This organelle is known as the “powerhouse of the cell” because it converts energy from food into ATP.
What is the mitochondria?
2 or more atoms make up a ________?
What is a molecule?
This type of transport does not require energy and involves the movement of water across a membrane.
What is osmosis?
Studying how the heart pumps blood involves understanding this field.
What is physiology?
What is the abbreviation or funny way to remember the steps of mitosis/meiosis?
This membrane surrounds the heart and reduces friction during heartbeats.
What is the pericardium?
This organelle contains the genetic information (DNA) and acts as the control center of the cell.
What is the nucleus?
This level includes the entire living individual.
What is the organismal level?
This process involves the cell engulfing large particles and is known as “cellular eating.”
What is phagocytosis?
Sarah has a cut on her left arm, and her doctor notes that the cut is closer to her shoulder than her elbow.
In the medical report, this would be described as ______________.
What is proximal?
In this phase of mitosis, chromosomes are separated and pull towards opposite poles of the cell.
What is anaphase?
This fluid is secreted by serous membranes to reduce friction between the visceral and parietal layers.
What is serous fluid?
This organelle contains ribosomes and acts as a “conveyor belt” moving proteins to the Golgi body.
What is the rough ER?
At this level, structures composed of two or more different types of tissues work together to perform specific functions.
What is the organ level?
This type of transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient.
What is active transport?
Learning about the structure and location of the liver falls under this field.
What is anatomy?
The process that results in four genetically unique haploid cells is called:
What is meiosis?
This membrane lines the abdominal cavity and covers most abdominal organs.
What is the peritoneum?
This organelle is responsible for packaging proteins into vesicles for distribution.
What is the Golgi body?
A group of different organs that work together to perform a particular function
What is an organ system?
This type of solution causes cells to swell due to water entering the cell.
What is a hypotonic solution?
Anna is experiencing pain in her lower abdomen, which is situated below her stomach. The doctor notes that this area is towards the bottom of her torso.
Which directional term best describes the location of Anna’s lower abdomen relative to her stomach?
What is inferior or caudal
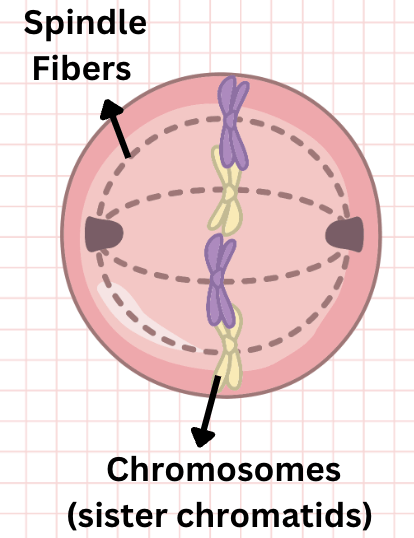
Draw a cell in metaphase and label the sister chromatids and spindle fibers
The layer of a serous membrane that adheres directly to the surface of internal organs.
What is the visceral layer?
This structure is made of microfilaments and microtubules, providing shape and support to the cell.
What is the cytoskeleton?
This level of organization consists of groups of similar cells working together
What is the tissue level?
During this process, cells form small vesicles to take in fluids and dissolved substances, also known as “cellular drinking.”
What is pinocytosis?
Emily injured her right ankle during a soccer game. Her physical therapist notes that the pain is present on the same side as her injury and not on the opposite side.
What is the term used to describe the relationship of the injured right ankle to the pain being discussed?
What is ipsilateral?
In a female what is the end product from meiosis?
What is one egg and 3 polar bodies?
The layer of a serous membrane that lines the walls of the body cavity.
What is the parietal layer?