Any physical location in which a crime has occurred or is suspected of having occurred.
Crime Scene
Memories are not literal. They are...
Constructive
An observer who claims to have seen something clearly enough to describe it
EYEWITNESS
This forensic-related occupation uses in-depth knowledge of fire chemistry and mechanics to investigate possible fire cases. They also gather evidence and eyewitness accounts, talk with insurance companies and provide expert testimony in court proceedings.
Arsonist or Arson Investigator
PERPETRATOR
The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
Perception
Includes oral or written statements given to police as well as testimony in court by people who witnessed an event.
Testimonial Evidence
This person spends time at crime scenes to collect evidence necessary to recreate a violent crime. Through careful documentation and evidence analysis, crime scene investigators provide proof that is the keystone of most criminal trials
Crime Scene Investigator
Use of science to solve crimes or legal cases
FORENSICS
A person who sees an event, typically a crime or accident
WITNESS
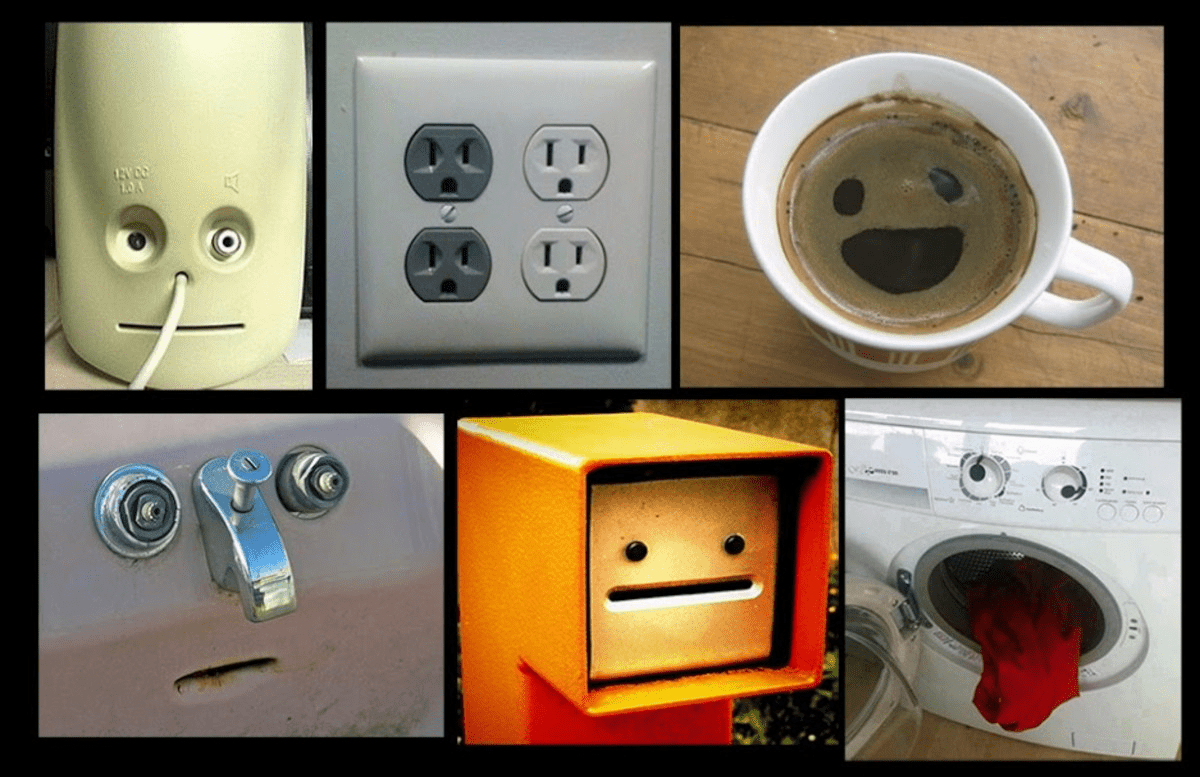
Pareidolia
Statement of where a suspect was at the time of a crime.
Alibi
Experts in the fields of criminal justice and science who, using their knowledge of how insects aid in bodily decomposition, can determine the time and source of death.
Forensic Entomologist
MORTIS
SUSPECT
A cognitive psychology term that describes how misleading information can alter a person's memory of an event.
The Misinformation Effect
A set of procedures in Forensic Science:
Step 1 - Interview
Step 2 - Examine
Step 3 - Document Step 4 - Process
CSI Protocols
A person who conducts autopsies and post-mortem examinations on individuals whose deaths may have been caused by unnatural circumstances. They also work closely with law enforcement officials and legal teams to provide expert opinions on their findings.
Forensic Pathologogist
The tendency to recognize faces of people in one's own racial group more easily than faces of people from other races.
Cross-Race Effect
The original location of a crime. Think 'first' or 'number 1.'
Primary Location
How often has research shown that mistaken eyewitness accounts have led to wrongful convictions?
THREE OUT OF FOUR CASES OR 75%
'A person who does not become actively involved in a situation where someone else requires help'
BYSTANDER
A person who addresses issues such as violence, criminal responsibility, competence to stand trial in both civil and criminal courts, child custody issues, psychic injury, mental disability, malpractice, involuntary treatment, ethics and human rights, and juvenile justice and rehabilitation.
Forensic Psychiatrist
A person who is involved in a crime with criminal intent, either by participating in the crime or by aiding and abetting its commission.
Person associated with someone suspected of committing a crime.
A concept that states memories may not be accurate reproductions of events but can be altered by new information related to beliefs, attitudes, and perceptions to fill in gaps in the memory
CONSTRUCTIVE MEMORY CONCEPT
Reason a person commits a crime, such as money, hate, or jealousy.
Motive
People who examine firearms, ammunition, and other evidence related to guns and projectiles.
Ballistics
A defense of having been somewhere other than at the scene of a crime at the time the crime was committed. The fact or state of having been elsewhere when a crime was committed.
An alternative location where evidence of a crime might be found.
Secondary Scene
A memory error where a person creates a false memory due to the addition of false information - without the intent to deceive. Could also occur based on questioning techniques.
CONFABULATION
Using science to solve crimes or legal cases - refers to LAW
FORENSICS
A scientist who analyzes bodily fluids and tissue samples to identify drugs and chemicals, and to help determine the effects of those substances on people.
FORENSIC TOXOLOGIST
Post Mortem
After Death
This person or persons solve crimes through the analysis of physical evidence (blood, prints, hair, fiber, etc...) related to suspects and may give evidence in legal cases
A psychological phenomenon that causes people to see a familiar object or structure in a random or ambiguous visual pattern.
PAREIDOLIA
This can lead to arrests, provide information to be used in the interrogation of suspects, and direct the creation of a lineup.
EYEWITNESS TESTIMONY
This occupation comes from the Greek anthropos and logia
ANTHROPOLOGY
A Latin term used to describe a criminal's distinct pattern of behavior or method of operation.
Modus Operandi (M.O.)
LOCARD'S EXCHANGE PRINCIPLE
A memory bias that occurred when people believed they saw Bugs Bunny at Disneyland after seeing Disneyland brochures with Bugs Bunny in them. The results are transferrable when considering eyewitness testimonial evidence.
The Bunny Effect
PATHOLOGY
PALLOR, RIGOR, LIVOR, ALGOR
MORTIS