cookie and falls unconscious when you arrive on scene, hitting their head. While checking their ABCs, the patient begins to seize and vomits ~500ml with blood. You also find a prescription for opioids in their pocket.
Explain your steps in this patient's initial management.
10-52
check pulse
clear airway
no breathing = BVM
give epi for suspected anaphylaxis
compressions if resistance from FBAO
give second epi if needed
hold c-spine when patient awakens
BGL + glucose if necessary
symptoms may be hypoglyc or post-ictal
naloxone indicated if suspected opioid OD
Differentiate these terms:
1) Psychosis
2) Schizophrenia
3) Delusion
4) Hallucination
5) Mania
6) Dissociation
Psychosis: A symptom characterized by a loss of contact with reality, often featuring hallucinations and delusions.
Schizophrenia: A mental disorder involving a range of symptoms, including psychosis, but also involving chronic problems with emotions, behaviors, and social functioning.
Delusion: A false, fixed belief held with strong conviction despite superior evidence to the contrary.
Hallucination: A sensory perception in the absence of external stimuli, like hearing voices or seeing things that aren't there.
Mania: A state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, often seen in bipolar disorder.
Dissociation: A disconnection and lack of continuity between thoughts, memories, surroundings, actions, and identity.
A ____ is a funny piece of equipment because it _____
A sager is a funny piece of equipment because it pulls your leg