New onset dyspepsia (early satiety, post-prandial fullness and epigastric pain)
Patient >60 years with GERD s/s
Next test
What is an upper endoscopy?
Achy sharp pain around patella with "locking", "giving way"
Worse with prolonged sitting, activities like squatting, running
O/E: Normal ROM, mild crepitus in retropatellar region
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome?
Pain typically occurs on direct compression of the patella during knee extension
T/t: PT, Quadriceps and hip abductor strengthening
Earliest and most sensitive echocardiographic finding of cardiac tamponade
What is R atrial collapse?

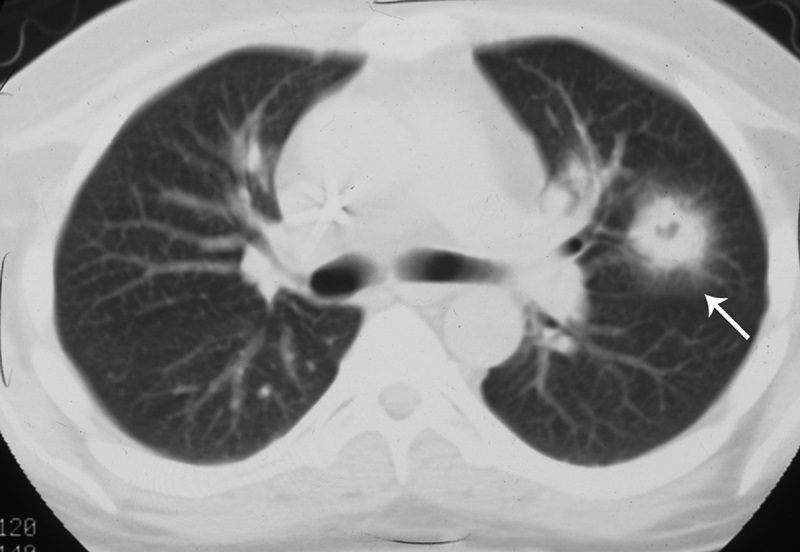
Ground glass attenuation surrounding nodule on lung CT
Name of sign and organism
What is "Halo sign"
Associated with angioinvasive fungi like aspergillosis-usually seen in patients with profound and prolonged neutropenia and stem cell and solid organ transplantation.
Halo sign: wedge-shaped densities
Primary CV Side effect of Bevacizumab
What is hypertension?
With a greater amount of gastric mucosal changes in the gastric antrum than the fundus, this condition occurs due to exposure to dietary carcinogens and H.pylori
HINT: also increases risk of gastric cancer
What is EMAG (Environmental Atrophic Gastritis)?
The other one is AMAG (AI Metaplastic Atrophic Gastritis): typically associated with other AI conditions like vitiligo and thyroid disease. These patients are more prone to developing pernicious anemia
This pharmacotherapy can be administered for patients with moderate to severe Alcohol use disorder
What is Naltrexone?
-helps to reduce cravings and heavy drinking. Can initiate in people still drinking and no significant liver disease
Other medications:
-Chlordiazepoxide
-Disulfiram
Drug treatment of HF related cardiogenic shock
What is Dobutamine or Milrinone?
Cardiogenic shock is defined by persistent symptomatic hypotension and end-organ dysfunction
Patients present with:
-AKI
-Evidence of liver dysfunction with elevated LFTs
-Poor peripheral perfusion with cool extremities and impaired mental status
Inotropes can improve cardiac function and perfusion. AVOID milrinone in those with impaired renal function as milrinone is excreted through kidneys and can accumulate
Prophylactic therapy in HIV + patients with CD4 <200
What is TMP-SMX?
Alternate therapies: -Dapsone
-Atovaquone
PCP is the main organism for CD 4<200
In CD4 <150: Histoplasma
In CD4 <100: T.gondii
Basophilic leukocytosis +/- eosinophilia with hepatosplenomegaly and fatigue is suspicious for this condition
What is CML?
Nearly 90-95% patients will have Philadelphia chromosome. The resulting BCR-ABL fusion can be detected in peripheral blood
Painless obstructive jaundice with 'sausage-shaped' pancreatic enlargement on imaging
Responds to steroids
BONUS (100): What serum level will be increased?
What is AI pancreatitis?
Type 1: Older men commonly associated with pancreatitis, Sjogren's syndrome, PSC, bile duct strictures.
