This variable in an experiment is often called the "manipulated" variable because it is the variable being tested.
What is the independent variable.
In scientific terms the Greek prefix bio means what?
What is life.
These three subatomic particles (with charges) are the foundation for every atom on the periodic table.
What is the proton (+), the neutron (+-), and the electron (-).
This property of water is what allows water to stick to molecules of different substances.
What is adhesion.
This macromolecule is made from an arrangment of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen.
What is a protein.
The ability to do what with a phenomenon is what separates a theory from a law.
What is explain.
This is known as the smallest building block of all things (matter), but is not living.
What is the atom.
This subatomic particle is responsible for facilitating ionic and covalent bonds among atoms?
What is the electron.
If something is said to be hydrophobic, what does this mean?
It is "water fearing" or isn't attracted to water.
Sugars are the monomers for which polymer (macromolecule)?
What is a carbohydrate.
A study is conducted on how room temperature affects test scores. Identify the independent and dependent variable in the experiment.
Dependent variable- Test Scores
Sink a putt from 5 feet for these points.

This type of bond can be found when Na and Cl join to form a compound?
What is an ionic bond.
What is a heterogeneous mixture or suspension.
Identify the type of sugar in the image.

What is a polysaccharide.
In a quality experiment the subjects that receive the independent variable is known as this group.
What is the experimental group.
These four macromolecules in combination with one another make up all living organisms?
What are carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, and nucleic acids.
When a compound is considered to have dipole moment this means the electrons are....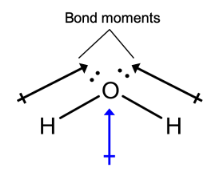
What is not shared evenly.
Water molecules can stick to one another because of a property called cohesion. How many other water molecules can one water molecule bond with and explain how.
What is four because each molecule contains 2 partial positive charges (the hydrogens) and 2 partial negative charges (the oxygen), and thus allowing them to become attracted to one another through opposite charges.
This structure is the monomer for a nucleic acid?
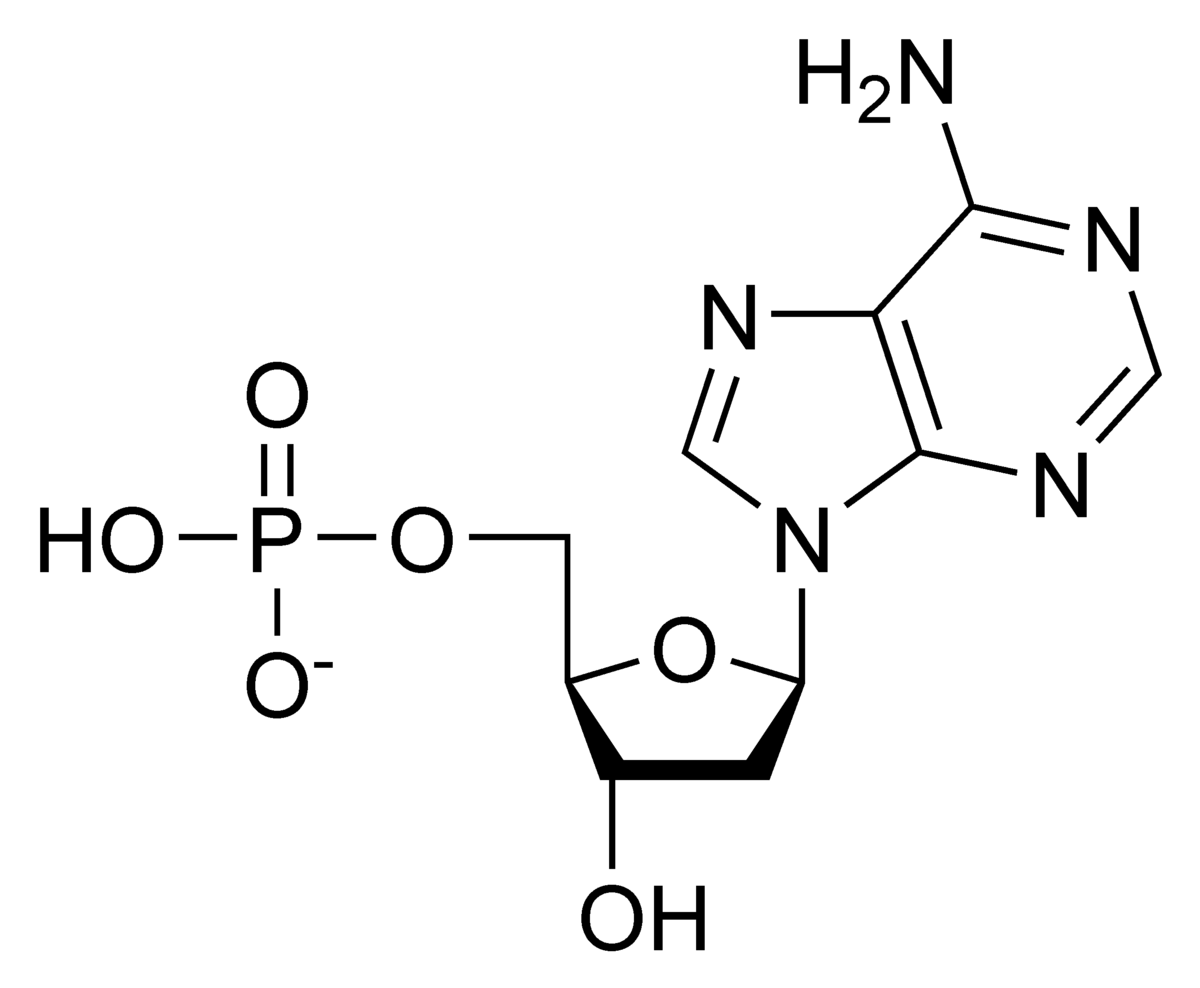
What is a nucleotide.
List all steps of the scientific method in order for these points.
What is (1) Observe, (2) Question, (3) Form a hypothesis, (4) Experiment, (5) Analyze, (6) Iterate, (7) Share.
List the hierarchy of life from smallest to largest.
What is the cell, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms.
Identify the two main types of chemical bonding and explain the difference between the two.
What is ionic and covalent. Ionic is between a metal and a nonmetal and the electrons are transferred. Covalent is between 2 nonmetals and the electrons are shared.
Draw the dipole moment in a water molecule and explain what property water has because of this electron sharing pattern.
What is a polarity and solubility (dissolves other polar molecules).
There are 20 of these that make up all the proteins needed to carry out the many functions of proteins. What are they, and what are two functions of proteins?
What are amino acids and proteins serve as structural support (build muscle tissue), biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes, immune support, and much more.