Type 2: Chronic pancreatitis and IBD
BONUS (100): Type 1 will often have elevated serum IgG4 (Type 2 may not)
Episodic vertigo (20 mins-several hours)
SNHL
low frequency tinnitus with a fullness in the affected ear
Diagnosis
BONUS 100: Treatment
What is Meniere's disease?
Inner ear disorder c/terised by increased volume and pressure of endolymph
BONUS (100): Salt restriction, reducing caffeine and alcohol use and diuretics
4 Indications for exercise stress testing with imaging
-LBBB
-LV hypertrophy
-Patient on digitalis
-Pre-excitation
-Paced beats
*Keep note that if a resting EKG demonstrates LV hypertrophy with significant repolarization abnormalities (ST segment depression >0.5mm), it limits the ability to interpret the EKG during exercise. So you need adjunctive imaging either an echo or a NM scan
In females with recurrent genital HSV, daily suppressive therapy with this medication is the most effective strategy to reduce HSV transmission
What is valacyclovir?
Will accept Acyclovir and Famciclovir
*Note: Condom use is beneficial to reduce male to female transmission but doesn't reduce female to male transmission
Treatment of choice for TTP
Do NOT order platelet transfusion use it can exacerbate microvascular occlusion
REMEMBER: Coagulation studies will be normal in TTP but there will be hemolytic anemia (Increased LDH, reduced haptoglobin), reduced PC
Chronic diarrhea with fever, cardiac disease, ocular symptoms and neurological symptoms
Diagnosis
BONUS (100): Duration of antibiotics
What is Whipple disease?
Diagnosis requires small bowel biopsy and PCR for Tropheryma whippleii
BONUS (100): Antibiotics for 12 months
Reduced sensation to pinprick and light touch over antero-lateral upper thigh in this disorder
BONUS (100): What is the nerve involved
What is Meralgia parasthetica
BONUS (100): Lateral cutaneous nerve
DIFFERENTIATE from Trochanteric bursitis: causes lateral hip pain over outer thigh WORSE with flexion (climbing stairs, getting out of a car)
Diagnostic test for PAD if ankle-brachial index is >1.4
What is toe-brachial index?
ABI of <0.9: PAD
ABI >1.4: calcified, noncompressible arteries. In this case, a toe-brachial index is measured
Toe-brachial index <0.7 is indicative of PAD
Cause of swimming pool diarrhea
What is Cryptosporidium?
Protozoal infection with Cryptosporidium is the most common cause of swimming pool related outbreaks of diarrhea
Diagnosis: stool Ag testing and stool microscopy
What is incentive spirometry?
Also start hydroxyurea
A 29 year old patient was diagnosed with hepatitis B infection (HBV) 10 years prior with likely vertical transmission (at birth)
Patient feels well. No other PMH
Labs: Positive HbeAg, HbsAg and serum HBV DNA level is 20,000, 000 IU/ml with normal LFTs
This is the next best step
A: Entecavir
B: Hepatic U/S
C: IFN
D: Repeat LFTs in 6 months
E: Tenofovir
What is
D: Repeat liver chemistry in 6 months
Manage immune tolerant phase of Hep B
There are 4 phases of HBV infection:
1. Immune tolerant
2. Immune active
3. Immune control
4. Reactivation
Not all patients go through each phase but patients in immune tolerant phase do not have significant inflammation, no fibrosis and don't require treatment
However, it can progress so serial LFTs need to be done
Sildenafil use can be associated with these ocular S/E
What is:
-Bluish discoloration of vision
-Non- arteritic Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
Think of this condition in patients with R sided HF and a history of radiation
EKG: low voltage QRS
Echo: pericardial thickening and biatrial enlargement
What is Constrictive pericarditis?
Characterized by adherent pericardium that restrains ventricular diastolic expansion causing impaired filling
CAUSES: Cardiac surgery, TB, Radiation and post-acute pericarditis
O/E: Kussmaul's sign, pericardial knock and a friction rub
CXR: calcified pericardium

Treatment regimen of Cryptococcal meningitis
Amphotericin B and Flucytosine x 2 weeks
Followed by Fluconazole 800mg daily x 8 weeks
Followed by Fluconazole 200mg daily x1 year
*NOTE: Steroids are of no use here. The aim is to reduce ICP not reduce vasogenic edema
Patient needs serial lumbar punctures to reduce ICP
Diagnosis
BONUS (200): Treatment
What is acute intermittent porphyria
Typically triggered by starvation, drugs (sulfa drugs), stress and infection
BONUS (200): Symptomatic therapy
-glucose loading
-Hemin (iv)